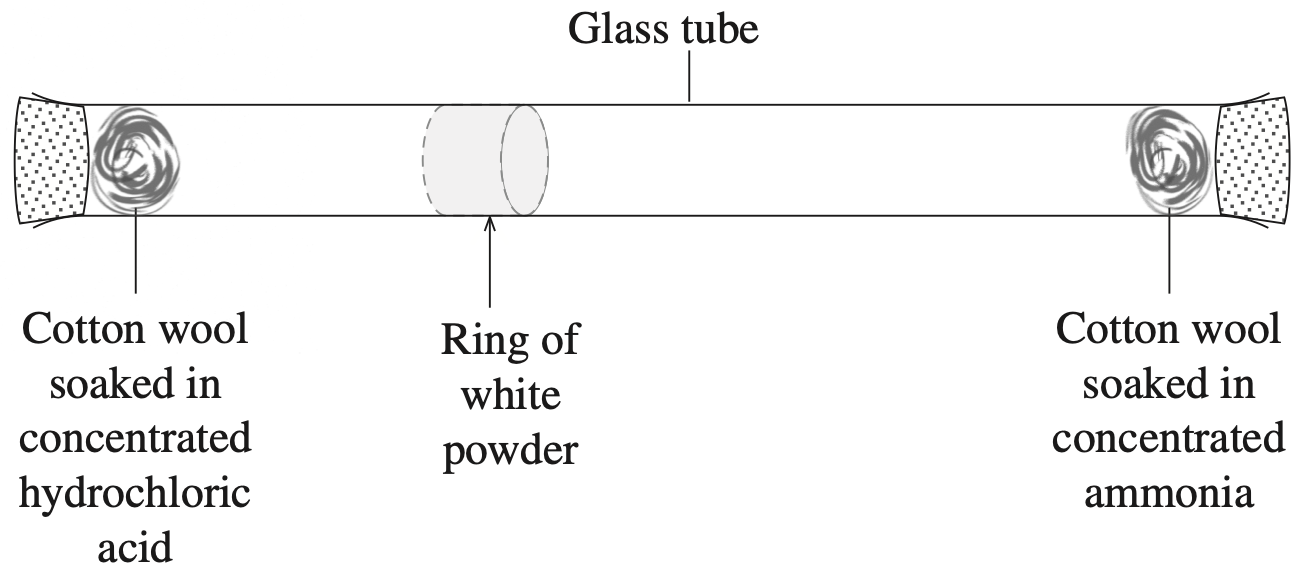
The structures of two substances, \(\text{X}\) and \(\text{Y}\), are shown.
Which row of the table correctly classifies these substances as a Brønsted-Lowry acid or a Brønsted-Lowry base?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ & \\
\ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{Brønsted-Lowry} & \textit{Brønsted-Lowry} \\
\textit{acid}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \textit{base} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{-}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&\text{X and Y}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{X and Y}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{-}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Y}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{X} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{X}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Y} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}