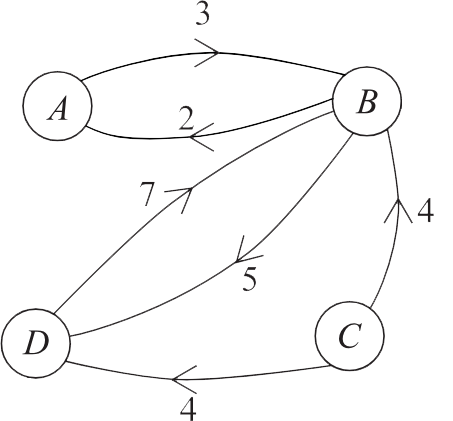
The graph displays the cost (`$c`) charged by two companies for the hire of a minibus for `x` hours.
Both companies charge $360 for the hire of a minibus for 3 hours.
- What is the hourly rate charged by Company A? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Company B charges an initial booking fee of $75.
Write a formula, in the form of `c = mx + b`, for the cost of hiring a minibus from Company B for `x` hours. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- A minibus is hired for 5 hours from Company B.
Calculate how much cheaper this is than hiring from Company A. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---