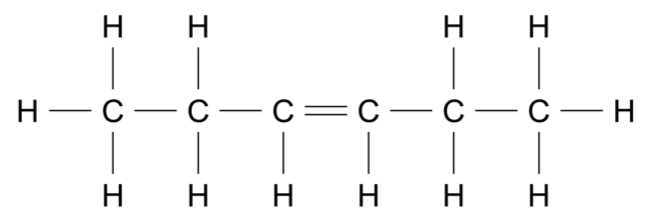
Compound A has the molecular formula \(\ce{C5H10}\). The information below shows some chemical reactions beginning with this compound.
- Compound A reacts with \(\ce{H+/H2O}\) to produce compounds B and C .
- Compound B does not react with \(\ce{H+/Cr2O7^{2-}}\).
- Compound C reacts with \(\ce{H+/Cr2O7^{2-}}\) to produce compound D .
- Compound D does not react with \(\ce{Na2CO3(aq)}\).
Determine the structure of compound A. Justify your answer using all the data given. (4 marks)
--- 14 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---