Strap bracing is used in the construction of many residential structures. It has holes punched along its length to allow tensioners to be applied as shown. A 6 mm diameter hole is to be punched into mild steel strap bracing. If the shear strength of the bracing is 380 MPa and the shear force required to punch the hole is 5.73 kN, what is the maximum allowable thickness of the strap bracing? (3 marks) --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
ENGINEERING, CS 2023 HSC 10 MC
ENGINEERING, CS 2023 HSC 26a
ENGINEERING, PPT 2016 HSC 24d
A mild steel nut and bolt is used to hold a bumper bar onto the chassis of a truck. The bolt needs to withstand a maximum shear load of 2 kN.
If the maximum shear stress of the material is 56 MPa and the factor of safety is 2, calculate the minimum bolt diameter. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
ENGINEERING, AE 2017 HSC 26b
Orthogonal and pictorial drawings of a sheet metal electrical cable cover are given below.
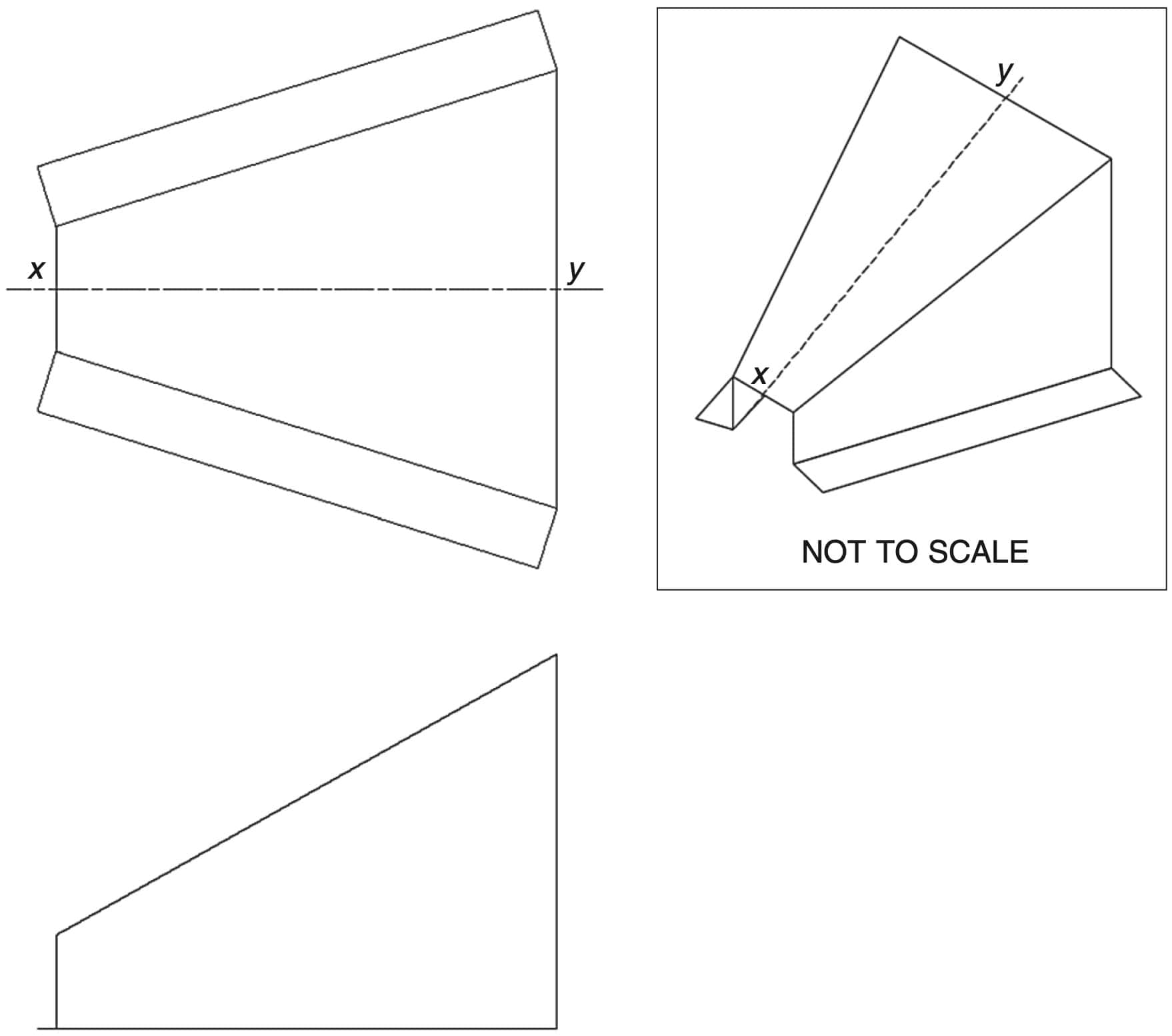
- Draw a half-development of the electrical cable cover. Use the centre line to position the development. (4 marks)
- A 20 mm diameter hole is to be punched through the top of the electrical cable cover before folding.
- The ultimate shear stress of the material used to manufacture the cover is 110 MPa.
- Calculate the force required to punch out the hole if the thickness of the sheet metal is 0.5 mm. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
