The diagram shows a simplified version of the process of polypeptide synthesis. --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 13 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- a. Process \(A\) vs DNA replication: b. mRNA and tRNA’s role in polypeptide synthesis: a. Process \(A\) vs DNA replication: b. mRNA and tRNA’s role in polypeptide synthesis:
BIOLOGY, M5 SM-Bank 22
Describe the roles of messenger RNA and transfer RNA in protein synthesis. (2 marks)
BIOLOGY, M5 EQ-Bank 14 MC
Haemophilia A is a blood clotting disorder that arises from a defect in the gene F8 which is carried on the X chromosome. The disorder affects the production of a glycoprotein that is one of many components needed to form the platelets which form blood clots when a bleed occurs. It is typically treated with infusions of FVIII product, an inactive single chain polypeptide of 2332 amino acids, which is manufactured using DNA technology on human endothelial cells.
Why is the inactive FVIII polypeptide chain used in the treatment of Haemophilia A?
- It will prevent bleeds from occurring.
- It can take the place of platelets in clotting blood.
- It can be used to manufacture the glycoprotein that is affected by the defective F8 gene.
- It is used as a gene therapy to help the patient manufacture FVIII in their own endothelial cells.
BIOLOGY, M5 2014 HSC 32a
- Name the process for the synthesis of a polypeptide chain from a messenger-RNA base sequence. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Outline the steps in the formation of a functional enzyme from polypeptide chains. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2019 HSC 33a
Alzheimer's disease causes destruction of brain tissue, dementia and eventually death.
The diagram shows the effect of Alzheimer's disease on the brain.
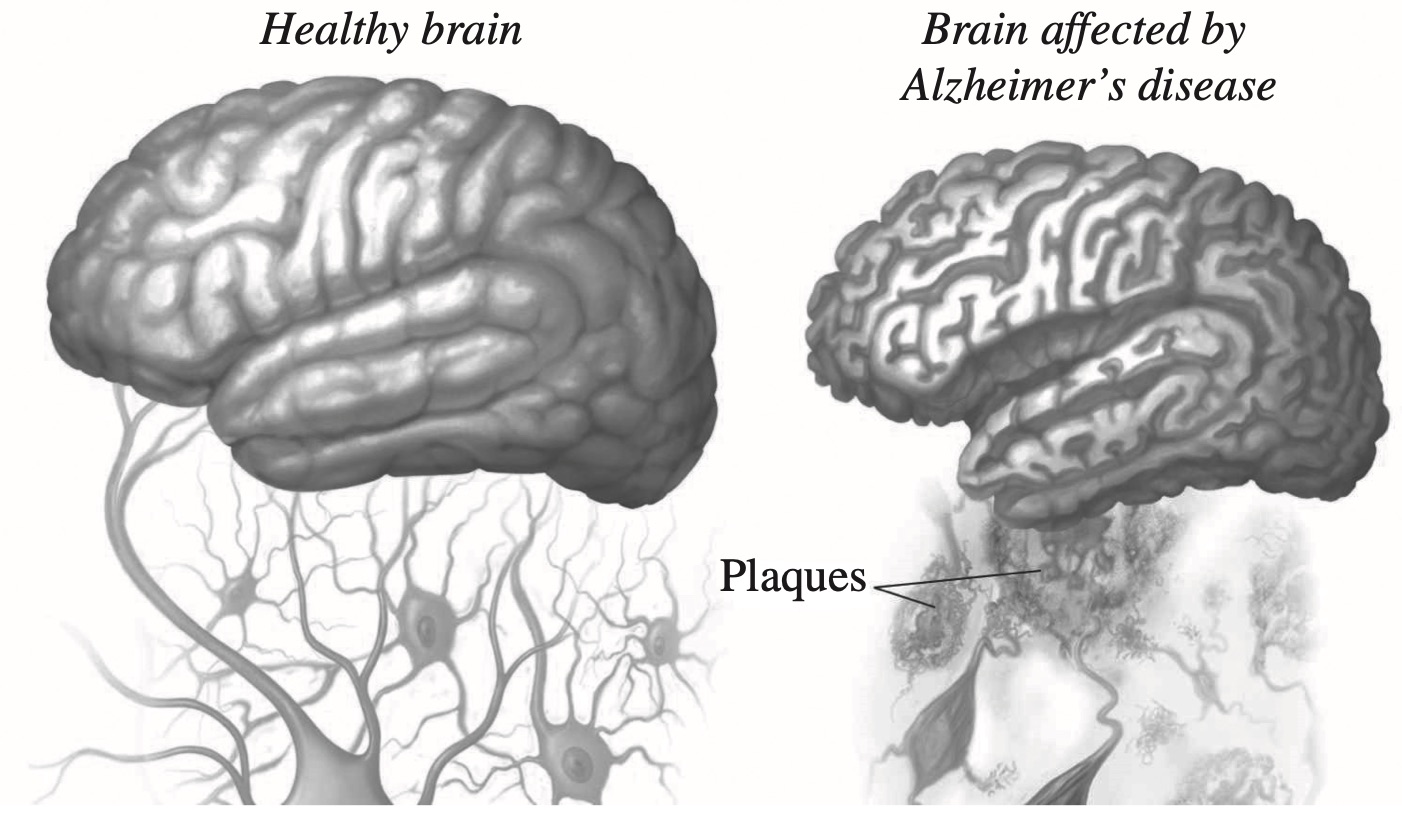
Amyloid beta protein is produced in the human brain throughout life. In people with Alzheimer's disease, it accumulates in excessive amounts.
Outline the main steps that brain cells use to make proteins such as amyloid beta. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2020 HSC 32b
The rabies virus is a single-stranded RNA virus. It contains and codes for only five proteins. The diagrams show the structure and reproduction of the virus.
- Use the information provided in Diagram 1 to explain why the rabies virus cannot be classified as a cellular pathogen. (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- After infection the virus reproduces in muscle cells near the bite site and in the central nervous system. This requires the single-stranded rabies RNA to be transcribed, translated and replicated in the cytoplasm of host cells. These processes are shown in Diagram 2.
- Use the information provided in Diagrams 1 and 2 to explain the role of viral RNA polymerase in the reproduction of the virus. (5 marks)
--- 12 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2015 HSC 14 MC
The table shows the base triplets in mRNA for amino acids.
From the table, the amino acid Serine (Ser) can be coded for by the base triplet UCG.
Which base triplet could code for the amino acid Tyrosine (Tyr)?
- `text{CCU}`
- `text{CAU}`
- `text{UAA}`
- `text{UAC}`
BIOLOGY, M5 2019 HSC 14 MC
The following DNA base sequence is used to code for a sequence of four amino acids.
`text{CGC ATC ATG CTA}`
Which of the following correctly represents the anticodons on the transfer RNA during synthesis of this string of amino acids?
- `text{GCG UAG UAC GAU}`
- `text{CGC AUC AUG CUA}`
- `text{CGC ATC ATG CTA}`
- `text{GCG TAG TAC GAT}`
BIOLOGY, M5 2021 HSC 28a
Describe the role of mRNA in human cells. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---