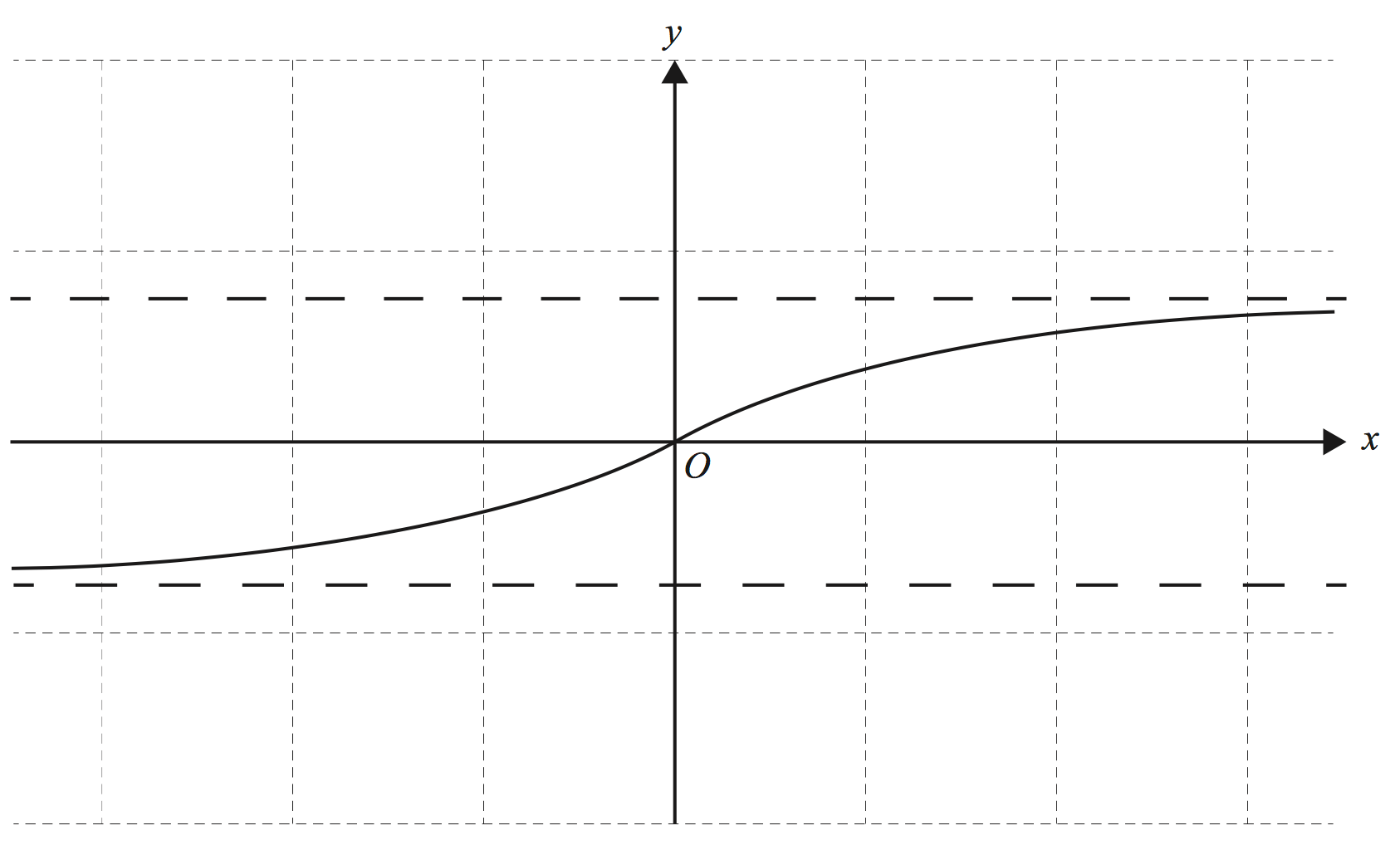
Part of the graph of `y = 1/2 sqrt(4x^2-1)` is shown below.
The curve shown is rotated about the `y`-axis to form a volume of revolution that is to model a fountain, where length units are in metres.
- Show that the volume, `V` cubic metres, of water in the fountain when it is filled to a depth of `h` metres is given by `V = pi/4(4/3h^3 + h)`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the depth `h` when the fountain is filled to half's its volume. Give your answer in metres, correct to two decimal places. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The fountain is initially empty. A vertical jet of water in the centre fills the fountain at a rate of 0.04 cubic metres per second and, at the same time, water flows out from the bottom of the fountain at a rate of `0.05 sqrt h` cubic metres per second when the depth is `h` metres.
- i. Show that `(dh)/(dt) = (4-5sqrt h)/(25 pi (4h^2 + 1))`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. Find the rate, in metres per second, correct to four decimal places, at which the depth is increasing when the depth is 0.25 m. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Express the time taken for the depth to reach 0.25 m as a definite integral and evaluate this integral correct to the nearest tenth of a second. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- After 25 seconds the depth has risen to 0.4 m.
Using Euler's method with a step size of five seconds, find an estimate of the depth 30 seconds after the fountain began to fill. Give your answer in metres, correct to two decimal places. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- How far from the top of the fountain does the water level ultimately stabilise? Give your answer in metres, correct to two decimal places. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---