The properties of some aluminium-magnesium-silicon alloys can be altered using the following procedure.
What type of hardening process is this?
- Case hardening
- Flame hardening
- Induction hardening
- Precipitation hardening
Aussie Maths & Science Teachers: Save your time with SmarterEd
The properties of some aluminium-magnesium-silicon alloys can be altered using the following procedure.
What type of hardening process is this?
`D`
`=>D`
Aircraft skins can be constructed using either fibre metal laminate (FML) or sheet aircraft-grade aluminium alloy.
FML is preferred in this application because it has
`D`
`=>D`
The components of the bearing assembly used in the fidget spinner are shown.
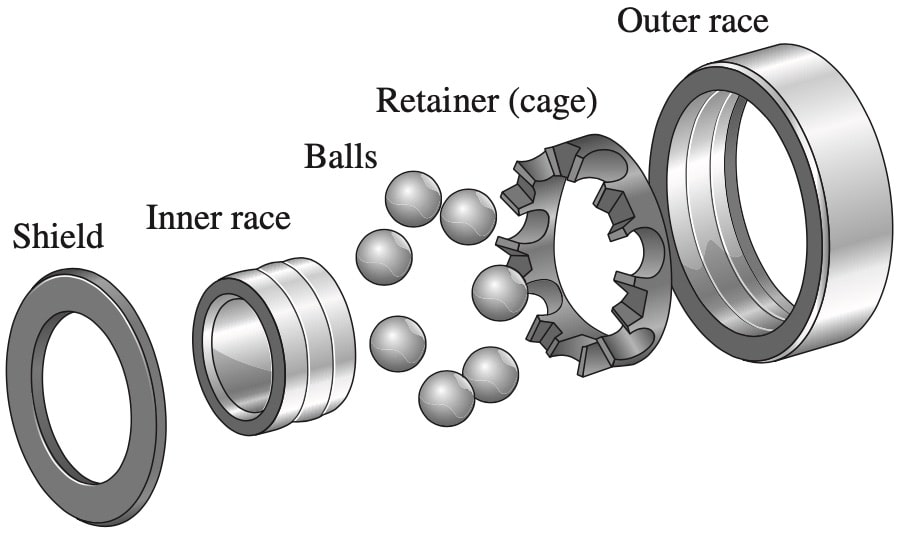
The retainer can be made from either glass fibre-reinforced nylon or stainless steel.
Compare the in-service properties of these materials for use in the retainer. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
In modern aircraft, the external skin is riveted to the frame using solution treated and quenched aluminium 4% copper alloy rivets. These rivets are used immediately to attach the external skin of the aircraft to the frame.
Describe the changes that occur to the structure and properties of these rivets after installation. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Changes to structure and properties of the rivet
Changes to structure and properties of the rivet
Carbon fibre was originally developed to produce aircraft bodies and high performance vehicles. Carbon fibre is now used in a wide range of applications, including the manufacture of the type of bicycle frame shown.
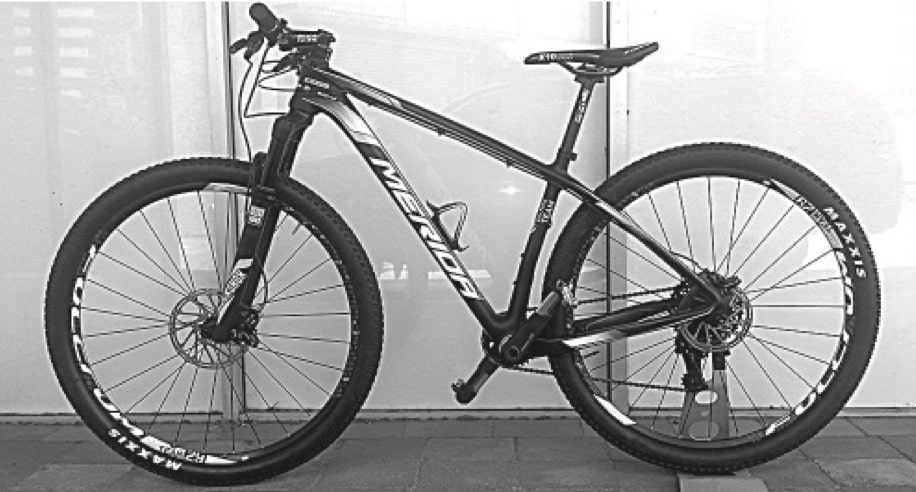

Outline the advantages of carbon fibre bicycle frames over steel bicycle frames. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Advantages of carbon fibre bicycle frames
Advantages of carbon fibre bicycle frames
Some materials have properties that allow them to be used in the manufacture of both modern racing yachts and aircraft. These materials include Kevlar® aramid fibre, carbon fibre epoxy composites and aluminium alloys.
Complete the table by providing a property which makes each of these materials suitable for the manufacture of both yachts and aircraft. (3 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
An image of an aeroplane is shown with the position of the wing support beam indicated.
Assume the engines are supported by the single beam. The beam runs through the plane, wing tip to wing tip.
Compare the use of composite materials with the use of metals for the manufacture of the beam. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Answers could include 3 of the following comparisons:
Composite materials vs Metals
Answers could include 3 of the following comparisons:
Composite materials vs Metals
Titanium is used to manufacture aircraft undercarriages that support landing wheels.
Why is titanium used in preference to alloy steel for this purpose?
`B`
`=>B`