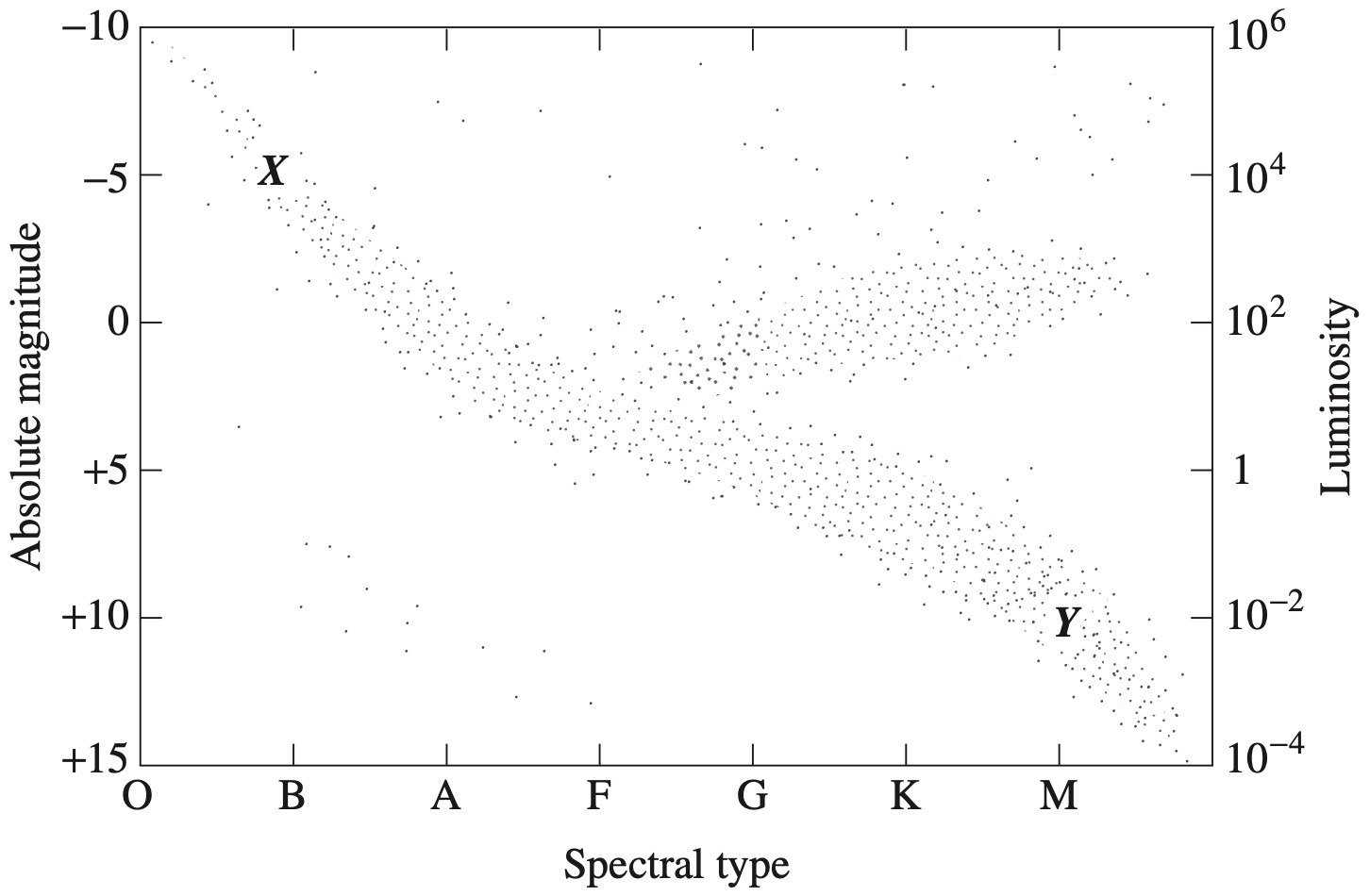
Two stars, \(X\) and \(Y\), are identified on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
In what way are these two stars different?
- \(X\) has a higher luminosity than \(Y\).
- \(X\) is a red star, and \(Y\) is a blue star.
- \(X\) has a lower core temperature than \(Y\).
- \(X\) has a higher surface temperature than \(Y\).