Iodic acid and sulfamic acid are monoprotic acids. A 0.100 mol L\(^{-1}\) solution of iodic acid has a pH of 1.151, as does a 0.120 mol L\(^{-1}\) solution of sulfamic acid. Show that neither iodic acid nor sulfamic acid dissociates completely in water, and determine which is the stronger acid. (3 marks) --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M6 2016 VCE 20 MC
How does diluting a 0.1 M solution of lactic acid, \(\ce{HC3H5O3}\), change its pH and percentage ionisation?
| pH | Percentage ionisation | |
| A. | increase | decrease |
| B. | increase | increase |
| C. | decrease | increase |
| D. | decrease | decrease |
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 23
Propanoic acid dissociation in water can is represented in the following equation:
\(\ce{CH3CH2COOH($aq$) + H2O($l$) \rightleftharpoons CH3CH2COO^-($aq$) + H3O^{+}($aq$)}\)
Explain how the pH of the propanoic acid solution would change if it was diluted. (3 marks)
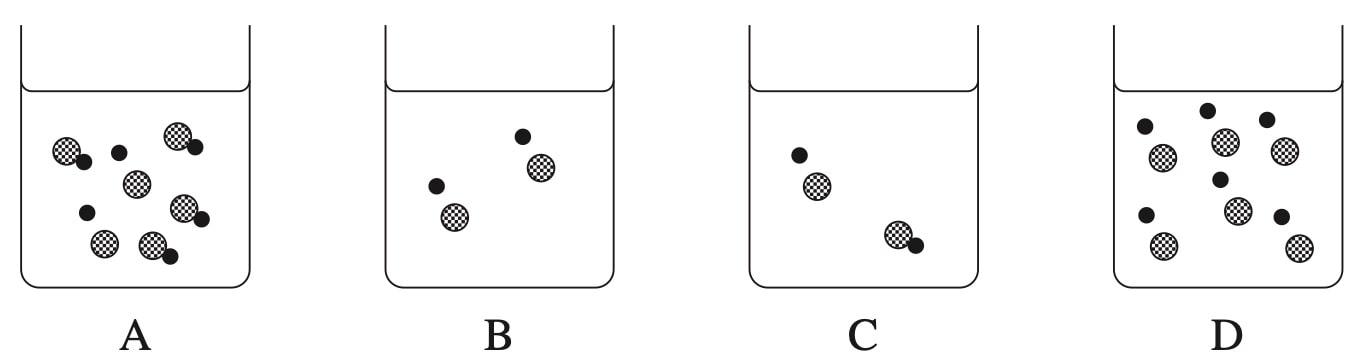
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 5 MC
Which beaker contains a concentrated strong acid?
CHEMISTRY, M6 2015 HSC 24
- Explain why the salt, sodium acetate, forms a basic solution when dissolved in water. Include an equation in your answer. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- A solution is prepared by using equal volumes and concentrations of acetic acid and sodium acetate.
- Explain how the pH of this solution would be affected by the addition of a small amount of sodium hydroxide solution. Include an equation in your answer. (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M6 2017 HSC 24
A solution of sodium hydroxide was titrated against a standardised solution of acetic acid which had a concentration of 0.5020 mol L¯1.
- The end point was reached when 19.30 mL of sodium hydroxide solution had been added to 25.00 mL of the acetic acid solution.
- Calculate the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain why the pH of the resulting salt solution was not 7. Include a relevant chemical equation in your answer. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M6 2020 HSC 34
The effect of concentration on the pH of acrylic acid `(text{C}_2 text{H}_3 text{COOH})` and hydrochloric acid `(text{HCl})` solutions is shown in the graph. Both of these acids are monoprotic.
Explain the trends in the graph. Include relevant chemical equations in your answer. (4 marks)
CHEMISTRY, M5 2020 HSC 27
A student makes up a solution of propan-2-amine in water with a concentration of 1.00 mol L ¯1.
- Using structural formulae, complete the equation for the reaction of propan-2-amine with water. (2 marks)
- The equilibrium constant for the reaction of propan-2-amine with water is `4.37 xx10^(-4)`.
- Calculate the concentration of hydroxide ions in this solution. (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M6 2020 HSC 18 MC
An aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate has a pH greater than 7 .
Which statement best explains this observation?
- `text{H}_(2) text{O}(l)` is a stronger acid than `text{HCO}_(3)^(\ -)(aq)`.
- `text{HCO}_(3)^(\ -)(aq)` is a weaker acid than `text{H}_(2) text{CO}_(3)(aq)`.
- `text{Na}^(+)(aq)` reacts with water to produce the strong base `text{NaOH}(aq)`.
- The conjugate acid of `text{HCO}_(3)^(\ -)(aq)` is a stronger acid than `text{H}_(2)text{O}(l)`.
CHEMISTRY, M6 2021 HSC 23
Methanoic acid reacts with aqueous potassium hydroxide. A salt is produced in this reaction.
- Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Is the salt acidic, basic or neutral? Justify your answer. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---