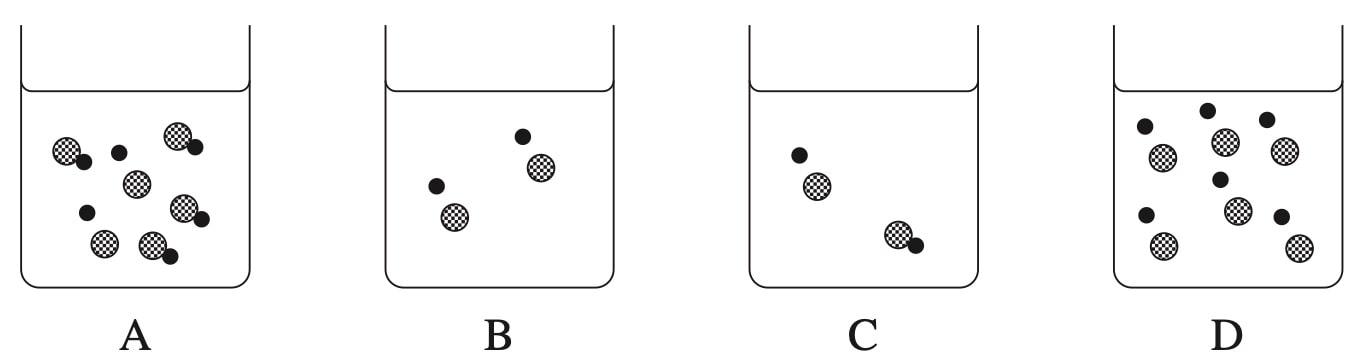
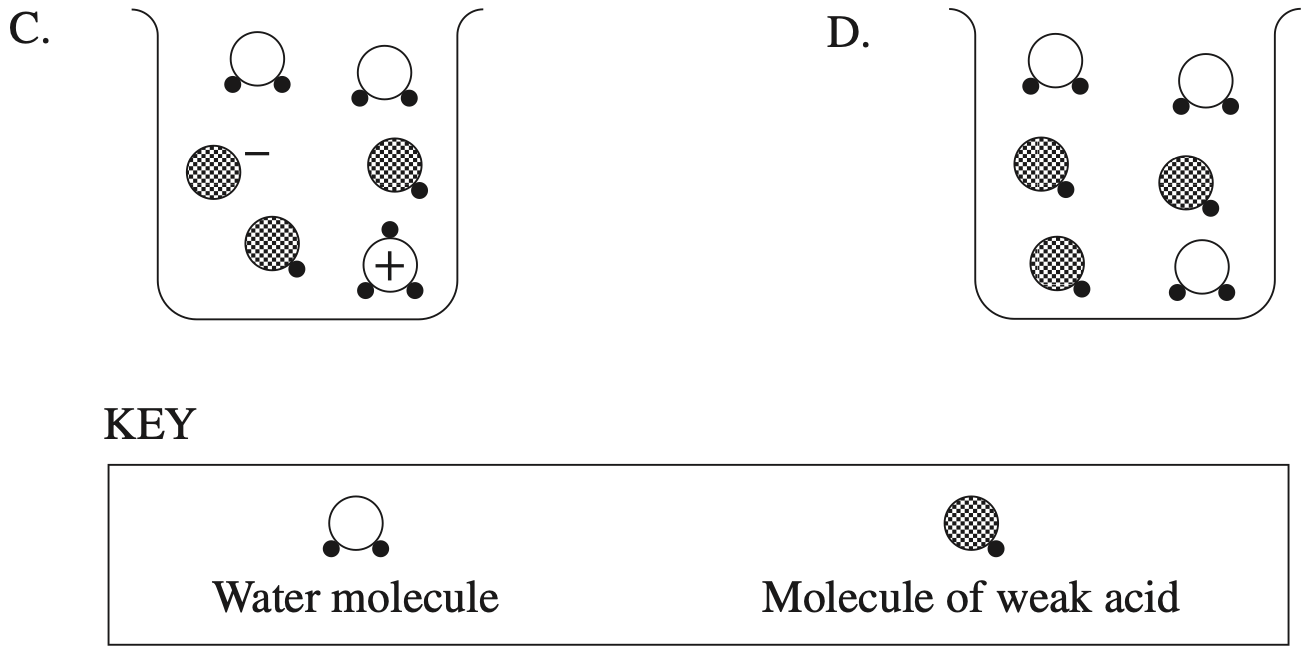
An aqueous solution of an unknown acid \(\ce{(HA)}\) is represented below.
Which row of the table best describes this solution?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\quad \quad \textit{Strong}\quad \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \ \ \textit{Concentrated} \ \ \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\checkmark\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&\checkmark\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\checkmark\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \large{\times}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\large{\times}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \checkmark \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\large{\times}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \large{\times} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}