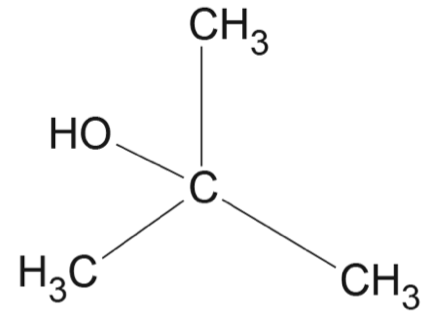
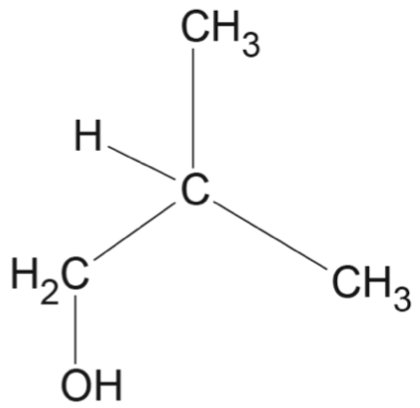
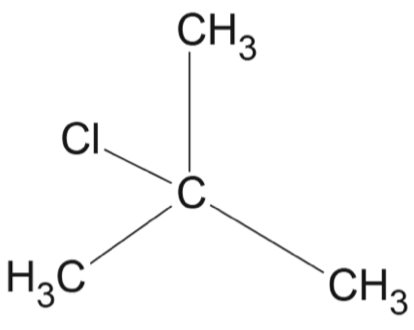
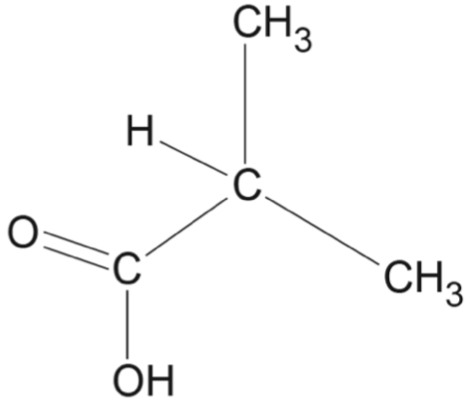
Consider the following sequence of reactions.
- Prop-2-en-1-ol was reacted with hydrogen gas to form liquid \(X\).
- \(X\) was oxidised, producing liquid \(Y\) that formed bubbles of a gas when reacted with aqueous sodium carbonate.
- \(Y\) was heated under reflux with methanol and a drop of concentrated sulfuric acid, producing an organic liquid, \(Z\).
This process has been presented in the flow chart below.
Which option correctly identifies the structures for \(X\), \(Y\) and \(Z\)?