A plant species found in the area immediately around Sydney has also been found in a small area in the Gibraltar Range in the far north of NSW. Predict what might happen to the TWO populations over the next 5 million years, in terms of Darwin/Wallace's theory of evolution. (3 marks)
BIOLOGY, M3 2009 HSC 27
Most offspring resemble their parents in a number of characteristics, but there are often some characteristics in the offspring that are unexpected.
Explain, using examples, how genetics and the environment can affect the phenotype of individuals. (8 marks)
--- 16 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M3 2010 HSC 30
BIOLOGY, M3 2013 SM-Bank 21
Explain how ONE secondary source has provided support for the theory of evolution. (4 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M3 2014 HSC 26
Explain how Darwin/Wallace's theory of evolution by natural selection and isolation accounts for convergent evolution. Use an example to support your answer. (5 marks)
BIOLOGY, M2 2014 HSC 24
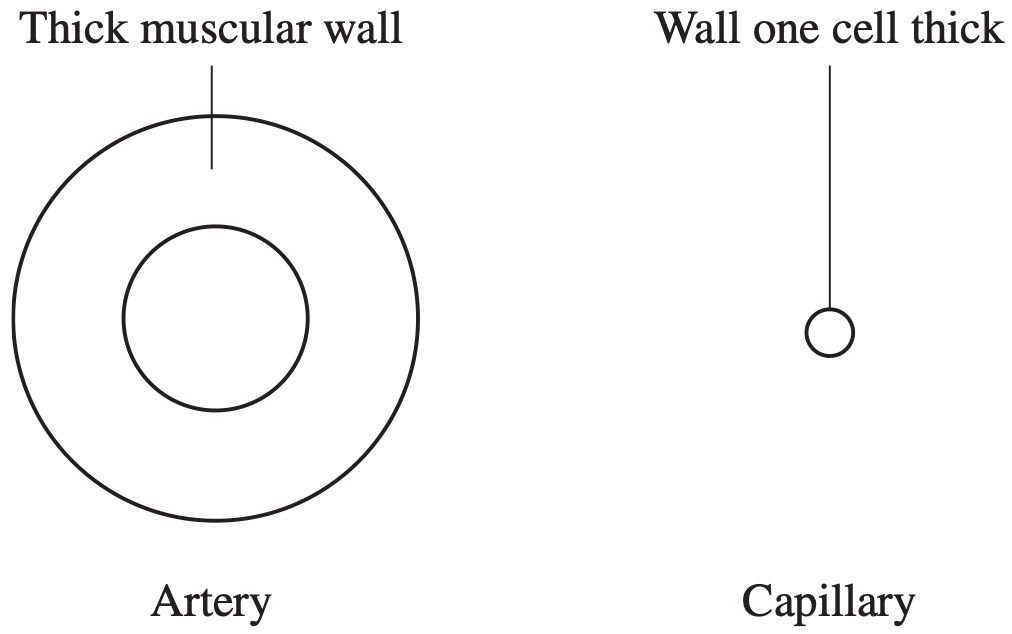
- Use labelled diagrams to distinguish between the structure of an artery and that of a capillary. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
- Relate one structure of a capillary to its function. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M2 2015 HSC 27
- Outline TWO differences between whole blood and plasma. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The steps below show the preparation and use of blood products in the treatment of Ebola Virus Disease. This disease is characterised by significant blood loss.
- Explain why this protocol produces an effective treatment for Ebola Virus Disease. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M2 2015 HSC 24
Data can be provided by a pulse oximeter pegged to a person's finger, as shown in the diagram.
- What is the oxygen saturation for this person? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Outline TWO limitations of using only the information provided in the diagram to determine the 'health' of a person. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain TWO advantages in using a pulse oximeter to measure oxygen saturation compared to using another named technology in a specific setting. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M2 2016 HSC 31
As altitude increases, the partial pressure of oxygen \( \text{(p} \ce{O_2)}\) in air decreases.
Species A and B are closely related endotherms that live in different habitats in Asia. The minimum \( \text{p} \ce{O_2}\) required for 100% blood oxygen saturation differs in these species because of differences in their haemoglobin structure. Data related to these two species are shown below.
\begin{equation}
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Endotherm species } & \text { Habitat altitude } & \text { Minimum } \mathrm{pO}_2 \text { for } 100 \%\ \mathrm{Hb} \text { saturation } \\
\hline \mathrm{A} & \mathrm{High} & 54 \\
\mathrm{~B} & \text { Low } & 80 \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{equation}
Explain how the differences in these species could have arisen, using the Darwin/Wallace theory of evolution and your understanding of the adaptive advantage of haemoglobin. (8 marks)
--- 18 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M2 2016 HSC 27
The diagram shows a vascular bundle from a flowering plant.
- On the diagram, clearly label a xylem vessel. (1 mark)
- A adaptation of this species causes the walls of the xylem vessels to be significantly reduced in thickness.
- Explain why the leaves of these adapted strains will wilt more easily. (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M2 2017 HSC 23
BIOLOGY, M1 2008 HSC 18
Using a light microscope, a student looked at a prepared slide of human blood, and drew a scaled diagram.
The diagram shown is a representation of the student's scaled diagram.

- Assess the accuracy of the diagram. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Why is it safer to use prepared slides instead of fresh blood? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M1 2012 HSC 24
You conducted first-hand investigations to test the effects of temperature, pH and substrate concentration on enzyme activity. \begin{array} {|l|c|c|} --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textit{Independent variable} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \textit{Dependent variable} & \textit{Kept constant} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & & \text{pH,} \\ & & \text{substrate concentration,} \\ \text{................................} & \text{................................} & \text{enzyme concentration} \\
\hline
\end{array}
BIOLOGY, M1 2013 HSC 29
- What chemicals are filtered out of the blood by the kidney? (2 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain the steps involved in the formation of urine. (4 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M1 2013 HSC 25
The graph below shows the results obtained from testing the activity of a bacterial enzyme.
- Name ONE variable, other than temperature, that would have been controlled in the experiment. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For what temperature range does the enzyme display the maximum rate of change in activity? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Account for the activity of the enzyme at the parts of the graph labelled A, B, C and D. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Based on the information in the graph, suggest the type of environment in which these bacteria might survive. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M1 2016 HSC 23
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M1 2017 HSC 26
A controlled experiment was performed to investigate the effect of substrate concentration on the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction. Data were collected and are presented in the graph.
- What is the independent variable in this experiment? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain the trends shown in the graph. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M1 2017 HSC 25
Explain the difference in the urine concentration of marine fish and freshwater fish. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M7 SM-Bank 23
Smallpox is widely believed to be the cause of the significant population decline in Indigenous populations during early European arrival in Australia. Recent research suggests that it may have been chickenpox that caused the change in population numbers rather than smallpox. It is thought that chickenpox did not exist in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities before European arrival. Chickenpox is fairly mild in young children and is easily transmitted. It can be a fatal disease in adults who were not infected as children.
The graph below shows population numbers during the period 1780 –1850:
-
- the estimated Aboriginal Australian population
- the colonist population
- the estimated total Australian population
With reference to chickenpox, explain how infection may have caused such a large impact on the Aboriginal Australian population and yet did not affect the population numbers of the colonists significantly, and why the Aboriginal population increased from 1790 to 1810. (3 marks)
BIOLOGY, M7 SM-Bank 22
A summary of case-control studies conducted from 1997 to 2003 showed that a single dose of varicella (chickenpox) vaccine was 97% effective in the first year after vaccination and 86% effective in the second year. From the second to eighth year after vaccination, the vaccine's effectiveness remained stable at 81% to 86%. Most vaccinated children who developed chickenpox during the eight years after vaccination had a mild case of the disease.
Why do most vaccinated individuals, if they are infected, show only a mild case of the disease? (2 marks)
BIOLOGY, M7 SM-Bank 27
Influenza is an infectious respiratory disease. In humans, it can be caused by the influenza A or influenza B viruses. Antigenic drift can result in small changes to the structure of the antigens on the surface of the influenza virus, as shown in the diagram below. --- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M7 SM-Bank 7 MC
The human body does not normally produce an immune response against self cells.
Cells in the human immune system can distinguish self cells from non-self cells
- because non-self cells have a faster reproduction rate.
- due to the presence of different antigens on non-self cells.
- only when antibodies are attached to the surface of non-self cells.
- because non-self cells are always smaller in size than self cells.
BIOLOGY, M5 SM-Bank 25
In fruit flies, eye colour is a sex-linked trait inherited on the X chromosome. The red-eye allele R is dominant over the white-eye allele (r). A red-eyed male and white-eyed female have 50 offspring.
Use a Punnett square to predict the number of male and female offspring and their eye colour. (3 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 SM-Bank 24
Explain how transcription factors control cell differentiation, using an example. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 SM-Bank 22
Describe the roles of messenger RNA and transfer RNA in protein synthesis. (2 marks)
BIOLOGY, M6 SM-Bank 24
In 1950 , the myxoma virus was released into Australian pest rabbit populations to reduce their numbers. The resulting disease, myxomatosis, initially wiped out 95% of the rabbit population; however, it quickly became less effective as a population control measure.
This graph shows the frequency of myxomatosis resistance in Australia's rabbit population from 1949 to 1956.
Use evidence from the graph and the principles of natural selection to explain how myxomatosis became ineffective as a population control measure. (3 marks)
BIOLOGY, M5 SM-Bank 23
Explain the purpose of gel electrophoresis in DNA profiling. (2 marks)
PHYSICS, M8 EQ-Bank 21
With reference to the earliest conditions present following the Big Bang, describe the processes that led to the transformation of radiation into matter. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M6 EQ-Bank 29
Prior to 2019, the ampere was characterized as the unvarying current that, when sustained in two infinitely long, straight parallel conductors with negligible circular cross-section and spaced one meter apart in a vacuum, would result in a force of `10 xx 10^{-7}` newton per metre of length between the conductors.
- How does Newton’s Third Law apply to this definition of the ampere? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Two parallel current carrying wires are 1.2 metres long each, both carrying 0.55 amperes at a distance of 25 mm apart. Calculate the force between the wires. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 EQ-Bank 29
The information in the table shows how the solubility of lead chloride is affected by temperature.
Using a graph, calculate the solubility product \((K_{sp})\) of the dissolution of lead chloride at 50°C. Include a fully labelled graph and a relevant chemical equation in your answer (6 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 EQ-Bank 28
A 100 mL saturated solution of calcium hydroxide at 25°C contains 0.173 g of calcium hydroxide.
- Calculate the solubility product \(\ce{($K_{sp}$)}\) of this salt at 25°C. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain why the undissolved solid is not included in the expression for the solubility product constant. (1 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 EQ-Bank 26
CHEMISTRY, M5 EQ-Bank 24
When a sample of solid silver chloride is added to a `1.00 xx10^(-2)` mol L−1 sodium chloride solution, only some of the silver chloride dissolves.
Calculate the equilibrium concentration of silver ions in the resulting solution, given that the `K_(sp)` of silver chloride is `1.8 xx10^(-10)`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 EQ-Bank 23
Butanoic acid is a natural product and a component of human sweat.
Calculate the value of \(\ce{$K_{a}$}\) for butanoic acid if a 0.10 mol L–1 solution has a pH of 2.9 at 298 K. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 13 MC
The pKa of trichloroacetic acid is 0.70 and the pKa of acetic acid is 4.8.
Which of the following identifies the acid with the higher pH and explain why?
- Acetic acid as it is less likely to lose a hydrogen ion
- Acetic acid as it is more likely to lose a hydrogen ion
- Trichloroacetic acid as it is less likely to lose a hydrogen ion
- Trichloroacetic acid as it is more likely to lose a hydrogen ion
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 28
The flowchart shown outlines the sequence of steps used to determine the concentration of an unknown hydrochloric acid solution.
Describe steps A, B and C including correct techniques, equipment and appropriate calculations. Determine the concentration of the hydrochloric acid. (8 marks)
--- 16 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M7 EQ-Bank 21
With the use of a labelled diagram, describe how grease can be removed from fabric using soap. (3 marks)
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 27
What determines the pH of a buffer solution? (2 marks)
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 23
Propanoic acid dissociation in water can is represented in the following equation:
\(\ce{CH3CH2COOH($aq$) + H2O($l$) \rightleftharpoons CH3CH2COO^-($aq$) + H3O^{+}($aq$)}\)
Explain how the pH of the propanoic acid solution would change if it was diluted. (3 marks)
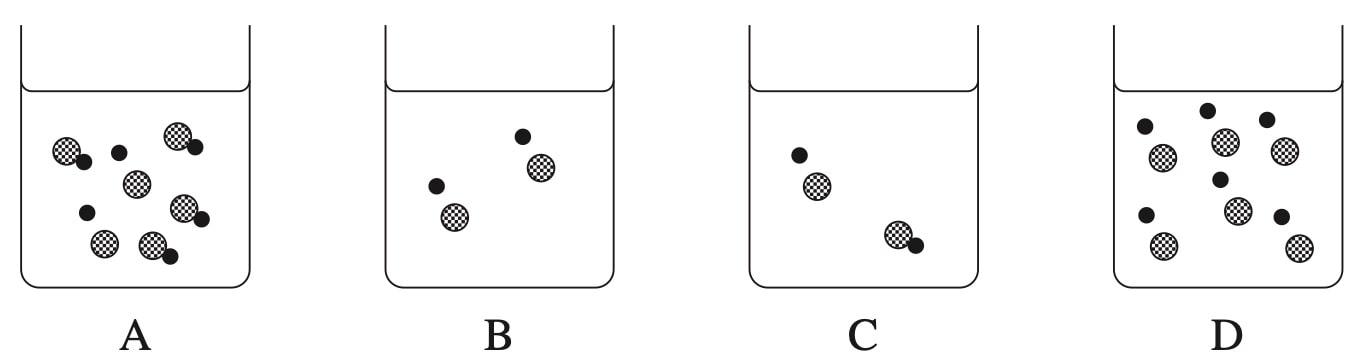
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 5 MC
Which beaker contains a concentrated strong acid?
CHEMISTRY, M6 EQ-Bank 8 MC
Which of the following is NOT a Bronsted-Lowry reaction?
- \(\ce{NH4^+ + NH2^- \rightleftharpoons 2NH3}\)
- \(\ce{CO2 + OH^- \rightleftharpoons HCO3^-}\)
- \(\ce{HClO4 + CH3COOH \rightleftharpoons CH3COOH2^+ + ClO4^-}\)
- \(\ce{CH3CH2O^- + CH3NH3^+ \rightleftharpoons CH3CH2OH + CH3NH2}\)
CHEMISTRY, M7 EQ-Bank 27
Contrast ONE addition polymer and ONE condensation polymer in terms of their structures, properties and uses. Include structural formulae in your answers. (7 marks)
--- 20 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 EQ-Bank 22
A bottle of solution is missing its label. It is either \(\ce{Pb(NO_3)_2, Ba(NO_3)_2 or Fe(NO_3)_2}\).
Using only \(\ce{HCl, NaOH}\) and \(\ce{H_2SO_4}\) solutions, outline a sequence of steps that could be followed to confirm the identity of the solution in the bottle. Include observed results and ionic equations in your answer. (4 marks)
CHEMISTRY, M5 EQ-Bank 10 MC
At a certain temperature, the \(\ce{$K_{eq}$}\) for the following reaction is 75.
\( \ce{2O3(g) \rightleftharpoons 3O2(g)}\)
0.4 mol of \(\ce{O3}\) and 1.2 mol of \(\ce{O2}\) were introduced to a 5 L reaction vessel.
Which row of the table correctly identifies the direction of the equilibrium shift and the reason for the shift?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{Direction favoured}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \quad \quad \textit{Reason} \quad \quad \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Left}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&Q>K_{e q}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Left}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& Q<K_{e q}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Right}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&Q>K_{e q} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Right}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& Q<K_{e q}\\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
Algebra, STD1 A1 2020 HSC 18
The distance, `d` metres, travelled by a car slowing down from `u` km/h to `v` km/h can be obtained using the formula
`v^2 = u^2-100 d`
What distance does a car travel while slowing down from 70 km/h to 40 km/h? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, STD1 A1 2019 HSC 34
Given the formula `C = (A(y + 1))/24`, calculate the value of `y` when `C = 120` and `A = 500`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD1 M1 2019 HSC 25
Measurement, STD1 M2 2020 HSC 15
The time in Melbourne is 11 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time in Honolulu is 10 hours behind UTC. A plane departs from Melbourne at 7 pm on Tuesday and lands in Honolulu 9 hours later.
What is the time and day in Honolulu when the plane lands? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, STD1 F3 2021 HSC 30
Blake opens a new credit card account on 1 May. He uses it, for the first time, on 4 May to buy concert tickets for $850.
He makes no further purchases or repayments during the month of May.
A statement for the credit card is issued on the last day of each month.
The statement for May shows that interest is charged at 19.75% per annum, compounding daily, from 20 May (included) until 31 May (included).
- What is the compound interest shown on the statement issued on 31 May? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The minimum payment is calculated as 3% of the closing balance on 31 May. Calculate the minimum payment. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M7 EQ-Bank 26
This flow chart shows reactions involving six different organic compounds (A to F).
Draw the structures of compounds A to F, justifying your diagrams with reference to the information provided. (7 marks)
--- 16 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M7 EQ-Bank 23
- Design a procedure that can be used to produce the ester, ethyl ethanoate, in a school laboratory. (4 marks)
--- 12 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Describe a safety precaution in the production of an ester in a school laboratory. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M7 EQ-Bank 22
Calculate the mass of methanol that must be burnt to increase the temperature of 325 g of water by 65°C, if exactly half of the heat released by this combustion is lost to the surroundings.
The heat of combustion of methanol is 726 kJ mol ¯1. (3 marks)
CHEMISTRY, M5 EQ-Bank 5 MC
CHEMISTRY, M7 EQ-Bank 25
Draw the structural formulae and name all possible isomers of hexane. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M7 EQ-Bank 24
Primary, unbranched alcohols and alkanes of the same carbon length have quite different boiling points.
Explain the difference in boiling point of these organic compounds, showing all intermolecular forces. Support your answer with diagrams. (4 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 EQ-Bank 22
- The diagram is a schematic representation of a mass spectrometer.
- Name and outline the function of the part labelled `A` in the diagram. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Outline the advantages of using mass spectrometry for analysis of a compound. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 EQ-Bank 25
The diagram shows the infrared spectrum of a compound.
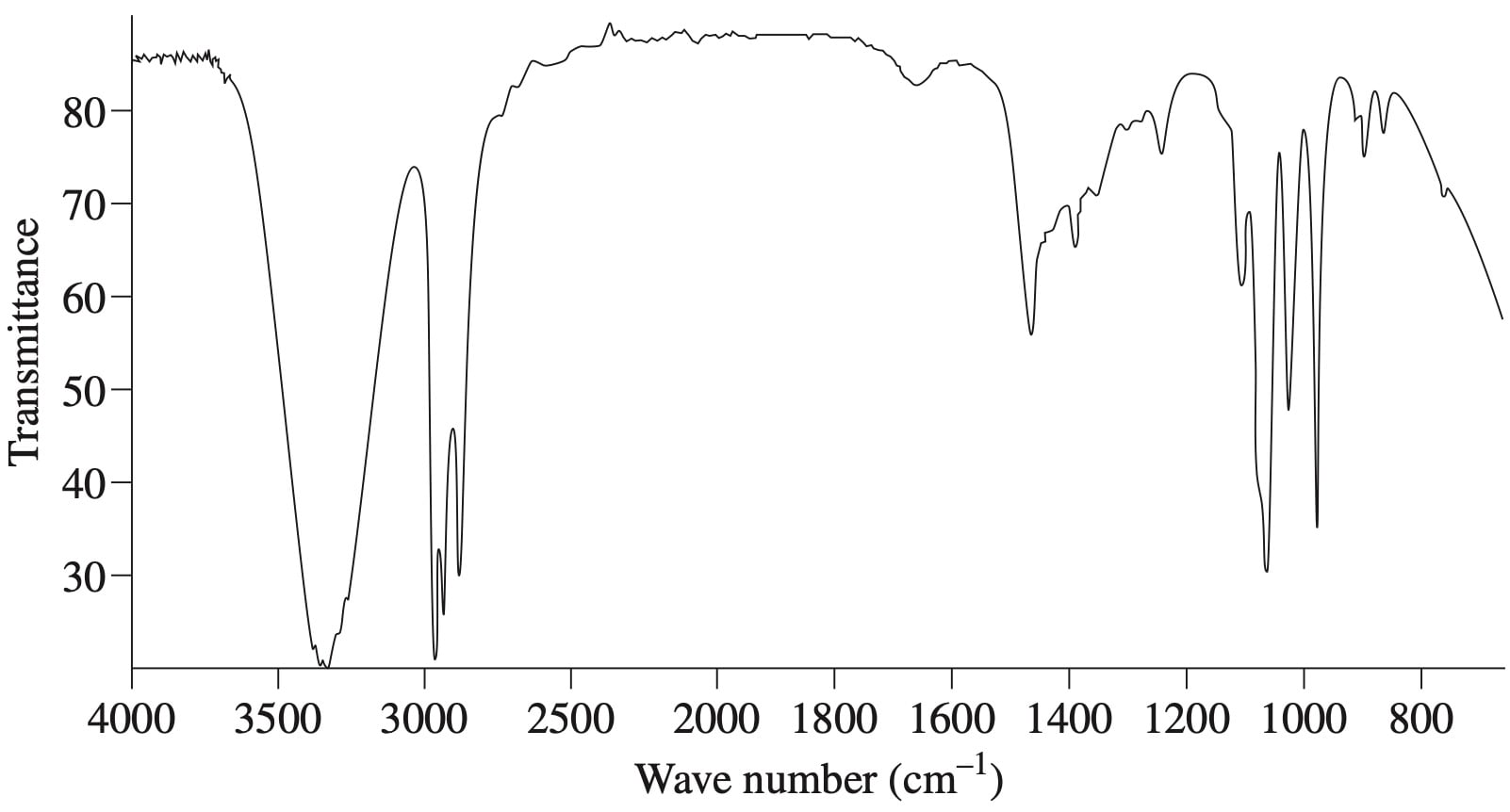
The molecular weight of the compound analysed is approximately 60 g mol ¯1. Suggest TWO possible compounds that could fit this spectrum and justify your selection. (4 marks)
CHEMISTRY, M8 EQ-Bank 23
\(\ce{Fe^2^+}\) and \(\ce{X} \) react to form an ionic compound according to the general equation
\(\ce{aFe^2^+ + $b$(X)\rightleftharpoons [Fe_a(X)_b]^2^a^+}\)
where \(\ce{$a$}\) and \(\ce{$b$}\) are numbers representing the ratio in which \(\ce{Fe^2^+}\) and \(\ce{X} \) combine.
Spectrophotometry was used to determine the stoichiometric ratio between \(\ce{Fe^2^+}\) and \(\ce{X} \). To do this, eight 10 mL samples were prepared by reacting solutions of \(\ce{Fe^2^+}\) with solutions of \(\ce{X} \) in varying ratios. All \(\ce{Fe^2^+}\) and \(\ce{X} \) solutions had the same concentration. The absorbance of the samples is tabulated below.
- On the grid, construct a graph of absorbance against volume of \(\ce{Fe^2^+}\) solution from 0.00 mL to 6.00 mL, and draw TWO lines of best fit. (3 marks)
- The reaction proceeds according to the general equation
- \(\ce{aFe^2^+ + $b$X \rightleftharpoons [Fe_a(X)_b]^2^a^+}\).
- Find the values of \(\ce{$a$}\) and \(\ce{$b$}\) . Justify your answer with reference to the data given and the graph in part (a). (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 EQ-Bank 12
A colorimeter was used to calculate the percentage of iron in a 0.200 gram tablet. The tablet was dissolved and oxidised, then reacted with thiosulfate according to the equation
\(\ce{Fe^3^+($aq$) + SCN^-($aq$)\rightarrow [FeSCN]^2^+($aq$)}\)
The resulting solution was made up to 200 mL with distilled water. The absorbance of the final solution was measured to be 0.6105.
The calibration curve shows the absorbance of various concentrations of \(\ce{Fe^3^+}\).
Calculate the percentage of iron in the tablet. (3 marks)
CHEMISTRY, M8 EQ-Bank 24
A common antacid tablet contains aluminium hydroxide to neutralise stomach acid. In order for the antacid to be effective, each 500 mg tablet must contain a minimum of 200 mg of aluminium hydroxide.
Two antacid tablets were crushed and reacted with 70 mL of 0.60 mol L¯ 1 hydrochloric acid. After the antacid had reacted with the acid, the remaining hydrochloric acid was titrated against 0.60 mol L¯ 1 sodium hydroxide. The average volume of sodium hydroxide used was 35 mL.
Calculate the amount of aluminium hydroxide present in each tablet and justify whether the tablets will be effective as an antacid. (4 marks)
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- …
- 88
- Next Page »