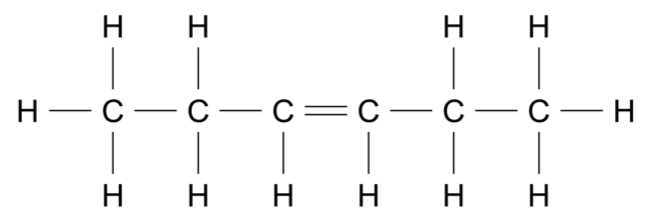
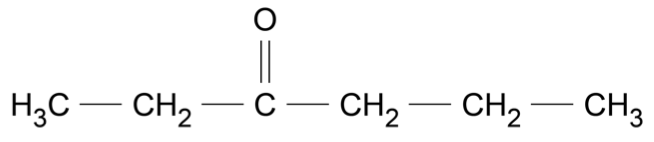An organic reaction pathway involving compounds \(\text{A, B,}\) and \(\text{C}\) is shown in the flow chart.
The molar mass of \(\text{A}\) is 84.156 g mol\(^{-1}\).
A chemist obtained some spectral data for the compounds as shown.
| \( \text{Data from} \ ^{1} \text{H NMR spectrum of compound C} \) | ||
| \( Chemical \ Shift \ \text{(ppm)} \) | \( Relative \ peak \ area \) | \( Splitting \ pattern \) |
| \(1.01\) | \(3\) | \(\text{Triplet}\) |
| \(1.05\) | \(3\) | \(\text{Triplet}\) |
| \(1.65\) | \(2\) | \(\text{Multiplet}\) |
| \(2.42\) | \(2\) | \(\text{Triplet}\) |
| \(2.46\) | \(2\) | \(\text{Quartet}\) |
| \( ^{1} \text{H NMR chemical shift data}\) | |
| \( Type \ of \ proton \) | \( \text{δ/ppm} \) |
| \( \ce{R - C\textbf{H}3,R - C\textbf{H}2 - R}\) | \(0.7-1.7\) |
| \( \left.\begin{array}{l}\ce{\textbf{H}3C - CO - \\-C\textbf{H}2 - CO -}\end{array}\right\} \begin{aligned} & \text { (aldehydes, ketones,} \\ &\text{carboxylic acids or esters) }\end{aligned}\) | \(2.0-2.6\) |
| \( \ce{R - C\textbf{H}O} \) | \(9.4-10.00\) |
| \( \ce{R - COO\textbf{H}} \) | \(9.0-13.0\) |
Identify the functional group present in each of compounds \(\text{A}\) to \(\text{C}\) and draw the structure of each compound. Justify your answer with reference to the information provided. (9 marks)
--- 28 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---