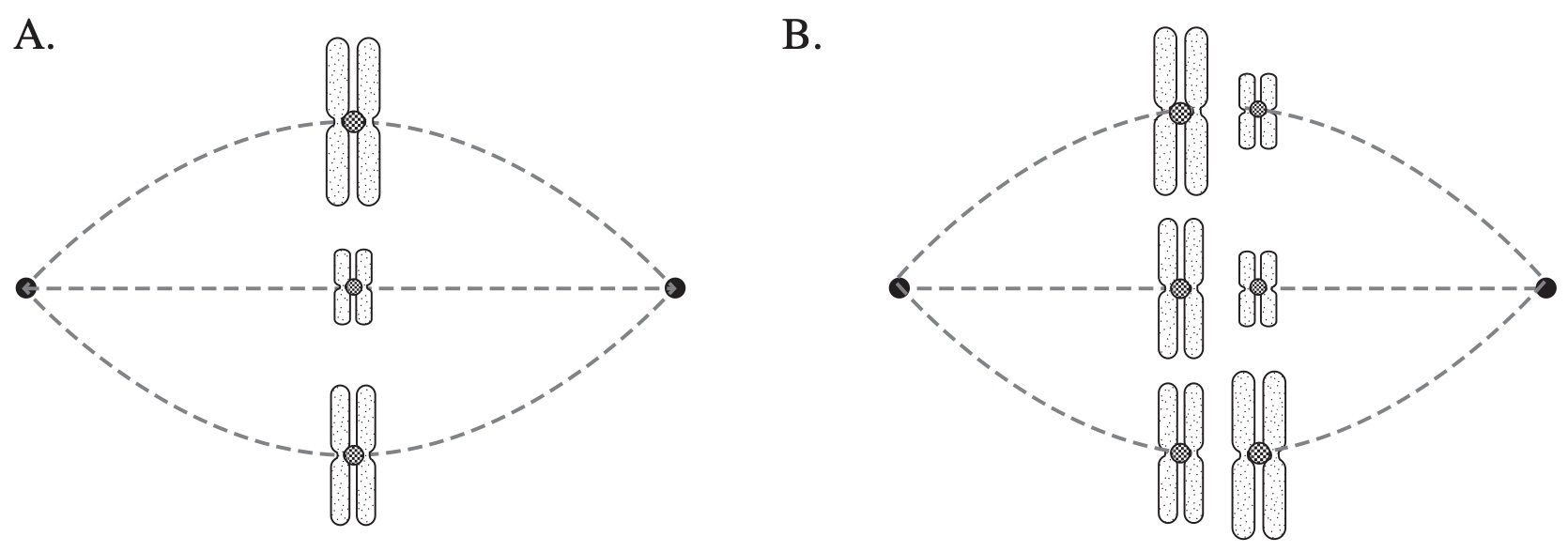
Female Jack Jumper ants (Myrmecia pilosula) have a single pair of chromosomes. During meiosis, crossing over occurs. The diagram shows the crossing over and the position of three genes on the chromosomes. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2024 HSC 6 MC
BIOLOGY, M5 EQ-Bank 26
The diagram shows a model developed in the early 20th century of crossing over of homologous chromosomes.
Explain how the difference between this model and our current model of crossing over reflects an increased understanding of the way in which new combinations of genotypes are produced. Support your answer with a diagram. (4 marks)
BIOLOGY, M5 EQ-Bank 7 MC
In which of the following do both processes result in genetic variation of offspring?
- DNA mutation and polypeptide production
- Cell differentiation and gamete formation
- DNA mutation and gamete formation
- Cell differentiation and polypeptide production
BIOLOGY, M5 2017 HSC 24
- Three genes are arranged along a homologous pair of chromosomes as shown.
-
- What is the individual's genotype before crossing over occurs? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Label, on the diagram below, the alleles after crossing over has occurred. (1 mark)
- What is the individual's genotype before crossing over occurs? (1 mark)
- Explain the effect of independent assortment of chromosomes on the genotype of the offspring. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2019 HSC 28
Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant condition caused by a mutation of a gene on chromosome 4. It causes nerve cells to break down.
Stargardt disease is an autosomal recessive condition caused by a mutation of a different gene on chromosome 4 . It causes damage to the retina.
A patient is heterozygous for both Huntington's (Hh) and Stargardt disease (Rr). His father's extended family has numerous cases of both of these diseases. His mother does not have either disease and is homozygous for both genes.
- Complete the tables, showing the TWO alleles the patient inherited from each parent. (2 marks)
\begin{aligned}
&\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\quad \quad \textit{ Alleles from father }\quad \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\hline
\end{array}
&\begin{array}{|c|}
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\quad \quad \textit{Alleles from mother } \quad \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{aligned}
- The diagram shows the patient's homologous pair of chromosome 4 at various stages of meiosis.
- Add the relevant alleles to the diagram to model the production of possible gamete combinations. Include a key and an example of crossing over. (4 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2020 HSC 28
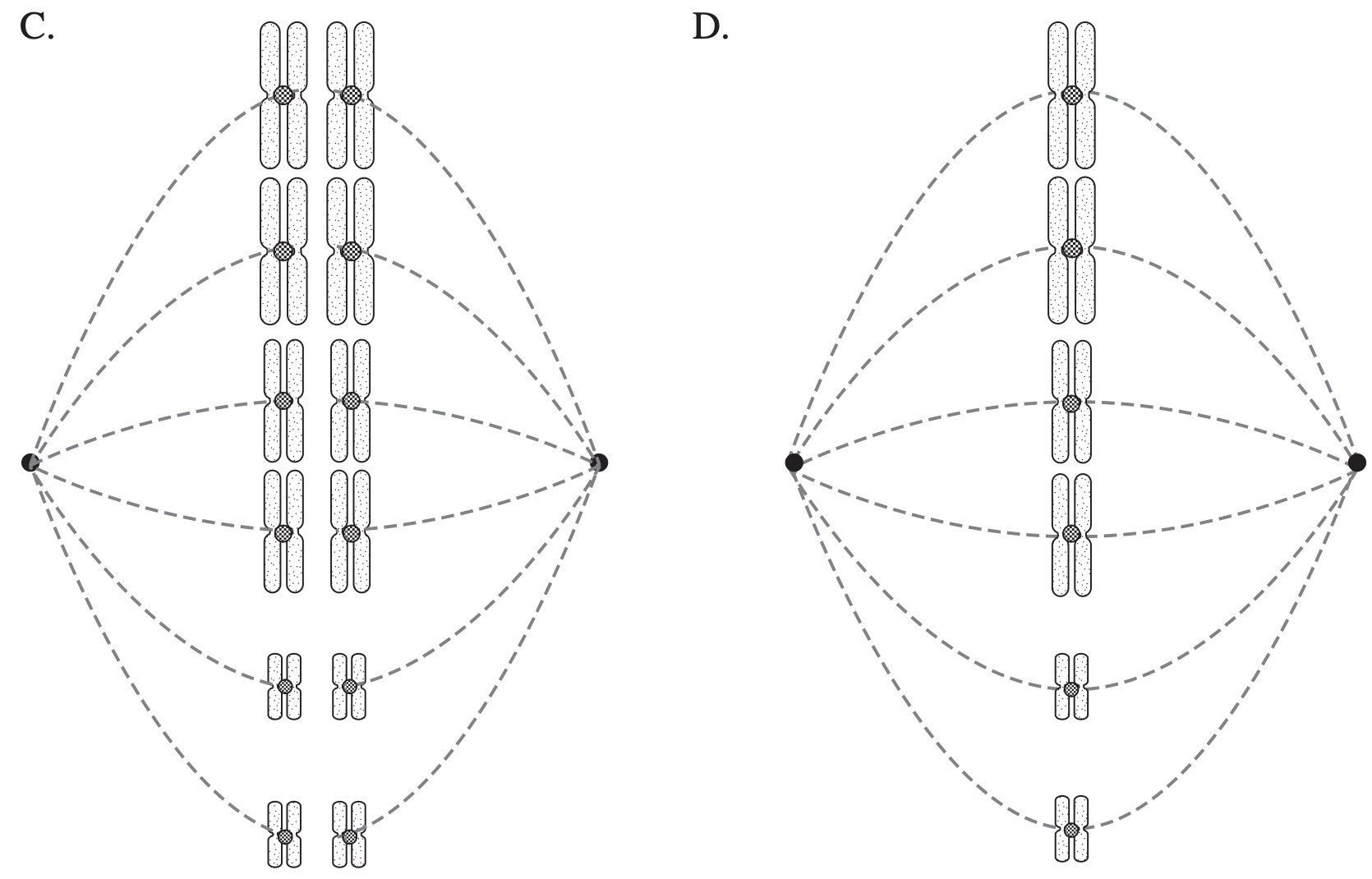
BIOLOGY, M5 2020 HSC 19 MC
Which diagram correctly models one phase of meiosis in an organism that has six chromosomes in its somatic cells?