Use the data sheet provided and the information in the table to answer this question.
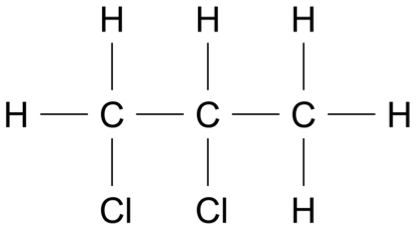
Consider the molecule shown.
For each of the following instrumental techniques, predict the expected features of the spectra produced.
Refer to the structural features of the molecule in your answer.
- Infrared (IR) (Ignore any absorptions due to \(\ce{C - C}\) or \(\ce{C - H}\) )
- Carbon-13 NMR
- Proton NMR
- Mass spectrometry (7 marks)
--- 30 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---