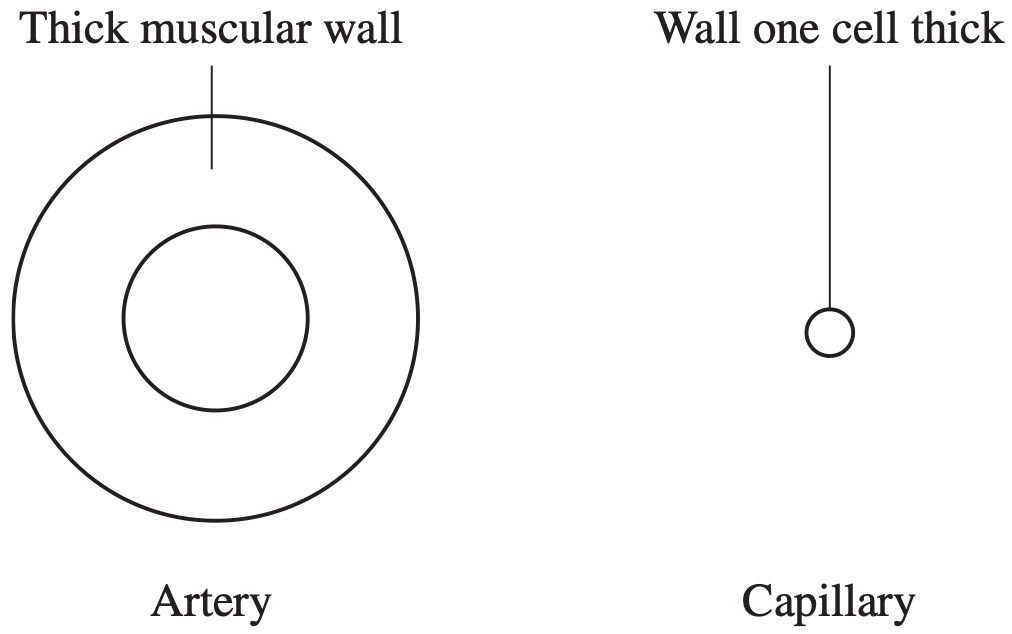
"The circulatory and excretory systems in humans are intricately linked, each depending on the other for optimal function."
- Describe two ways in which the circulatory system and the excretory system of humans exhibit interdependence. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Provide one example of a disorder that could affect both systems. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---