Which device is used to measure the airspeed of an aircraft in flight?
- Altimeter
- Pitot tube
- Wind gauge
- Potentiometer
Aussie Maths & Science Teachers: Save your time with SmarterEd
Which device is used to measure the airspeed of an aircraft in flight?
`B`
`=>B`
Outline benefits of digital signal transmission. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Benefits of digital signal transmission include:
Benefits of digital signal transmission include:
Why would an engineer refer to shear force diagrams and bending moment diagrams when determining the effects of loads on a beam? (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A 6-metre beam is loaded as shown.
On the following page, draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams. Support your answer with relevant calculations. Ignore the weight of the beam.
Space for calculations is provided below. (6 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
“
`text{Shear Force calculations:}`
`text{SF}_1=+↑ SigmaF = 16\ text{kN}`
`text{SF}_2=+↑ SigmaF = 16-15 = 1\ text{kN}`
`text{SF}_3=+↑ SigmaF = 16-15-12 = -11\ text{kN}`
`text{Bending Moment calculations:}`
`text{BM}_1=+↓ SigmaM = 16 xx 2=32\ text{kNM}`
`text{BM}_2=+↓ SigmaM = 16 xx 3-15xx1=48-15=33\ text{kNM}`
`text{BM}_3=+↓ SigmaM = 16 xx 6-15xx4-12xx3=96-60-36=0\ text{kNM}`
The components of the bearing assembly used in the fidget spinner are shown.
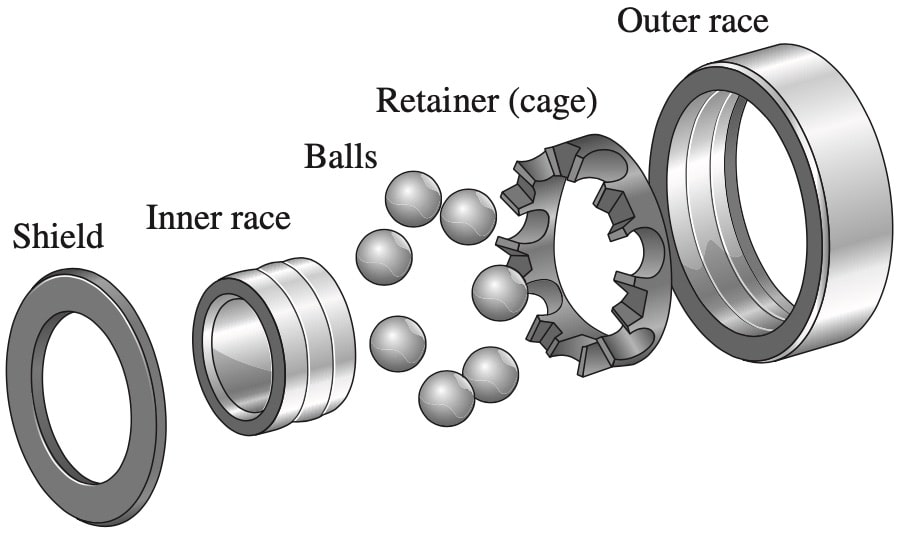
The retainer can be made from either glass fibre-reinforced nylon or stainless steel.
Compare the in-service properties of these materials for use in the retainer. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A fidget spinner is shown. It is a toy that contains a ball bearing in its centre and is designed to spin on its axis with little effort.
The central components of a fidget spinner are press fitted together using a press punch.
The press punch diameter is 21 mm. The force applied by the press punch to the bearing is 17.3 N.
Calculate the compressive stress in the press punch. (2 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`50\ 000\ text{Pa}`
| `F` | `=17.3\ text{N}` | |
| `a` | `=(pi xx 21^2)/4=346\ text{mm}^2=0.000346\ text{m}^2` |
`sigma=F/a=17.3/0.000346=50\ 000\ text{Pa}`
Identify factors that contribute to stress corrosion cracking in aluminium alloy aircraft components. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A two-engine aircraft with mass 330 tonnes is climbing at 15°. Each engine produces 510 kN of thrust. The aircraft maintains a constant velocity.
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i.
ii. `text{Find Induced drag} (D):`
`text{Weight}\ (W)=text{m} xx text{g}=330 xx 10^3 xx 10=33 xx 10^5\ text {N}`
`text{Thrust}\ (T)=510 xx 10^3 xx 2=102 xx 10^4\ \text{N}`
| `T` | `= D + W\ sin\ gamma` | |
| `D` | `= T-W\ sin\ gamma` | |
| `=102 xx 10^4 – 33 xx 10^5\ sin15^\circ` | ||
| `=165\ 897.1512` | ||
| `=166 xx 10^3` | ||
| `=166\ text{kN}` |
Describe the basic operational principles of jet propulsion. Use a labelled sketch to support your answer. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
The cross-section of an extruded aluminium alloy plank is shown.
Outline the steps of the extrusion process. (2 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The extruded aluminium plank is made by:
The extruded aluminium plank is made by:
The diagram shows a scaffold supporting planks. The planks can be made from laminated timber, aluminium alloy or galvanised steel.
Outline an in-service advantage of each of these materials when used as a scaffold plank. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Answers could include one advantage from each material type below:
Laminated timber plank
Aluminium scaffold plank
Galvanised steel planks
Answers could include one advantage from each material type below:
Laminated timber plank
Aluminium scaffold plank
Galvanised steel planks
Telecommunication signals can be carried by a variety of transmission media. A common form of connection between a television set and an antenna is a coaxial cable.
Why is copper-coated steel used for the central wire? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The self-driving vehicle has a mass of 1.5 tonnes and is travelling at 60 km/h.
Calculate its kinetic energy. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`208.4\ text{kJ}`
`text{Converting km/h to m/second:}`
`v=60\ text{km/h}=(60\ 000)/3600\ text{m/s}= 16.67\ text{m/s}`
`m=1.5\ text{tonnes} =1500\ text{kg}`
| `KE` | `=1/2mv^2` | |
| `=1/2 xx 1500 xx 16.67^2` | ||
| `=208\ 416.675\ text{J}` | ||
| `=208.4\ text{kJ}` |
A pulley system is shown.
What is the mechanical advantage of this pulley system?
`C`
`=>C`
An engineer has been asked to investigate and report on the failure of a component.
Which row of the table correctly identifies what the engineer would need to do before finalising the report?
`B`
`=>B`
Orthogonal and pictorial drawings of a sheet metal electrical cable cover are given below.
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
i.

ii. `3.46\ text{kN}`
i.

Key Points for this Drawing:
| ii. | `delta_S` | `=F_S/A_S` |
| `F_S` | `=delta_S xx A_S` |
`A_S = pid xx t=pi xx 20 xx 0.5 = 31.4\ text{mm}^2`
`:.F_S= 110 xx 31.4=3455.7\ text{N}=3.46\ text{kN}`
Compare proteins and polypeptides. (2 marks)
Proteins and Polypeptides
Proteins and Polypeptides
The U-bolt clamp shown is used to hold a Ø42 digital TV aerial pipe in place.
Draw an assembled half-sectional front view of this U-bolt clamp to AS 1100 standards. The front is indicated by the direction of the arrow.
Use a scale of 2 : 1 and place the half section on the right-hand side. (6 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The AS 1100 drawing reflects the correct scale, but we note exact measurements are required for the exam diagram.
Key Points for this Drawing:
Explain how TWO different methods used to treat drinking water reduce the risk of infection. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Pasteur performed an experiment to identify the role of microbes in decay.
Justify a conclusion that can be drawn from his results. (2 marks)
Pasteur’s swan-neck flask experiment
Pasteur’s swan-neck flask experiment
Mean mark (b)(ii) 51%
Why is the routine testing of engineering components important during service? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The flaps of an executive jet are controlled using a hydraulic system. A force of 1 kN acts on the 40 mm diameter master piston.
What force would need to be developed to move the flap if the slave piston has a diameter of 100 mm? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`6.25\ text{kN}`
`P=F/A`
| `1000/(pi xx 20^2)` | `=F_S/(pi xx 50^2)` | |
| `F_S` | `=(1000 xx pi xx 50^2)/(pi xx 20^2)=6250\ text{N}=6.25\ text{kN}` |
A pin-jointed truss designed to support a roadside sign is shown.
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. `R_B=37\ text{N} larr`
`R_A=44.7\ text{kN}, \ theta=26.6^(@)`
ii. `F_C=17\ text{kN (compression)}`
iii. Suitability of concrete
\[\textbf{i}. \ \ \ce{->[\ce{+}]} \sum M_A = 0 \]
`3xx1.5-20 xx3+R_(B)xx1.5=0`
`4.5-60+1.5R_(B)=0`
| `1.5R_(B)` | `=55.5` | |
| `R_(B)` | `=(55.5)/(1.5)=37\ text{N} larr` |
`uarr sumF_(V)=0`
`R_(AV)=20\ text{kN} +uarr`
\[\ce{->[\ce{+}]} \sum F_H = 0 \]
`R_(AH)=37+3=40\ text{kN} rarr^(+)`
`R_A=sqrt(20^(2)+40^(2))=sqrt2000=44.7\ text{kN}`
| `tan\ theta` | `=(R_(AV))/(R_(AH))=20/40=0.5` | |
| `:.theta` | `=26.6^(@)` |
iii. Suitability of concrete
A child and sled with a combined mass of 23 kg are being pulled along a horizontal snow-covered surface using a rope.
The coefficient of static friction between the sled and the snow is 0.14.
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Sleds are used to slide loads over soft surfaces such as grass, sand and snow. They can be made using polypropylene.
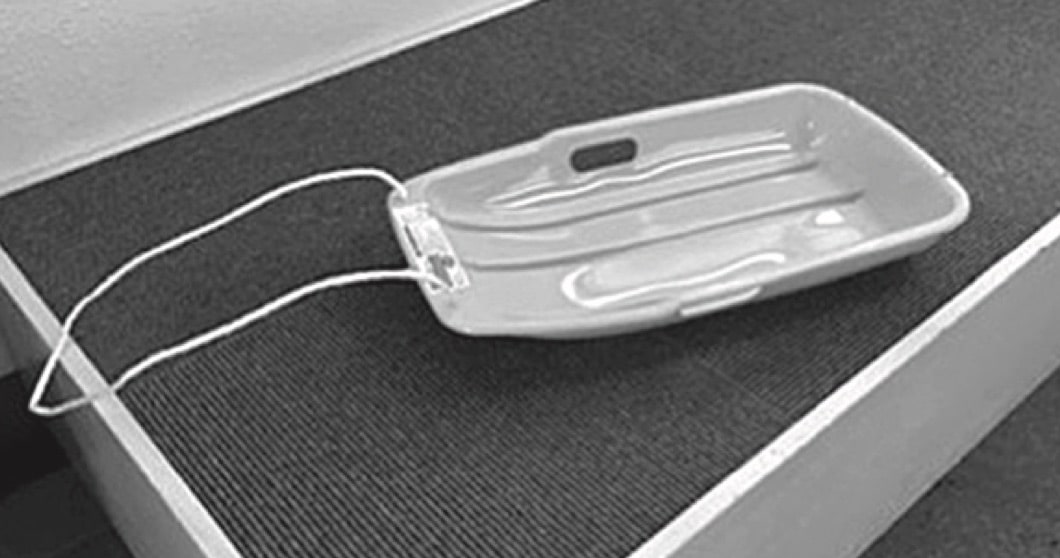

--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. Polypropylene properties
ii. Manufacturing method:
i. Polypropylene properties
ii. Manufacturing method:
A digital TV receiver circuit uses logic gates as shown.
Complete the truth table for this logic circuit. (2 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\begin{array} {|c|c|c|}
\hline \ \text{A}\ & \text{B}\ & \text{Z}\ \\
\hline \ \ \ \ 0\ \ \ \ & \ \ \ \ 0 \ \ \ \ & \ \ \ \ 1\ \ \ \ \ \\
\hline \ 0 & 1 & 0 \\
\hline \ 1 & 0 & 0 \\
\hline \ 1 & 1 & 0 \\
\hline \end{array}
\begin{array} {|c|c|c|}
\hline \ \text{A}\ & \text{B}\ & \text{Z}\ \\
\hline \ \ \ \ 0\ \ \ \ & \ \ \ \ 0 \ \ \ \ & \ \ \ \ 1\ \ \ \ \ \\
\hline \ 0 & 1 & 0 \\
\hline \ 1 & 0 & 0 \\
\hline \ 1 & 1 & 0 \\
\hline \end{array}
When a bike goes over a bump, there is a vertical force of 3 kN exerted axially on the main pillar.
The cross-section of the pillar is shown.
Calculate the compressive stress acting in the pillar. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`15.9\ text{MPa}`
| `text{CSA}` | `=(pi(d_1)^2)/4-(pi(d_2)^2)/4` | |
| `=pi/4(32^2 – 28^2)` | ||
| `=(240pi)/4` | ||
| `=188.5\ text{mm}^2` |
`sigma_c=F/A=3000/188.5=15.9\ text{MPa}`
A bike with a rider rolls down a hill without braking from a standing start at point `A`.
The combined weight of the bike and the rider is 100 kg.
Calculate the speed of the rider at point `B`. (Assume no wind resistance and 100 % efficiency.) (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`20\ text{m/s}`
`KE_text(bottom) = PE_text(top)`
| `1/2 mv^2` | `=mgh` | |
| `v^2` | `=2gh` | |
| `v` | `=sqrt(2xx10xx20)` | |
| `=sqrt(400)` | ||
| `=20\ text{m/s}` |
Carbon fibre was originally developed to produce aircraft bodies and high performance vehicles. Carbon fibre is now used in a wide range of applications, including the manufacture of the type of bicycle frame shown.
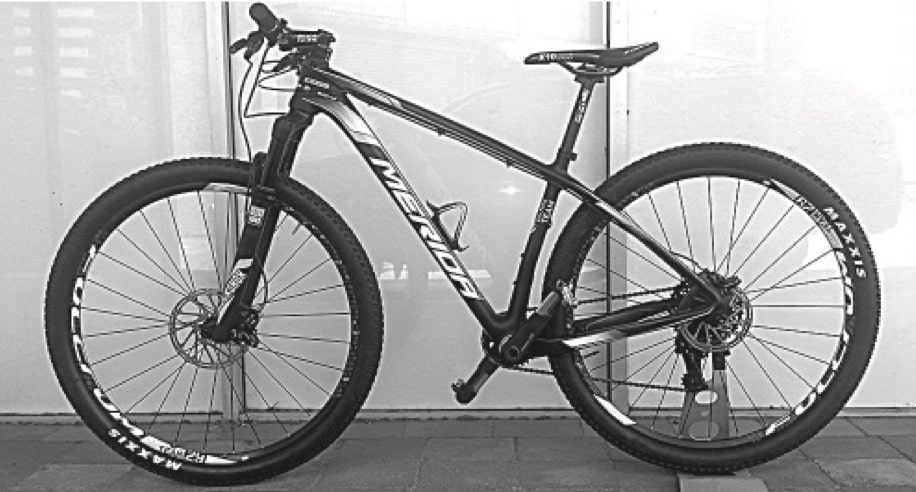

Outline the advantages of carbon fibre bicycle frames over steel bicycle frames. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Advantages of carbon fibre bicycle frames
Advantages of carbon fibre bicycle frames
Using examples, explain why gears are used in the design of vehicles. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
An assembly drawing of a bracket and lock pin with the flange removed is shown.
Using the starting lines and centre mark provided, draw a fully sectioned top view, to AS 1100 drawing standards. The section plane passes through the centre of the mounting holes. Use the dimensions on the drawing and the lock pin diameter determined in part (b)(i). Use a scale of 1:2. (3 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
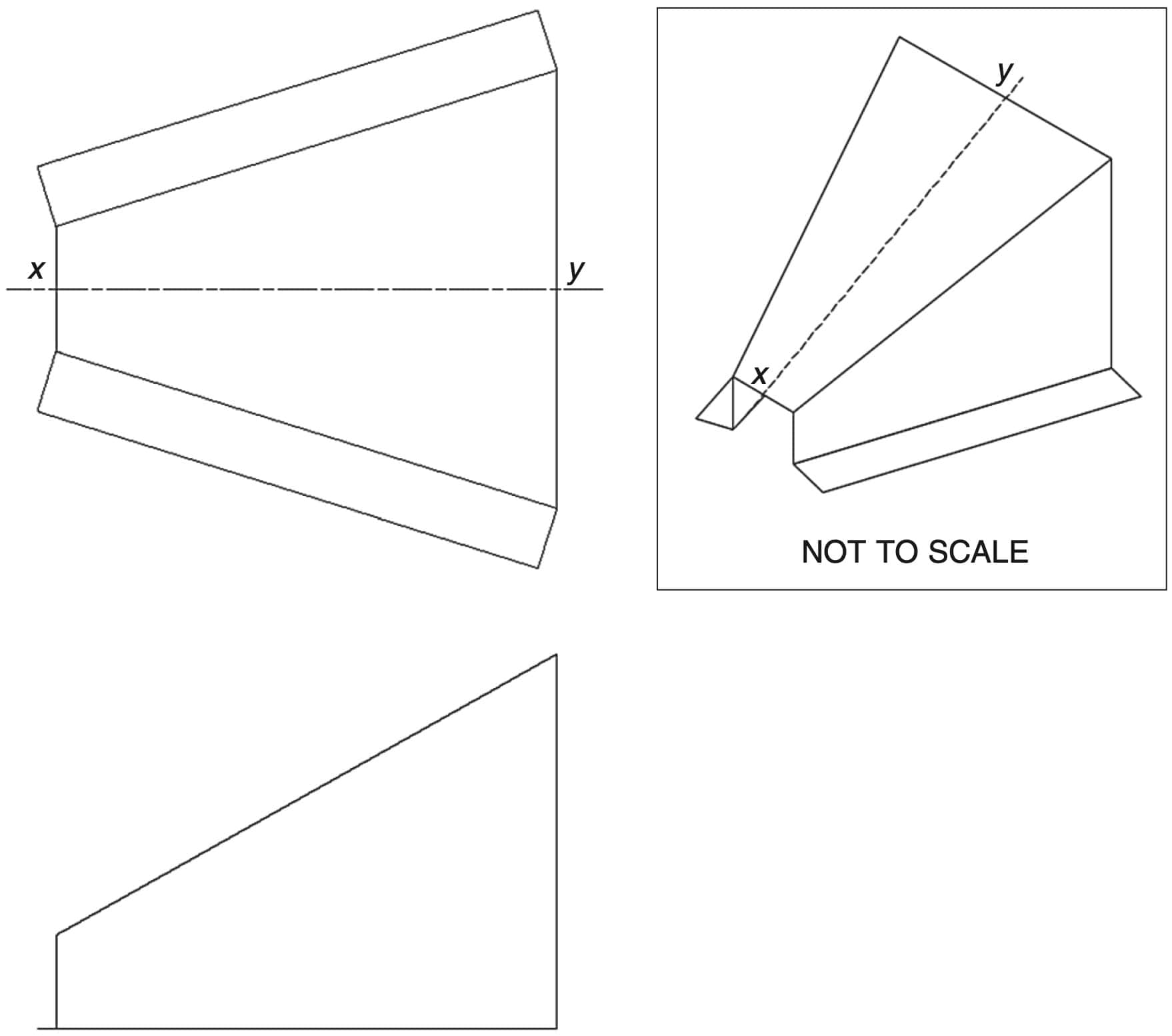
A transition piece is shown.
Which of the following correctly represents the development of the transition piece?
`A`
`=>A`
An orthogonal view of a smart watch is shown.
Construct a freehand pictorial sketch of the smart watch as viewed in the direction of the arrow. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
Notes on this drawing:
Notes on this drawing:
Genetically engineered Atlantic salmon have been produced and approved for aquaculture in the US.
The graph summarises the growth of standard salmon and transgenic salmon.
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The photograph shows an AM radio coupled to a pedal-powered generator. This radio allowed communication in remote areas of Australia during the 1920s.
Explain how the mechanical energy from pedalling was converted into electrical energy in the generator to power the AM radio. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The photograph shows a board with a hydrofoil attached underneath.
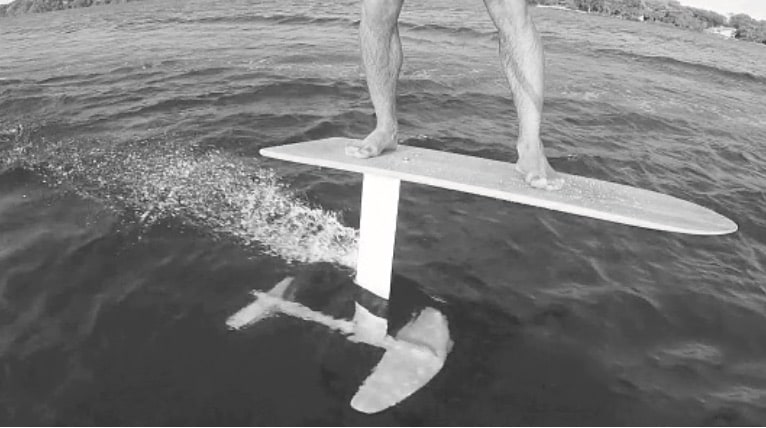

The hydrofoil is used to lift the board out of the water as the rider is towed behind a boat at high speed.
Explain why the hydrofoil can lift the board out of the water when it is travelling at high speed. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
An intricate component used on racing yachts is shown below being modelled using computer-aided drawing (CAD) software.
Explain why engineers use CAD software to design and model intricate components. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Some materials have properties that allow them to be used in the manufacture of both modern racing yachts and aircraft. These materials include Kevlar® aramid fibre, carbon fibre epoxy composites and aluminium alloys.
Complete the table by providing a property which makes each of these materials suitable for the manufacture of both yachts and aircraft. (3 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Modern racing yachts are now designed using aeronautical engineering principles.
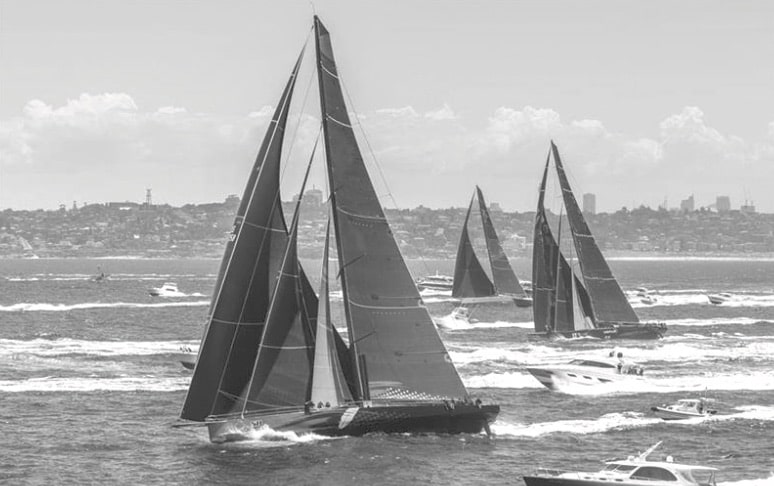

The diagram shows the hull of a racing yacht.
How can engineers use an understanding of the effects of drag to improve the design of racing yacht hulls? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
An image of an aeroplane is shown with the position of the wing support beam indicated.
Assume the engines are supported by the single beam. The beam runs through the plane, wing tip to wing tip.
Compare the use of composite materials with the use of metals for the manufacture of the beam. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Answers could include 3 of the following comparisons:
Composite materials vs Metals
Answers could include 3 of the following comparisons:
Composite materials vs Metals
A scooter and rider enter the half pipe shown at a velocity of 3 m/s. The scooter and rider have a combined mass of 55 kg.
Calculate the maximum height, `h`, the scooter and rider will reach above the other side of the pipe wall. Assume no loss of energy. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`0.45\ text{metres}
| `:.\ KE_2 + PE_2` | `= KE_1 + PE_1` | |
| `0 + mgh_2` | `= 1/2mv_1^2 + mgh_1` | |
| `10 xx (2 + h)` | `= (1/2 xx 3^2) + (10 xx 2)` | |
| `20 + 10h` | `= 4.5 + 20` | |
| `h` | `= 4.5/10= 0.45\ text{metres}` |
Titanium is used to manufacture aircraft undercarriages that support landing wheels.
Why is titanium used in preference to alloy steel for this purpose?
`B`
`=>B`
Which row of the table indicates the effects of retrofitting winglets to a plane?
`B`
`=>B`
A sketch of a post-tensioned concrete beam is shown.
Which of the following shows the most likely loading condition the beam is designed to resist when viewed from the front?
`D`
`=>D`
Which row of the table correctly identifies the routine maintenance responsibilities of an aeronautical engineer working for a small commercial airline?
`A`
`=>A`
The schematic diagram shows a bridge rectifier.
What is the function of this bridge rectifier?
`D`
`=>D`
Which of the following identifies TWO properties of polymers that make them better suited than ceramics for the insulation of telecommunication cables?
`B`
By Elimination:
`=>B`
Describe TWO different uses of polymers in telecommunications. (4 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Answers could include any two of the following:
Cable protection and insulation
Circuit components
Device casings and housings
Answers could include any two of the following:
Cable protection and insulation
Circuit components
Device casings and housings
Different modes of transport emit different amounts of carbon dioxide `(\text{CO}_2)`. For example, petrol cars emit more `\text{CO}_2` than electric cars while in motion.
Describe engineering innovations that have led to lower carbon dioxide emissions from electric transportation. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Answers should discuss one of the following:
Electric powered cars
Electric powered bikes
Answers should discuss one of the following:
Electric powered cars
Electric powered bikes
Explain how engineers have used their knowledge of both mechanics and hydraulics to contribute to aircraft design. Support your answer with specific examples. (5 marks)
--- 17 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
An aeronautical engineer is developing a prototype for a new propeller design.
Identify a suitable method of developing the prototype and outline the benefits of using this method. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Possible methods include:
CAD software
3D printing
CNC Milling
Scaled physical model
Possible methods include:
CAD software
3D printing
CNC Milling
Scaled physical model
In 1927, Davisson and Germer reported the results of an experiment in which they fired electrons at a crystal of nickel and observed how the electrons were scattered.
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. Experiment Results:
ii. The Rutherford-Bohr model:
i. Experiment Results:
ii. The Rutherford-Bohr model:
The mass of a polonium-218 nucleus is 218.00897 u, the mass of a lead-214 nucleus is 213.99981 u, and the mass of an alpha particle is 4.00260 u.
Calculate the energy released by this alpha decay. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`9.8 xx10^(-13)\ text{J}`
\(\text{Mass}_{i} = 218.00897\ \text{u} \)
\(\text{Mass}_{f} = 213.99981 + 4.00260 = 218.00241\ \text{u} \)
\(\text{Difference} = 218.00897-218.00241 = 0.00656\ \text{u} \)
\(\text{Difference (kg)} = 0.00656 \times 1.661 \times 10^{-27} = 1.08962 \times 10^{-29}\ \text{kg} \)
| `E` | `=mc^2` | |
| `=1.08962xx10^(-29)xx(3 xx10^8)^2` | ||
| `=9.8 xx10^(-13)\ text{J}` |
The position of the Sun, star `W` and star `Z` are shown on the H-R diagram.
The curves `A` and `B` show intensity versus frequency for star `W` and the Sun, measured from the same distance.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. Curve A represents star `W`:
ii. Differences displayed in H-R graph:
Other possible answers could include:
i. Curve A represents star `W`:
ii. Differences displayed in H-R graph:
Other possible answers could include:
Calculate the initial energy level of an electron in a hydrogen atom if it emitted `4.089 × 10^{-19}` J on transition to the `n` = 2 level. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`n_i = 4`
`E/(hc) = 1/lambda`
| `E/(hc)` | `=R(1/((n_f)^2)-1/((n_i)^2))=R(1/(2^2)-1/((n_i)^2))` | |
| `1/(n_i)^2` | `=1/4-(E)/(Rhc)` | |
| `=1/4-(4.089 xx 10^{-19})/(1.097 xx 10^7 xx 6.626 xx 10^(-34) xx 3 xx 10^8)` | ||
| `=0.06248` |
`n_i=sqrt(1/0.06248) = 4`
Outline features of the hydrogen spectrum that Bohr's model could not explain. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Explain the stability of `\ _(2)^(4)text{He}` nuclei in terms of TWO forces. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Repulsive electrostatic force:
Attractive strong nuclear force:
Repulsive electrostatic force:
Attractive strong nuclear force:
The diagrams show features of the hydrogen emission spectrum.
With reference to Bohr's postulates, explain how the line at 434.0 nm in the hydrogen emission spectrum is produced. Support your answer with calculations. (4 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
| `1/lambda` | `=R(1/((n_f)^2)-1/((n_i)^2))` | |
| `=R(1/(2^2)-1/((n_i)^2))` | ||
| `1/(n_i)^2` | `=1/4-1/(lambdaR)` | |
| `(n_i)^2` | `=1/(1/4-1/(1.097 xx 10^7 xx 434 xx 10^9))` | |
| `n_i` | `=5` | |
| `1/lambda` | `=R(1/((n_f)^2)-1/((n_i)^2))` | |
| `=R(1/(2^2)-1/((n_i)^2))` | ||
| `1/(n_i)^2` | `=1/4-1/(lambdaR)` | |
| `(n_i)^2` | `=1/(1/4-1/(1.097 xx 10^7 xx 434 xx 10^9))` | |
| `n_i` | `=5` | |