For what values of `k` does the quadratic equation `x^2 – 8x + k = 0` have real roots? (2 marks)
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2015 HSC 10 MC
L&E, 2ADV E1 2015 HSC 8 MC
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2015 HSC 7 MC
Trig Calculus, 2UA 2015 HSC 6 MC
What is the value of the derivative of `y = 2 sin 3x - 3 tan x` at `x = 0`?
(A) `-1`
(B) `0`
(C) `3`
(D) `-9`
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2015 HSC 5 MC
Using the trapezoidal rule with 4 subintervals, which expression gives the approximate area under the curve `y = xe^x` between `x = 1` and `x = 3`?
- `1/4(e^1 + 6e^1.5 + 4e^2 + 10e^2.5 + 3e^3)`
- `1/4(e^1 + 3e^1.5 + 4e^2 + 5e^2.5 + 3e^3)`
- `1/2(e^1 + 6e^1.5 + 4e^2 + 10e^2.5 + 3e^3)`
- `1/2(e^1 + 3e^1.5 + 4e^2 + 5e^2.5 + 3e^3)`
Plane Geometry, 2UA 2006 HSC 10b
A rectangular piece of paper `PQRS` has sides `PQ = 12` cm and `PS = 13` cm. The point `O` is the midpoint of `PQ`. The points `K` and `M` are to be chosen on `OQ` and `PS` respectively, so that when the paper is folded along `KM`, the corner that was at `P` lands on the edge `QR` at `L`. Let `OK = x` cm and `LM = y` cm.
Copy or trace the diagram into your writing booklet.
- Show that `QL^2 = 24x`. (1 mark)
- Let `N` be the point on `QR` for which `MN` is perpendicular to `QR`.
- By showing that `Delta QKL\ text(|||)\ Delta NLM`, deduce that `y = {sqrt 6 (6 + x)}/sqrt x`. (3 marks)
- Show that the area, `A`, of `Delta KLM` is given by
- `A = {sqrt 6 (6 + x)^2}/(2 sqrt x)` (1 mark)
- Use the fact that `12 <= y <= 13` to find the possible values of `x`. (2 marks)
- Find the minimum possible area of `Delta KLM`. (3 marks)
Integration, 2UA 2006 HSC 10a
Use Simpson’s rule with three function values to find an approximation to the value of
`int_0.5^1.5 (log_e x )^3\ dx`.
Give your answer correct to three decimal places. (2 marks)
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2006 HSC 9b
During a storm, water flows into a 7000-litre tank at a rate of `(dV)/(dt)` litres per minute, where `(dV)/(dt) = 120 + 26t-t^2` and `t` is the time in minutes since the storm began.
- At what times is the tank filling at twice the initial rate? (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the volume of water that has flowed into the tank since the start of the storm as a function of `t`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Initially, the tank contains 1500 litres of water. When the storm finishes, 30 minutes after it began, the tank is overflowing.
How many litres of water have been lost? (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Quadratic, 2UA 2006 HSC 9a
Find the coordinates of the focus of the parabola `12y = x^2 - 6x - 3`. (2 marks)
Quadratic, 2UA 2006 HSC 7c
- Write down the discriminant of `2x^2 + (k - 2)x + 8` where `k` is a constant. (1 mark)
- Hence, or otherwise, find the values of `k` for which the parabola `y = 2x^2 + kx + 9` does not intersect the line `y = 2x + 1`. (2 marks)
Quadratic, 2UA 2006 HSC 7a
Let `alpha` and `beta` be the solutions of `x^2 - 3x + 1 = 0`.
- Find `alpha beta`. (1 mark)
- Hence find `alpha + 1/alpha`. (1 mark)
Calculus, EXT1* C1 2006 HSC 6b
A rare species of bird lives only on a remote island. A mathematical model predicts that the bird population, `P`, is given by
`P = 150 + 300 e^(-0.05t)`
where `t` is the number of years after observations began.
- According to the model, how many birds were there when observations began? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- According to the model, what will be the rate of change in the bird population ten years after observations began? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What does the model predict will be the limiting value of the bird population? (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The species will become eligible for inclusion in the endangered species list when the population falls below `200`. When does the model predict that this will occur? (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Plane Geometry, 2UA 2006 HSC 6a
In the diagram, `AD` is parallel to `BC`, `AC` bisects `/_BAD` and `BD` bisects `/_ABC`. The lines `AC` and `BD` intersect at `P`.
Copy or trace the diagram into your writing booklet.
- Prove that `/_BAC = /_BCA`. (1 mark)
- Prove that `Delta ABP ≡ Delta CBP`. (2 marks)
- Prove that `ABCD` is a rhombus. (3 marks)
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2006 HSC 5b
- Show that `d/dx log_e (cos x) = -tan x.` (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
-
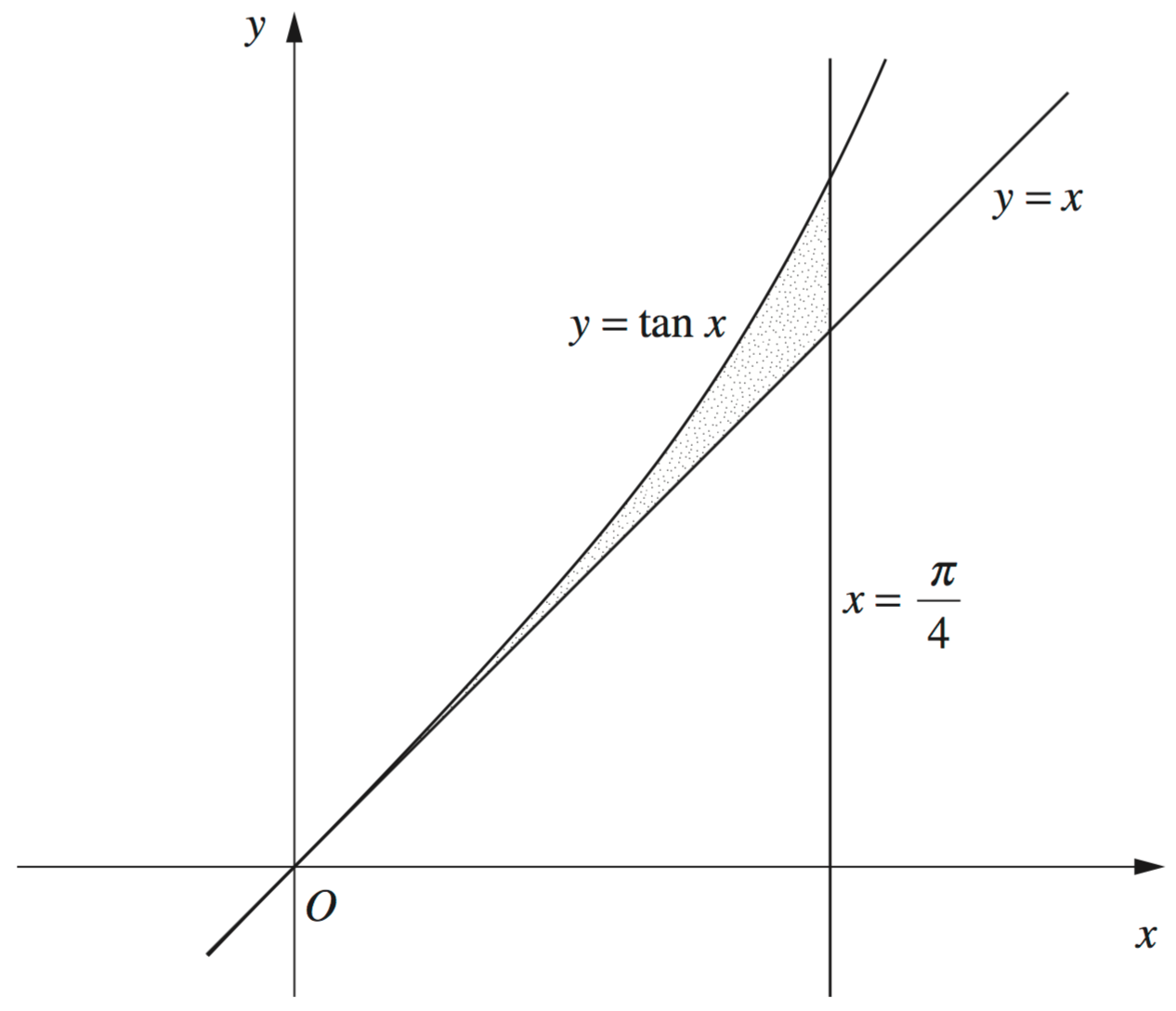
The shaded region in the diagram is bounded by the curve `y =tan x` and the lines `y =x` and `x = pi/4.`
Using the result of part (i), or otherwise, find the area of the shaded region. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2004 HSC 4b
Consider the function `f(x) = x^3 − 3x^2`.
- Find the coordinates of the stationary points of the curve `y = f(x)` and determine their nature. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the curve showing where it meets the axes. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the values of `x` for which the curve `y = f(x)` is concave up. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Trigonometry, 2ADV T1 2004 HSC 4a
Trigonometry, 2ADV T1 2004 HSC 3c
The diagram shows a point `P` which is 30 km due west of the point `Q`.
The point `R` is 12 km from `P` and has a bearing from `P` of 070°.
- Find the distance of `R` from `Q`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the bearing of `R` from `Q`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, 2ADV S1 2006 HSC 4c
A chessboard has 32 black squares and 32 white squares. Tanya chooses three different squares at random.
- What is the probability that Tanya chooses three white squares? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the probability that the three squares Tanya chooses are the same colour?. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the probability that the three squares Tanya chooses are not the same colour? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1* C3 2006 HSC 4b
Trigonometry, 2ADV T1 2006 HSC 4a
In the diagram, `ABCD` represents a garden. The sector `BCD` has centre `B` and `/_DBC = (5 pi)/6`
The points `A, B` and `C` lie on a straight line and `AB = AD = 3` metres.
Copy or trace the diagram into your writing booklet.
- Show that `/_DAB = (2 pi)/3.` (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the length of `BD`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the area of the garden `ABCD`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Linear Functions, 2UA 2006 HSC 3a
In the diagram, `A, B and C` are the points `(1, 4), (5, –4) and (–3, –1)` respectively. The line `AB` meets the y-axis at `D`.
- Show that the equation of the line `AB` is `2x + y - 6 = 0`. (2 marks)
- Find the coordinates of the point `D`. (1 mark)
- Find the perpendicular distance of the point `C` from the line `AB`. (1 mark)
- Hence, or otherwise, find the area of the triangle `ADC`. (2 marks)
Trigonometry, 2ADV T1 2005 HSC 9b
The triangle `ABC` has a right angle at `B, \ ∠BAC = theta` and `AB = 6`. The line `BD` is drawn perpendicular to `AC`. The line `DE` is then drawn perpendicular to `BC`. This process continues indefinitely as shown in the diagram.
- Find the length of the interval `BD`, and hence show that the length of the interval `EF` is `6 sin^3\ theta`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show that the limiting sum
`qquad BD + EF + GH + ···`
is given by `6 sec\ theta tan\ theta`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1* C1 2005 HSC 9a
A particle is initially at rest at the origin. Its acceleration as a function of time, `t`, is given by
`ddot x = 4sin2t`
- Show that the velocity of the particle is given by `dot x = 2 − 2\ cos\ 2t`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the graph of the velocity for `0 ≤ t ≤ 2π` AND determine the time at which the particle first comes to rest after `t = 0`. (3 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the distance travelled by the particle between `t = 0` and the time at which the particle first comes to rest after `t = 0`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, 2ADV M1 2005 HSC 8c
Weelabarrabak Shire Council borrowed $3 000 000 at the beginning of 2005. The annual interest rate is 12%. Each year, interest is calculated on the balance at the beginning of the year and added to the balance owing. The debt is to be repaid by equal annual repayments of $480 000, with the first repayment being made at the end of 2005.
Let `A_n` be the balance owing after the `n`-th repayment.
- Show that `A_2 = (3 × 10^6)(1.12)^2 - (4.8 × 10^5)(1 + 1.12)`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show that `A_n = 10^6[4 − (1.12)^n]`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- In which year will Weelabarrabak Shire Council make the final repayment? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2005 HSC 8b
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2005 HSC 8a
A cylinder of radius `x` and height `2h` is to be inscribed in a sphere of radius `R` centred at `O` as shown.
- Show that the volume of the cylinder is given by
`V = 2pih(R^2 − h^2).` (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, or otherwise, show that the cylinder has a maximum volume when `h = R/sqrt3.` (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1* C1 2005 HSC 7b
The graph shows the velocity, `(dx)/(dt)`, of a particle as a function of time. Initially the particle is at the origin.
- At what time is the displacement, `x`, from the origin a maximum? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- At what time does the particle return to the origin? Justify your answer. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Draw a sketch of the acceleration, `(d^2x)/(dt^2)`, as a function of time for `0 ≤ t ≤ 6`. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, 2ADV M1 2005 HSC 7a
Anne and Kay are employed by an accounting firm.
Anne accepts employment with an initial annual salary of $50 000. In each of the following years her annual salary is increased by $2500.
Kay accepts employment with an initial annual salary of $50 000. In each of the following years her annual salary is increased by 4%.
- What is Anne’s annual salary in her thirteenth year? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is Kay’s annual salary in her thirteenth year? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- By what amount does the total amount paid to Kay in her first twenty years exceed that paid to Anne in her first twenty years? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, STD2 A4 2006 HSC 28b
A new tunnel is built. When there is no toll to use the tunnel, 6000 vehicles use it each day. For each dollar increase in the toll, 500 fewer vehicles use the tunnel.
- Find the lowest toll for which no vehicles will use the tunnel. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For a toll of $5.00, how many vehicles use the tunnel each day and what is the total daily income from tolls? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- If `d` (dollars) represents the value of the toll, find an equation for the number of vehicles `(v)` using the tunnel each day in terms of `d`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Anne says ‘A higher toll always means a higher total daily income’.
Show that Anne is incorrect and find the maximum daily income from tolls. (Use a table of values, or a graph, or suitable calculations.) (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, STD2 F4 2006 HSC 27c
Kai purchased a new car for $30 000. It depreciated in value by $2000 per year for the first three years.
After the end of the third year, Kai changed the method of depreciation to the declining balance method at the rate of 25% per annum.
- Calculate the value of the car at the end of the third year. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Calculate the value of the car seven years after it was purchased. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Without further calculations, sketch a graph to show the value of the car over the seven years.
Use the horizontal axis to represent time and the vertical axis to represent the value of the car. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, STD2 S4 2006 HSC 27b
Each member of a group of males had his height and foot length measured and recorded. The results were graphed and a line of fit drawn.
- Why does the value of the `y`-intercept have no meaning in this situation? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- George is 10 cm taller than his brother Harry. Use the line of fit to estimate the difference in their foot lengths. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sam calculated a correlation coefficient of −1.2 for the data. Give TWO reasons why Sam must be incorrect. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, STD2 F4 2006 HSC 27a
Liliana wants to borrow money to buy a house. The bank sent her an email with the following table attached.
- Liliana decides that she can afford $1000 per month on repayments.
What is the maximum amount she can borrow, and how many years will she have to repay the loan? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Zali intends to borrow $160 000 over 15 years from the same bank.
If she chooses to borrow $160 000 over 20 years instead, how much more interest will she pay? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD2 M2 2006 HSC 26d
Cassie flew from London to Manila. Manila is 8 hours ahead of London.
Her plane left London at 9.30 am Monday (London time), stopped for 5 hours in Singapore and arrived in Manila at 4.00 pm Tuesday (Manila time).
What was the total flying time? (Ignore time zones.) (2 marks)
Probability, STD2 S2 2006 HSC 26c
A new test has been developed for determining whether or not people are carriers of the Gaussian virus.
Two hundred people are tested. A two-way table is being used to record the results.
- What is the value of `A`? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- A person selected from the tested group is a carrier of the virus.
What is the probability that the test results would show this? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For how many of the people tested were their test results inaccurate? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD2 M6 2006 HSC 26a
Daniel conducts an offset survey to sketch a diagram, `ABCD`, of a block of land.
Daniel walks from `A` to `C`, a distance of 62 m.
When he is 15 m from `A`, he notes that point `D` is 25 m to his right.
When he is 57 m from `A`, he notes that point `B` is 20 m to his left.
This is his notebook entry.
- Draw a neat sketch of the block of land. Label `A, B, C` and `D` on your diagram. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Calculate the distance from `C` to `D`. (Give your answer to the nearest metre.) (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, STD2 S2 2006 HSC 25c
Calculus, EXT1* C3 2005 HSC 6c
The graphs of the curves `y = x^2` and `y = 12 - 2x^2` are shown in the diagram.
- Find the points of intersection of the two curves. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The shaded region between the curves and the `y`-axis is rotated about the `y`-axis. By splitting the shaded region into two parts, or otherwise, find the volume of the solid formed. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2005 HSC 6b
A tank initially holds 3600 litres of water. The water drains from the bottom of the tank. The tank takes 60 minutes to empty.
A mathematical model predicts that the volume, `V` litres, of water that will remain in the tank after `t` minutes is given by
`V = 3600(1 − t/60)^2,\ \ text(where)\ \ 0 ≤ t ≤ 60`.
- What volume does the model predict will remain after ten minutes? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- At what rate does the model predict that the water will drain from the tank after twenty minutes? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- At what time does the model predict that the water will drain from the tank at its fastest rate? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Integration, 2UA 2005 HSC 6a
Probability, 2ADV S1 2005 HSC 5d
A total of 300 tickets are sold in a raffle which has three prizes. There are 100 red, 100 green and 100 blue tickets.
At the drawing of the raffle, winning tickets are NOT replaced before the next draw.
- What is the probability that each of the three winning tickets is red? (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the probability that at least one of the winning tickets is not red? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the probability that there is one winning ticket of each colour? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2005 HSC 5c
Find the coordinates of the point `P` on the curve `y = 2e^x + 3x` at which the tangent to the curve is parallel to the line `y = 5x - 3`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Plane Geometry, 2UA 2005 HSC 5b
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2005 HSC 4b
A function `f(x)` is defined by `f(x) = (x + 3)(x^2- 9)`.
- Find all solutions of `f(x) = 0` (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the coordinates of the turning points of the graph of `y = f(x)`, and determine their nature. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence sketch the graph of `y = f(x)`, showing the turning points and the points where the curve meets the `x`-axis. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For what values of `x` is the graph of `y = f(x)` concave down? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Trigonometry, 2ADV T1 2005 HSC 4a
A pendulum is 90 cm long and swings through an angle of 0.6 radians. The extreme positions of the pendulum are indicated by the points `A` and `B` in the diagram.
- Find the length of the arc `AB`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the straight-line distance between the extreme positions of the pendulum. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the area of the sector swept out by the pendulum. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Plane Geometry, 2UA 2005 HSC 3c
In the diagram, `A`, `B` and `C` are the points `(6, 0), (9, 0)` and `(12, 6)` respectively. The equation of the line `OC` is `x - 2y = 0`. The point `D` on `OC` is chosen so that `AD` is parallel to `BC`. The point `E` on `BC` is chosen so that `DE` is parallel to the `x`-axis.
- Show that the equation of the line `AD` is `y = 2x - 12`. (2 marks)
- Find the coordinates of the point `D`. (2 marks)
- Find the coordinates of the point `E`. (1 marks)
- Prove that `ΔOAD\ text(|||)\ ΔDEC`. (2 marks)
- Hence, or otherwise, find the ratio of the lengths `AD` and `EC`. (1 marks)
Trigonometry, 2ADV T1 2005 HSC 3b
The lengths of the sides of a triangle are 7 cm, 8 cm and 13 cm.
- Find the size of the angle opposite the longest side. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the area of the triangle. (1 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, 2ADV M1 2006 HSC 8b
Joe borrows $200 000 which is to be repaid in equal monthly instalments. The interest rate is 7.2% per annum reducible, calculated monthly.
It can be shown that the amount, `$A_n`, owing after the `n`th repayment is given by the formula:
`A_n = 200\ 000r^n - M(1 + r + r^2 + … + r^(n-1))`,
where `r = 1.006` and `$M` is the monthly repayment. (Do NOT show this.)
- The minimum monthly repayment is the amount required to repay the loan in 300 instalments.
Find the minimum monthly repayment. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Joe decides to make repayments of $2800 each month from the start of the loan.
How many months will it take for Joe to repay the loan? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C1 2006 HSC 8a
A particle is moving in a straight line. Its displacement, `x` metres, from the origin, `O`, at time `t` seconds, where `t ≥ 0`, is given by `x = 1 - 7/(t + 4)`.
- Find the initial displacement of the particle. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the velocity of the particle as it passes through the origin. (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show that the acceleration of the particle is always negative. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the graph of the displacement of the particle as a function of time. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Trigonometry, 2ADV T3 2006 HSC 7b
A function `f(x)` is defined by `f(x) = 1 + 2 cos x`.
- Show that the graph of `y = f(x)` cuts the `x`-axis at `x = (2 pi)/3`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the graph of `y = f(x)` for `-pi <= x <= pi` showing where the graph cuts each of the axes. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the area under the curve `y = f(x)` between `x = -pi/2` and `x = (2 pi)/3`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2006 HSC 5a
A function `f(x)` is defined by `f(x) =2x^2(3-x)`.
- Find the coordinates of the turning points of `y =f(x)` and determine their nature. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the coordinates of the point of inflection. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence sketch the graph of `y =f(x)`, showing the turning points, the point of inflection and the points where the curve meets the `x`-axis. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the minimum value of `f(x)` for `–1 ≤ x ≤4`? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2005 HSC 2ci
Find `int (6x^2)/(x^3 + 1)\ dx`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Quadratics, 2UA 2005 HSC 1f
Find the coordinates of the focus of the parabola `x^2 = 8(y − 1)`. (2 marks)
Algebra, 2UA 2005 HSC 1b
Factorise `x^3 − 27`. (2 marks)
Probability, STD2 S2 2006 HSC 28a
On a bridge, the toll of $2.50 is paid in coins collected by a machine. The machine only accepts two-dollar coins, one-dollar coins and fifty-cent coins.
- List the different combinations of coins that could be used to pay the $2.50 toll. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Jill has three two-dollar coins, six one-dollar coins and two fifty-cent coins. She selects two coins at random.
What is the probability that she selects exactly $2.50? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- At the end of a day, the machine contains `x` two-dollar coins, `y` one-dollar coins and `w` fifty-cent coins.
Write an expression for the total value of coins in dollars in the machine. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, STD2 A4 2005 HSC 28b
Sue and Mikey are planning a fund-raising dance. They can hire a hall for $400 and a band for $300. Refreshments will cost them $12 per person.
- Write a formula for the cost ($C) of running the dance for `x` people. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The graph shows planned income and costs when the ticket price is $20
- Estimate the minimum number of people needed at the dance to cover the costs. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- How much profit will be made if 150 people attend the dance? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Sue and Mikey plan to sell 200 tickets. They want to make a profit of $1500.
- What should be the price of a ticket, assuming all 200 tickets will be sold? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD2 M1 2005 HSC 28a
The Mitchell family has moved to a new house which has an empty swimming pool. The base of the pool is in the shape of a rectangle, with a semicircle on each end.
- Explain why the expression for the area of the base of the pool is `2xy + πy^2`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The pool is 1.1 metres deep.
- The sides and base of the pool are covered in tiles. If `x =6` and `y = 2.5`, find the total area covered by tiles. (Give your answer correct to the nearest square metre.) (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Before filling the pool, the Mitchells need to install a new shower head, which saves 6 litres of water per minute.
The shower is used 5 times every day, for 3 minutes each time.
- If the charge for water is $1.013 per kilolitre, how much money would be saved in one year by using this shower head? (Assume there are 365 days in a year.) (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, STD2 S1 2005 HSC 27d
Nine students were selected at random from a school, and their ages were recorded.
\begin{array} {|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textbf{Ages} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ \ \ \text{12 11 16} \ \ \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\ \rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{14 16 15} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\ \rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{14 15 14} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\
\hline
\end{array}
- What is the sample standard deviation, correct to two decimal places? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Briefly explain what is meant by the term standard deviation. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD2 M6 2005 HSC 27c
The bearing of `C` from `A` is 250° and the distance of `C` from `A` is 36 km.
- Explain why `theta` is 110°. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- If `B` is 15 km due north of `A`, calculate the distance of `C` from `B`, correct to the nearest kilometre. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, 2UG 2005 HSC 27b
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- …
- 114
- Next Page »



















































