Consider the function \( f: R \rightarrow R, f(x)=(x+1)(x+a)(x-2)(x-2 a) \text { where } a \in R \text {. } \) --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- ii. exactly four \(x\)-intercepts. (1 mark) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- ii. Find the coordinates of the local maximum of \(g\). (1 mark) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- iii. Find the values of \(x\) for which \(g^{\prime}(x)>0\). (1 mark) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- iv. Consider the two tangent lines to the graph of \(y=g(x)\) at the points where --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Let \(h\) be the function \(h: R \rightarrow R, h(x)=(x+1)(x-1)(x+2)(x-2)\), which is the function \(f\) where \(a=-1\). --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- ii. Using a dilation and translations, describe a different sequence of transformations of \(h\), for which its image would have both local minimums at the same coordinates as that of \(g\). (2 marks) --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. exactly three \(x\)-intercepts. (2 marks)
i. Find \(g^{\prime}(x)\) (1 mark)
\(x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\) and \(x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\). Determine the coordinates of the point of intersection of these two tangent lines. (2 marks)
i. Using translations only, describe a sequence of transformations of \(h\), for which its image would have a local maximum at the same coordinates as that of \(g\). (1 mark)
Calculus, MET2 2022 VCAA 1
The diagram below shows part of the graph of `y=f(x)`, where `f(x)=\frac{x^2}{12}`.
- State the equation of the axis of symmetry of the graph of `f`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- State the derivative of `f` with respect to `x`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The tangent to `f` at point `M` has gradient `-2` .
- Find the equation of the tangent to `f` at point `M`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The diagram below shows part of the graph of `y=f(x)`, the tangent to `f` at point `M` and the line perpendicular to the tangent at point `M`.
- i. Find the equation of the line perpendicular to the tangent passing through point `M`. (1 mark)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. The line perpendicular to the tangent at point `M` also cuts `f` at point `N`, as shown in the diagram above.
- Find the area enclosed by this line and the curve `y=f(x)`. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Another parabola is defined by the rule `g(x)=\frac{x^2}{4 a^2}`, where `a>0`.
- A tangent to `g` and the line perpendicular to the tangent at `x=-b`, where `b>0`, are shown below.
- Find the value of `b`, in terms of `a`, such that the shaded area is a minimum. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2023 VCAA 1
Let \(f:R \rightarrow R, f(x)=x(x-2)(x+1)\). Part of the graph of \(f\) is shown below.
- State the coordinates of all axial intercepts of \(f\). (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the coordinates of the stationary points of \(f\). (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
-
- Let \(g:R\rightarrow R, g(x)=x-2\).
- Find the values of \(x\) for which \(f(x)=g(x)\). (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
-
- Write down an expression using definite integrals that gives the area of the regions bound by \(f\) and \(g\). (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, find the total area of the regions bound by \(f\) and \(g\), correct to two decimal places. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Write down an expression using definite integrals that gives the area of the regions bound by \(f\) and \(g\). (2 marks)
- Let \(h:R\rightarrow R, h(x)=(x-a)(x-b)^2\), where \(h(x)=f(x)+k\) and \(a, b, k \in R\).
- Find the possible values of \(a\) and \(b\). (4 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2023 VCAA 14 MC
A polynomial has the equation \(y=x(3x-1)(x+3)(x+1)\).
The number of tangents to this curve that pass through the positive \(x\)-intercept is
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Calculus, MET2 2020 VCAA 5
Let `f: R to R, \ f(x)=x^{3}-x`.
Let `g_{a}: R to R` be the function representing the tangent to the graph of `f` at `x=a`, where `a in R`.
Let `(b, 0)` be the `x`-intercept of the graph of `g_{a}`.
- Show that `b= {2a^{3}}/{3 a^{2}-1}`. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- State the values of `a` for which `b` does not exist. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- State the nature of the graph of `g_a` when `b` does not exist. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- i. State all values of `a` for which `b=1.1`. Give your answer correct to four decimal places. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. The graph of `f` has an `x`-intercept at (1, 0).
- State the values of `a` for which `1 <= b <= 1.1`.
- Give your answers correct to three decimal places. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The coordinate `(b, 0)` is the horizontal axis intercept of `g_a`.
Let `g_b` be the function representing the tangent to the graph of `f` at `x=b`, as shown in the graph below.
- Find the values of `a` for which the graphs of `g_a` and `g_b`, where `b` exists, are parallel and where `b!=a`. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Let `p:R rarr R, \ p(x)=x^(3)+wx`, where `w in R`.
- Show that `p(-x)=-p(x)` for all `w in R`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A property of the graphs of `p` is that two distinct parallel tangents will always occur at `(t, p(t))` and `(-t,p(-t))` for all `t!=0`.
- Find all values of `w` such that a tangent to the graph of `p` at `(t, p(t))`, for some `t > 0`, will have an `x`-intercept at `(-t, 0)`. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Let `T:R^(2)rarrR^(2),T([[x],[y]])=[[m,0],[0,n]][[x],[y]]+[[h],[k]]`, where `m,n in R text(\{0})` and `h,k in R`.
State any restrictions on the values of `m`, `n`, `h`, and `k`, given that the image of `p` under the transformation `T` always has the property that parallel tangents occur at `x = -t` and `x = t` for all `t!=0`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2021 VCAA 7 MC
The tangent to the graph of `y = x^3 - ax^2 + 1` at `x = 1` passes through the origin.
The value of `a` is
- `1/2`
- `1`
- `3/2`
- `2`
- `5/2`
Calculus, MET2 2019 VCAA 5
Let `f: R -> R, \ f(x) = 1-x^3`. The tangent to the graph of `f` at `x = a`, where `0 < a < 1`, intersects the graph of `f` again at `P` and intersects the horizontal axis at `Q`. The shaded regions shown in the diagram below are bounded by the graph of `f`, its tangent at `x = a` and the horizontal axis.
- Find the equation of the tangent to the graph of `f` at `x = a`, in terms of `a`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the `x`-coordinate of `Q`, in terms of `a`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the `x`-coordinate of `P`, in terms of `a`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Let `A` be the function that determines the total area of the shaded regions.
- Find the rule of `A`, in terms of `a`. (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `a` for which `A` is a minimum. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Consider the regions bounded by the graph of `f^(-1)`, the tangent to the graph of `f^(-1)` at `x = b`, where `0 < b < 1`, and the vertical axis.
- Find the value of `b` for which the total area of these regions is a minimum. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of the acute angle between the tangent to the graph of `f` and the tangent to the graph of `f^(-1)` at `x = 1`. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2016 VCAA 2
Consider the function `f(x) = -1/3 (x + 2) (x-1)^2.`
- i. Given that `g^{′}(x) = f (x) and g (0) = 1`,
- show that `g(x) = -x^4/12 + x^2/2-(2x)/3 + 1`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. Find the values of `x` for which the graph of `y = g(x)` has a stationary point. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The diagram below shows part of the graph of `y = g(x)`, the tangent to the graph at `x = 2` and a straight line drawn perpendicular to the tangent to the graph at `x = 2`. The equation of the tangent at the point `A` with coordinates `(2, g(2))` is `y = 3-(4x)/3`.
The tangent cuts the `y`-axis at `B`. The line perpendicular to the tangent cuts the `y`-axis at `C`.
- i. Find the coordinates of `B`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. Find the equation of the line that passes through `A` and `C` and, hence, find the coordinates of `C`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- iii. Find the area of triangle `ABC`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The tangent at `D` is parallel to the tangent at `A`. It intersects the line passing through `A` and `C` at `E`.
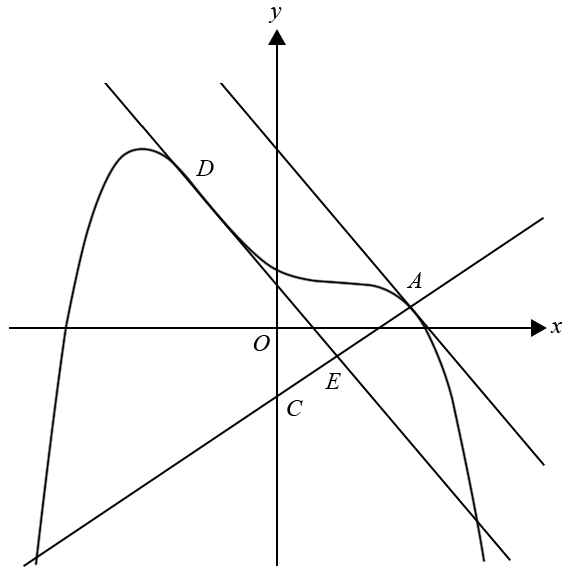
i. Find the coordinates of `D`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. Find the length of `AE`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2016 VCAA 10 MC
For the curve `y = x^2 - 5`, the tangent to the curve will be parallel to the line connecting the positive x-intercept and the y-intercept when `x` is equal to
A. `sqrt 5`
B. `5`
C. `−5`
D. `sqrt 5/2`
E. `1/sqrt 5`
Calculus, MET2 2015 VCAA 1
Let `f: R -> R,\ \ f(x) = 1/5 (x-2)^2 (5-x)`. The point `P(1, 4/5)` is on the graph of `f`, as shown below.
The tangent at `P` cuts the y-axis at `S` and the x-axis at `Q.`
- Write down the derivative `f^{prime} (x)` of `f (x)`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- i. Find the equation of the tangent to the graph of `f` at the point `P(1, 4/5)`. (1 mark)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
ii. Find the coordinates of points `Q` and `S`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the distance `PS` and express it in the form `sqrt b/c`, where `b` and `c` are positive integers. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the area of the shaded region in the graph above. (3 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2013 VCAA 4
Part of the graph of a function `g: R -> R, \ g (x) = (16-x^2)/4` is shown below.
- Points `B` and `C` are the positive `x`-intercept and `y`-intercept of the graph `g`, respectively, as shown in the diagram above. The tangent to the graph of `g` at the point `A` is parallel to the line segment `BC.`
- Find the equation of the tangent to the graph of `g` at the point `A.` (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
-
The shaded region shown in the diagram above is bounded by the graph of `g`, the tangent at the point `A`, and the `x`-axis and `y`-axis.
- Evaluate the area of this shaded region. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the equation of the tangent to the graph of `g` at the point `A.` (2 marks)
- Let `Q` be a point on the graph of `y = g(x)`.
- Find the positive value of the `x`-coordinate of `Q`, for which the distance `OQ` is a minimum and find the minimum distance. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The tangent to the graph of `g` at a point `P` has a negative gradient and intersects the `y`-axis at point `D(0, k)`, where `5 <= k <= 8.`
- Find the gradient of the tangent in terms of `k.` (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- i. Find the rule `A(k)` for the function of `k` that gives the area of the shaded region. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. Find the maximum area of the shaded region and the value of `k` for which this occurs. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- iii. Find the minimum area of the shaded region and the value of `k` for which this occurs. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2015 VCAA 4 MC
Consider the tangent to the graph of `y = x^2` at the point `(2, 4).`
Which of the following points lies on this tangent?
A. `text{(1, −4)}`
B. `(3, 8)`
C. `text{(−2, 6)}`
D. `(1, 8)`
E. `text{(4, −4)}`







