Plane Geometry, EXT1 2018 HSC 14c
In triangle `ABC, BC` is perpendicular to `AC`. Side `BC` has length `a`, side `AC` has length `b` and side `AB` has length `c`. A quadrant of a circle of radius `x`, centered at `C`, is constructed. The arc meets side `BC` at `E`. It touches the side `AB` at `D`, and meets side `AC` at `F`. The interval `CD` is perpendicular to `AB`.
- Show that `Delta ABC` and `Delta ACD` are similar. (1 mark)
- Show that
`qquad x = (ab)/c`. (1 mark)
- From `F`, a line perpendicular to `AC` is drawn to meet `AB` at `G`, forming the right-angled triangle `GFA`. A new quadrant is constructed in triangle `GFA` touching side `AB` at `H`. The process is then repeated indefinitely.
- Show that the limiting sum of the areas of all the quadrants is
`qquad (pi ab^2)/(4(2c - a)).` (4 marks)
- Hence, or otherwise, show that
`qquad pi/2 < (2c - a)/b`. (1 mark)
Binomial, EXT1 2018 HSC 14b
- By considering the expansions of `(1 + (1 + x))^n` and `(2 + x)^n,` show that
`((n),(r))((r),(r)) + ((n),(r +1))((r + 1),(r)) + ((n),(r + 2))((r + 2),(r)) +`
`… + ((n),(n))((n),(r)) = ((n),(r)) 2^(n - r)`. (3 marks)
- There are 23 people who have applied to be selected for a committee of 4 people.
The selection process starts with Selector `A` choosing a group of at least 4 people from the 23 people who applied.
Selector `B` then chooses the 4 people to be on the committee from the group Selector `A` has chosen.
In how many ways could this selection process be carried out? (2 marks)
Plane Geometry, EXT1 2018 HSC 14a
The diagram shows quadrilateral `ABCD` and the bisectors of the angles at `A, B, C` and `D`. The bisectors at `A` and `B` intersect at the point `P`. The bisectors at `A` and `D` meet at `Q`. The bisectors at `C` and `D` meet at `R`. The bisectors at `B` and `C` meet at `S`.
Copy or trace the diagram into your writing booklet.
Show that `PQRS` is a cyclic quadrilateral. (3 marks)
Functions, EXT1 F1 2018 HSC 13b
The diagram shows the graph `y = x/(x^2 + 1)`, for all real `x`.
Consider the function `f(x) = x/(x^2 + 1)`, for `x >= 1.`
The function `f(x)` has an inverse. (Do NOT prove this.)
- State the domain and range of `f^(-1) (x).` (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the graph `y = f^(-1)(x).` (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find an expression for `f^(-1)(x).` (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Mechanics, EXT2* M1 2018 HSC 13c
An object is projected from the origin with an initial velocity of `V` at an angle `theta` to the horizontal. The equations of motion of the object are
| `x(t)` | `= Vt cos theta` |
| `y(t)` | `= Vt sin theta - (g t^2)/2.` (Do NOT prove this.) |
- Show that when the object is projected at an angle `theta`, the horizontal range is
`V^2/g sin 2 theta` (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show that when the object is projected at an angle `pi/2 - theta`, the horizontal range is also
`V^2/g sin 2 theta`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The object is projected with initial velocity `V` to reach a horizontal distance `d`, which is less than the maximum possible horizontal range. There are two angles at which the object can be projected in order to travel that horizontal distance before landing.
Let these angles be `alpha` and `beta`, where `beta = pi/2 - alpha.`
Let `h_alpha` be the maximum height reached by the object when projected at the angle `alpha` to the horizontal.
Let `h_beta` be the maximum height reached by the object when projected at the angle `beta` to the horizontal.
Show that the average of the two heights, `(h_alpha + h_beta)/2`, depends only on `V` and `g`. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Quadratic, EXT1 2018 HSC 12e
The points `P(2ap, ap^2)` and `Q(2aq, aq^2)` lie on the parabola `x^2 = 4ay`. The focus of the parabola is `S(0, a)` and the tangents at `P` and `Q` intersect at `T(a(p + q), apq)`. (Do NOT prove this.)
The tangents at `P` and `Q` meet the `x`-axis at `A` and `B` respectively, as shown.
- Show that `/_ PAS = 90^@`. (2 marks)
- Explain why `S, B, A, T` are concyclic points. (1 mark)
- Show that the diameter of the circle through `S, B, A` and `T` has length
`qquad qquad a sqrt((p^2 + 1)(q^2 + 1))`. (2 marks)
Calculus, EXT1 C2 2018 HSC 12c
Let `f(x) = sin^(-1) x + cos^(-1) x`.
- Show that `f^{′}(x) = 0` (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, or otherwise, prove
`qquad sin^(-1) x + cos^(-1) x = pi/2`. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, sketch
`qquad f(x) = sin^(-1) x + cos^(-1) x`. (1 mark)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
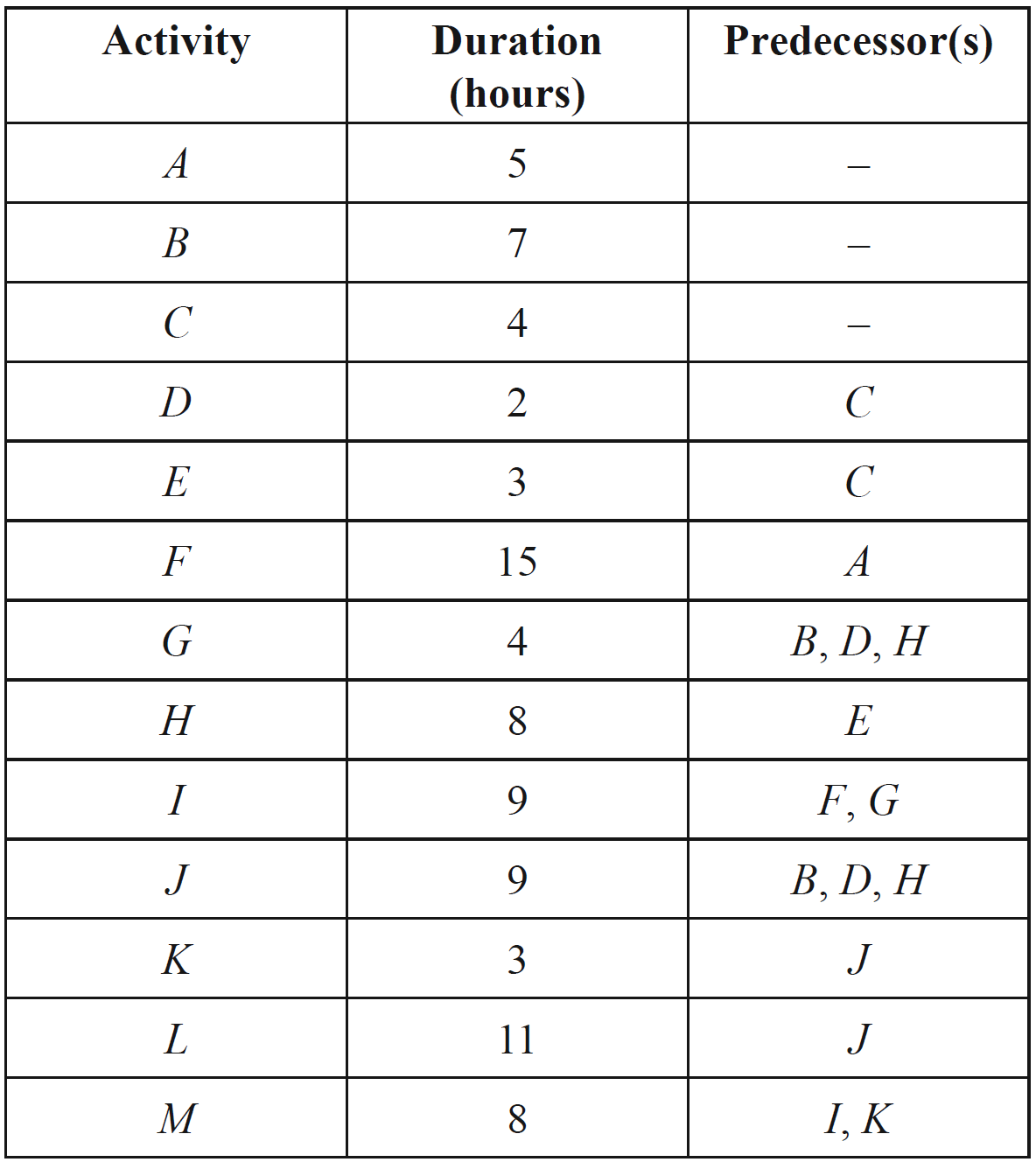
Networks, STD2 N3 EQ-Bank 19
An engineering project requires activities A to G to be completed, as shown in the table.
The minimum completion time for the project is 25 days and the critical path includes activities B, D, E and F. The float for activity G is two days and the float for activity C is four days.
Find the possible duration for each of the activities A, C, F and G. Include a network diagram in your answer. (5 marks)
Networks, STD2 N3 EQ-Bank 18
An engineering project requires activities A to G to be completed, as shown in the table.
The minimum completion time for the project is 40 weeks and the critical path includes activities A, C, E and G. The float for activity F is six weeks and the float for activity D is 9 weeks.
Find the possible duration for each of the activities B, D, F and G. Include a network diagram in your answer. (5 marks)
Mechanics, EXT2* M1 2018 HSC 10 MC
A particle is moving in simple harmonic motion. The displacement of the particle is `x` and its velocity, `v`, is given by the equation `v^2 = n^2 (2kx - x^2)`, where `n` and `k` are constants.
The particle is initially at `x = k`.
Which function, in terms of time `t`, could represent the motion of the particle?
A. `x = k cos (nt)`
B. `x = k sin (nt) + k`
C. `x = 2k cos (nt) - k`
D. `x = 2k sin (nt) + k`
Trig Ratios, EXT1 2018 HSC 9 MC
Which of the following is a general solution of the equation `sin 2x = -1/2`?
A. `x = n pi + (-1)^n pi/12`
B. `x = (n pi)/2 + (-1)^n pi/12`
C. `x = n pi + (-1)^(n + 1) pi/12`
D. `x = (n pi)/2 + (-1)^(n + 1) pi/12`
Combinatorics, EXT1 A1 2018 HSC 8 MC
Six men and six women are to be seated at a round table.
In how many different ways can they be seated if men and women alternate?
A. `5!\ 5!`
B. `5!\ 6!`
C. `2!\ 5!\ 5!`
D. `2!\ 5!\ 6!`
Networks, STD2 N3 2007 FUR2 4
A community centre is to be built on the new housing estate.
Nine activities have been identified for this building project.
The directed network below shows the activities and their completion times in weeks.

- Determine the minimum time, in weeks, to complete this project. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Determine the float time, in weeks, for activity `D`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The builders of the community centre are able to speed up the project.
Some of the activities can be reduced in time at an additional cost.
The activities that can be reduced in time are `A`, `C`, `E`, `F` and `G`.
- Which of these activities, if reduced in time individually, would not result in an earlier completion of the project? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The owner of the estate is prepared to pay the additional cost to achieve early completion.
The cost of reducing the time of each activity is $5000 per week.
The maximum reduction in time for each one of the five activities, `A`, `C`, `E`, `F`, `G`, is `2` weeks.
- Determine the minimum time, in weeks, for the project to be completed now that certain activities can be reduced in time. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Determine the minimum additional cost of completing the project in this reduced time. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 2006 FUR2 3
The five musicians are to record an album. This will involve nine activities.
The activities and their immediate predecessors are shown in the following table.
The duration of each activity is not yet known.
- Use the information in the table above to complete the network below by including activities `G`, `H` and `I`. (2 marks)
There is only one critical path for this project.
- How many non-critical activities are there? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The following table gives the earliest start times (EST) and latest start times (LST) for three of the activities only. All times are in hours.
- Write down the critical path for this project. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The minimum time required for this project to be completed is 19 hours.
- What is the duration of activity `I`? (1 mark)
The duration of activity `C` is 3 hours.
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Determine the maximum combined duration of activities `F` and `H`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 2013 FUR2 2
A project will be undertaken in the wildlife park. This project involves the 13 activities shown in the table below. The duration, in hours, and predecessor(s) of each activity are also included in the table.
Activity `G` is missing from the network diagram for this project, which is shown below.
- Complete the network diagram above by inserting activity `G`. (1 mark)
- Determine the earliest starting time of activity `H`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Given that activity `G` is not on the critical path
- write down the activities that are on the critical path in the order that they are completed (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- find the latest starting time for activity `D`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- write down the activities that are on the critical path in the order that they are completed (1 mark)
- Consider the following statement.
‘If the time to complete just one of the activities in this project is reduced by one hour, then the minimum time to complete the entire project will be reduced by one hour.’
Explain the circumstances under which this statement will be true for this project. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Assume activity `F` is reduced by two hours.
What will be the minimum completion time for the project? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 2012 FUR2 2
Thirteen activities must be completed before the produce grown on a farm can be harvested.
The directed network below shows these activities and their completion times in days.
- Determine the earliest starting time, in days, for activity `E`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- An activity with zero duration starts at the end of activity `B`.
Explain why this activity is used on the network diagram. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Determine the earliest starting time, in days, for activity `H`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- In order, list the activities on the critical path. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Determine the latest starting time, in days, for activity `J`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 2009 FUR2 4
A walkway is to be built across the lake.
Eleven activities must be completed for this building project.
The directed network below shows the activities and their completion times in weeks.
- What is the earliest start time for activity E? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Write down the critical path for this project. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The project supervisor correctly writes down the float time for each activity that can be delayed and makes a list of these times.
Determine the longest float time, in weeks, on the supervisor’s list. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A twelfth activity, L, with duration three weeks, is to be added without altering the critical path.
Activity L has an earliest start time of four weeks and a latest start time of five weeks.
- Draw in activity L on the network diagram above. (1 mark)
- Activity L starts, but then takes four weeks longer than originally planned.
Determine the total overall time, in weeks, for the completion of this building project. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 2011 FUR1 7 MC
Andy, Brian and Caleb must complete three activities in total (K, L and M)
The table shows the person selected to complete each activity, the time it will take to complete the activity in minutes and the immediate predecessor for each activity.
All three activities must be completed in a total of 40 minutes.
The instant that Andy starts his activity, Caleb gets a telephone call.
The maximum time, in minutes, that Caleb can speak on the telephone before he must start his allocated activity is
A. `5`
B. `13`
C. `18`
D. `24`
Networks, STD2 N3 2014 FUR1 8 MC
Which one of the following statements about critical paths is true?
- There can be only one critical path in a project.
- A critical path will always include the activity that takes the longest time to complete.
- Reducing the time of any activity on a critical path for a project will always reduce the minimum completion time for the project.
- If there are no other changes, increasing the time of any activity on a critical path will always increase the completion time of a project.
Networks, STD2 N3 SM-Bank 49
The directed graph below shows the sequence of activities required to complete a project.
The time to complete each activity, in hours, is also shown.
- Find the earliest starting time, in hours, for activity `N`. (2 marks)
To complete the project in minimum time, some activities cannot be delayed.
- Calculate the number of activities that cannot be delayed. (1 mark)
Networks, STD2 N3 SM-Bank 47
The directed graph below shows the sequence of activities required to complete a project.
All times are in hours.
- Find the number of activities that have exactly two immediate predecessors. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Identify the critical path for this project. (3 marks)
- If Activity E is reduced by one hour, identify the two new critical paths. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 SM-Bank 48
The network shows the activities that are needed to complete a particular project.
- Find the total number of activities that need to be completed before activity L can begin. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The duration of every activity is initially 5 hours.
- If the completion times of both activity F and activity K are reduced to 3 hours each, calculate the effect on the completion time for the project. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 2008 FUR1 8-9 MC
The network below shows the activities that are needed to finish a particular project and their completion times (in days).
Part 1
The earliest start time for Activity K, in days, is
A. `7`
B. `15`
C. `16`
D. `19`
Part 2
This project currently has one critical path.
A second critical path, in addition to the first, would be created by
A. increasing the completion time of D by 7 days.
B. increasing the completion time of G by 1 day.
C. increasing the completion time of I by 2 days.
D. decreasing the completion time of C by 1 day.
Networks, FUR2 2007 VCE 3
As an attraction for young children, a miniature railway runs throughout a new housing estate.
The trains travel through stations that are represented by nodes on the directed network diagram below.
The number of seats available for children, between each pair of stations, is indicated beside the corresponding edge.
Cut 1, through the network, is shown in the diagram above.
- Determine the capacity of Cut 1. (1 mark)
- Determine the maximum number of seats available for children for a journey that begins at the West Terminal and ends at the East Terminal. (1 mark)
On one particular train, 10 children set out from the West Terminal.
No new passengers board the train on the journey to the East Terminal.
- Determine the maximum number of children who can arrive at the East Terminal on this train. (1 mark)
Networks, FUR2 2013 VCE 3
The rangers at the wildlife park restrict access to the walking tracks through areas where the animals breed.
The edges on the directed network diagram below represent one-way tracks through the breeding areas. The direction of travel on each track is shown by an arrow. The numbers on the edges indicate the maximum number of people who are permitted to walk along each track each day.
- Starting at `A`, how many people, in total, are permitted to walk to `D` each day? (1 mark)
One day, all the available walking tracks will be used by students on a school excursion.
The students will start at `A` and walk in four separate groups to `D`.
Students must remain in the same groups throughout the walk.
Networks, FUR1 2017 VCE 8 MC
The flow of oil through a series of pipelines, in litres per minute, is shown in the network below.
The weightings of three of the edges are labelled `x`.
Four cuts labelled A–D are shown on the network.
The maximum flow of oil from the source to the sink, in litres per minute, is given by the capacity of
- `text(Cut A if)\ \ x = 1`
- `text(Cut B if)\ \ x = 2`
- `text(Cut C if)\ \ x = 2`
- `text(Cut D if)\ \ x = 3`
Networks, STD2 N3 2009 FUR1 3 MC
Networks, STD2 N3 2008 FUR1 6 MC
Networks, STD2 N3 SM-Bank 36
In the network below, the values on the edges give the maximum flow possible between each pair of vertices. The arrows show the direction of flow. A cut that separates the source from the sink in the network is also shown.
- Calculate the capacity of the cut shown in the diagram. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Calculate the maximum flow between source and sink. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, FUR2 2016 VCE 1
A map of the roads connecting five suburbs of a city, Alooma (`A`), Beachton (`B`), Campville (`C`), Dovenest (`D`) and Easyside (`E`), is shown below.
- Starting at Beachton, which two suburbs can be driven to using only one road? (1 mark)
A graph that represents the map of the roads is shown below.
One of the edges that connects to vertex `E` is missing from the graph.
-
- Add the missing edge to the graph above. (1 mark)
(Answer on the graph above.)
- Explain what the loop at `D` represents in terms of a driver who is departing from Dovenest. (1 mark)
- Add the missing edge to the graph above. (1 mark)
Networks, FUR1 2017 VCE 3 MC
Consider the following graph.
The matrix for this graph that records the number of direct routes between points, is shown below.
This adjacency table contains 16 values when complete.
Of the 12 missing elements
- eight are ‘1’ and four are ‘2’.
- four are ‘1’ and eight are ‘2’.
- six are ‘1’ and six are ‘2’.
- two are ‘0’, six are ‘1’ and four are ‘2’.
Networks, STD2 N2 2016 FUR1 4 MC
Networks, FUR1 2013 VCE 6 MC
Geometry, NAP-K3-CA03
Patchouli draws a shape on some grid paper.
She puts a pin through the dot.
She then rotates the paper a half turn clockwise.
Which of the following shows Patchouli's shape after the rotation?
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number, NAP-K3-CA05
The entry fees to visit the Toorak Aquarium are $15 for an adult and $7 for a child.
A group of 8 people paid $88 in total to visit the aquarium.
How many adults are in the group?
| `2` | `3` | `4` | `5` |
|
|
|
|
|
Geometry, NAP-K4-CA01
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 17
The diagram shows a point `T` on the unit circle `x^2+y^2=1` at an angle `theta` from the positive `x`-axis, where `0<theta<pi/2`.
The tangent to the circle at `T` is perpendicular to `OT`, and intersects the `x`-axis at `P`, and the line `y=1` intersects the `y`-axis at `B`
- Show that the equation of the line `PT` is `xcostheta+ysin theta=1`. (2 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the length of `BQ` in terms of `theta`. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show that the area, `A`, of the trapezium `OPQB` is given by
- `A=(2-sintheta)/(2costheta)` (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the angle `theta` that gives the minimum area of the trapezium. (3 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 27
A cone is inscribed in a sphere of radius `a`, centred at `O`. The height of the cone is `x` and the radius of the base is `r`, as shown in the diagram.
- Show that the volume, `V`, of the cone is given by
- `V = 1/3 pi(2ax^2-x^3)`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `x` for which the volume of the cone is a maximum. You must give reasons why your value of `x` gives the maximum volume. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 35
The diagram shows two parallel brick walls `KJ` and `MN` joined by a fence from `J` to `M`. The wall `KJ` is `s` metres long and `/_KJM=alpha`. The fence `JM` is `l` metres long.
A new fence is to be built from `K` to a point `P` somewhere on `MN`. The new fence `KP` will cross the original fence `JM` at `O`.
Let `OJ=x` metres, where `0<x<l`.
- Show that the total area, `A` square metres, enclosed by `DeltaOKJ` and `DeltaOMP` is given by
- `A=s(x-l+l^2/(2x))sin alpha`. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `x` that makes `A` as small as possible. Justify the fact that this value of `x` gives the minimum value for `A`. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, find the length of `MP` when `A` is as small as possible. (1 mark)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 34
A cylinder of radius `x` and height `2h` is to be inscribed in a sphere of radius `R` centred at `O` as shown.
- Show that the volume of the cylinder is given by
- `V = 2pih(R^2-h^2).` (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, or otherwise, show that the cylinder has a maximum volume when
- `h = R/sqrt3.` (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 24
The rule for function `f` is `f(x) = x^3 - 3x^2 + kx + 8`, where `k` is a constant.
Find the values of `k` for which `f(x)` is an increasing function. (2 marks)
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 30
A function is given by `f(x) = 3x^4 + 4x^3-12x^2`.
- Find the coordinates of the stationary points of `f(x)` and determine their nature. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, sketch the graph `y = f(x)` showing the stationary points. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For what values of `x` is the function increasing? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For what values of `k` will `f(x) = 3x^4 + 4x^3-12x^2 + k = 0` have no solution? (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2016 VCAA 6b
Let `f : [-π, π] → R`, where `f (x) = 2 sin (2x)-1`.
Calculate the average value of `f` over the interval `-pi/3 <= x <= pi/6`. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 SM-Bank 13
The figure shown represents a wire frame where `ABCE` is a convex quadrilateral. The point `D` is on line segment `EC` with `AB = ED = 2\ text(cm)` and `BC = a\ text(cm)`, where `a` is a positive constant.
`/_ BAE = /_ CEA = pi/2`
Let `/_ CBD = theta` where `0 < theta < pi/2.`
- Find `BD` and `CD` in terms of `a` and `theta`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the length, `L` cm, of the wire in the frame, including length `BD`, in terms of `a` and `theta`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find `(dL)/(d theta)`, and hence show that `(dL)/(d theta) = 0` when `BD = 2CD`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the maximum value of `L` if `a = 3 sqrt 5`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C4 SM-Bank 12
Let `f(x) = 2e^(-x/5)\ \ \ text(for)\ \ x>=0`
A right-angled triangle `OQP` has vertex `O` at the origin, vertex `Q` on the `x`-axis and vertex `P` on the graph of `f`, as shown. The coordinates of `P` are `(x, f(x)).`
- Find the area, `A`, of the triangle `OPQ` in terms of `x`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the maximum area of triangle `OQP` and the value of `x` for which the maximum occurs. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Let `S` be the point on the graph of `f` on the `y`-axis and let `T` be the point on the graph of `f` with the `y`-coordinate `1/2`.Find the area of the region bounded by the graph of `f` and the line segment `ST`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
GRAPHS, FUR2 2017 VCAA 3
Lifeguards are required to ensure the safety of swimmers at the beach.
Let `x` be the number of junior lifeguards required.
Let `y` be the number of senior lifeguards required.
The inequality below represents the constraint on the relationship between the number of senior lifeguards required and the number of junior lifeguards required.
Constraint 1 `y >= x/4`
- If eight junior lifeguards are required, what is the minimum number of senior lifeguards required? (1 mark)
There are three other constraints.
Constraint 2 `x ≥ 6`
Constraint 3 `y ≥ 4`
Constraint 4 `x + y ≥ 12`
- Interpret Constraint 4 in terms of the number of junior lifeguards and senior lifeguards required. (1 mark)
The shaded region of the graph below contains the points that satisfy Constraints 1 to 4.
All lifeguards receive a meal allowance per day.
Junior lifeguards receive $15 per day and senior lifeguards receive $25 per day.
The total meal allowance cost per day, `$C`, for the lifeguards is given by
`C = 15x + 25y`
- Determine the minimum total meal allowance cost per day for the lifeguards. (2 marks)
- On rainy days there will be no set minimum number of junior lifeguards or senior lifeguards required, therefore:
• Constraint 2 `(x ≥ 6)` and Constraint 3 `(y ≥ 4)` are removed
• Constraint 1 and Constraint 4 are to remain.
Constraint 1 `y >= x/4`
Constraint 4 `x + y >= 12`
The total meal allowance cost per day, `$C`, for the lifeguards remains as
`C = 15x + 25y`
How many junior lifeguards and senior lifeguards work on a rainy day if the total meal allowance cost is to be a minimum?
Write your answers in the boxes provided below. (1 mark)
GRAPHS, FUR2 2017 VCAA 2
A swimming race is being held in the ocean.
From the shore, competitors swim 500 m out to a buoy in the ocean and then return to the shore.
One competitor, Edgar, reaches the buoy after 12.5 minutes and completes the race in 25 minutes.
The graph below shows his distance from shore, in metres, `t` minutes after the race begins.
- What distance, in metres, has Edgar swum after 15 minutes? (1 mark)
- Let `E` be Edgar’s distance from the shore, in metres, `t` minutes after the race begins.
The linear relation that represents his swim out to the buoy is of the form
`E = kt,` where `0 < t ≤ 12.5`
The slope of the line `k` is the speed at which Edgar is swimming, in metres per minute.
Show that `k = 40`. (1 mark)
A second competitor, Zlatko, began the race at the same time as Edgar.
Below is the relation that describes Zlatko’s swim, where `Z` is his distance from the shore, in metres, `t` minutes after the race begins and `F` is the time it took Zlatko to finish the race.
`Z = {(qquadqquadqquad50t,0 < t <= 10),(−62.5t + 1125, 10 < t <= F):}`
- The graph below again shows the relation representing Edgar’s swim.
Sketch the relation representing Zlatko’s swim on the graph below. (2 marks)
- How many minutes after the start of the race were Zlatko and Edgar the same distance from the shore?
Round your answer to two decimal places. (1 mark)
GEOMETRY, FUR2 2017 VCAA 3
Some hostel buildings are arranged around a grassed area.
The grassed area is shown shaded in the diagram below.
The grassed area is made up of a square overlapping a circle.
The square has side lengths of 65 m.
The circle has a radius of 50 m.
An angle, `theta`, is also shown on the diagram.
- Use the cosine rule to show that the angle `theta`, correct to the nearest degree, is equal to 81°. (1 mark)
- What is the perimeter, in metres, of the entire grassed area?
Round your answer to the nearest metre. (1 mark)
- The hostel’s management is planning to build a pathway from point A to point B, as shown on the diagram below.
Calculate the length, in metres, of the planned pathway.
Round your answer to the nearest metre. (2 marks)
GEOMETRY, FUR2 2017 VCAA 2
Miki will travel from Melbourne (38° S, 145° E) to Tokyo (36° N, 140° E) on Wednesday, 20 December.
The flight will leave Melbourne at 11.20 am, and will take 10 hours and 40 minutes to reach Tokyo.
The time difference between Melbourne and Tokyo is two hours at that time of year.
- On what day and at what time will Miki arrive in Tokyo? (1 mark)
Miki will travel by train from Tokyo to Nemuro and she will stay in a hostel when she arrives.
The hostel is located 186 m north and 50 m west of the Nemuro railway station.
-
- What distance will Miki have to walk if she were to walk in a straight line from the Nemuro railway station to the hostel?
Round your answer to the nearest metre. (1 mark)
- What is the three-figure bearing of the hostel from the Nemuro railway station?
Round your answer to the nearest degree. (1 mark)
- What distance will Miki have to walk if she were to walk in a straight line from the Nemuro railway station to the hostel?
The city of Nemuro is located 43° N, 145° E.
Assume that the radius of Earth is 6400 km.
- The small circle of Earth at latitude 43° N is shown in the diagram below.
What is the radius of the small circle of Earth at latitude 43° N?
Round your answer to the nearest kilometre. (1 mark)
- Find the shortest great circle distance between Melbourne (38° S, 145° E) and Nemuro (43° N, 145° E).
Round your answer to the nearest kilometre. (1 mark)
GEOMETRY, FUR2 2017 VCAA 1
Miki is planning a gap year in Japan.
She will store some of her belongings in a small storage box while she is away.
This small storage box is in the shape of a rectangular prism.
The diagram below shows that the dimensions of the small storage box are 40 cm × 19 cm × 32 cm.
The lid of the small storage box is labelled on the diagram above.
-
- What is the surface area of the lid, in square centimetres? (1 mark)
- What is the total outside surface area of this storage box, including the lid and base, in square centimetres? (1 mark)
- Miki has a large storage box that is also a rectangular prism.
The large storage box and the small storage box are similar in shape.
The volume of the large storage box is eight times the volume of the small storage box.
The length of the small storage box is 40 cm.
What is the length of the large storage box, in centimetres? (1 mark)
NETWORKS, FUR2 2017 VCAA 4
The rides at the theme park are set up at the beginning of each holiday season.
This project involves activities A to O.
The directed network below shows these activities and their completion times in days.
- Write down the two immediate predecessors of activity I. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The minimum completion time for the project is 19 days.
i. There are two critical paths. One of the critical paths is A–E–J–L–N.
Write down the other critical path. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
ii. Determine the float time, in days, for activity F. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The project could finish earlier if some activities were crashed.
Six activities, B, D, G, I, J and L, can all be reduced by one day.
The cost of this crashing is $1000 per activity.
i. What is the minimum number of days in which the project could now be completed? (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
ii. What is the minimum cost of completing the project in this time? (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
NETWORKS, FUR2 2017 VCAA 2
Bai joins his friends Agatha, Colin and Diane when he arrives for a holiday in Seatown.
Each person will plan one tour that the group will take.
Table 1 shows the time, in minutes, it would take each person to plan each of the four tours.
The aim is to minimise the total time it takes to plan the four tours.
Agatha applies the Hungarian algorithm to Table 1 to produce Table 2.
Table 2 shows the final result of all her steps of the Hungarian algorithm.
- In Table 2 there is a zero in the column for Colin.
When all values in the table are considered, what conclusion about minimum total planning time can be made from this zero? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Determine the minimum total planning time, in minutes, for all four tours. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
MATRICES, FUR2 2017 VCAA 3
Senior students at a school choose one elective activity in each of the four terms in 2018.
Their choices are communication (`C`), investigation (`I`), problem-solving (`P`) and service (`S`).
The transition matrix `T` shows the way in which senior students are expected to change their choice of elective activity from term to term.
`{:(qquadqquadqquadqquadquadtext(this term)),(qquadqquadqquad\ CqquadquadIqquadquadPqquad\ S),(T = [(0.4,0.2,0.3,0.1),(0.2,0.4,0.1,0.3),(0.2,0.3,0.3,0.4),(0.2,0.1,0.3,0.2)]{:(C),(I),(P),(S):}qquadtext(next term)):}`
Let `S_n` be the state matrix for the number of senior students expected to choose each elective activity in Term `n`.
For the given matrix `S_1`, a matrix rule that can be used to predict the number of senior students in each elective activity in Terms 2, 3 and 4 is
`S_1 = [(300),(200),(200),(300)],qquadS_(n + 1) = TS_n`
- How many senior students will not change their elective activity from Term 1 to Term 2? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Complete `S_2`, the state matrix for Term 2, below. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Of the senior students expected to choose investigation (`I`) in Term 3, what percentage chose service (`S`) in Term 2? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the maximum number of senior students expected in investigation (`I`) at any time during 2018? (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
MATRICES, FUR2 2017 VCAA 2
Junior students at a school must choose one elective activity in each of the four terms in 2018.
Students can choose from the areas of performance (`P`), sport (`S`) and technology (`T`).
The transition diagram below shows the way in which junior students are expected to change their choice of elective activity from term to term.
- Of the junior students who choose performance (`P`) in one term, what percentage are expected to choose sport (`S`) the next term? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Matrix `J_1` lists the number of junior students who will be in each elective activity in Term 1.
`J_1 = [(300),(240),(210)]{:(P),(S),(T):}`
- 306 junior students are expected to choose sport (`S`) in Term 2.
Complete the calculation below to show this. (1 mark)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- In Term 4, how many junior students in total are expected to participate in performance (`P`) or sport (`S`) or technology (`T`)? (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CORE, FUR2 2017 VCAA 7
Alex sold his mechanics’ business for $360 000 and invested this amount in a perpetuity.
The perpetuity earns interest at the rate of 5.2% per annum.
Interest is calculated and paid monthly.
- What monthly payment will Alex receive from this investment? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Later, Alex converts the perpetuity to an annuity investment.
This annuity investment earns interest at the rate of 3.8% per annum, compounding monthly.
For the first four years Alex makes a further payment each month of $500 to his investment.
This monthly payment is made immediately after the interest is added.
After four years of these regular monthly payments, Alex increases the monthly payment.
This new monthly payment gives Alex a balance of $500 000 in his annuity after a further two years.
What is the value of Alex’s new monthly payment?
Round your answer to the nearest cent. (2 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CORE, FUR2 2017 VCAA 6
Alex sends a bill to his customers after repairs are completed.
If a customer does not pay the bill by the due date, interest is charged.
Alex charges interest after the due date at the rate of 1.5% per month on the amount of an unpaid bill.
The interest on this amount will compound monthly.
- Alex sent Marcus a bill of $200 for repairs to his car.
Marcus paid the full amount one month after the due date.
How much did Marcus pay? (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Alex sent Lily a bill of $428 for repairs to her car.
Lily did not pay the bill by the due date.
Let `A_n` be the amount of this bill `n` months after the due date.
- Write down a recurrence relation, in terms of `A_0`, `A_(n + 1)` and `A_n`, that models the amount of the bill. (2 marks)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Lily paid the full amount of her bill four months after the due date.
How much interest was Lily charged?
Round your answer to the nearest cent. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CORE, FUR2 2017 VCAA 4
The eggs laid by the female moths hatch and become caterpillars.
The following time series plot shows the total area, in hectares, of forest eaten by the caterpillars in a rural area during the period 1900 to 1980.
The data used to generate this plot is also given.
The association between area of forest eaten by the caterpillars and year is non-linear.
A log10 transformation can be applied to the variable area to linearise the data.
- When the equation of the least squares line that can be used to predict log10 (area) from year is determined, the slope of this line is approximately 0.0085385
- Round this value to three significant figures. (1 mark)
- Perform the log10 transformation to the variable area and determine the equation of the least squares line that can be used to predict log10 (area) from year.
- Write the values of the intercept and slope of this least squares line in the appropriate boxes provided below.
- Round your answers to three significant figures. (2 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The least squares line predicts that the log10 (area) of forest eaten by the caterpillars by the year 2020 will be approximately 2.85
- Using this value of 2.85, calculate the expected area of forest that will be eaten by the caterpillars by the year 2020.
- i. Round your answer to the nearest hectare. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. Give a reason why this prediction may have limited reliability. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 SM-Bank 7
The graph of `f(x) = sqrt x (1 - x)` for `0<=x<=1` is shown below.
- Calculate the area between the graph of `f(x)` and the `x`-axis. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For `x` in the interval `(0, 1)`, show that the gradient of the tangent to the graph of `f(x)` is `(1 - 3x)/(2 sqrt x)`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The edges of the right-angled triangle `ABC` are the line segments `AC` and `BC`, which are tangent to the graph of `f(x)`, and the line segment `AB`, which is part of the horizontal axis, as shown below.
Let `theta` be the angle that `AC` makes with the positive direction of the horizontal axis.
- Find the equation of the line through `B` and `C` in the form `y = mx + c`, for `theta = 45^@`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Trigonometry, 2ADV T2 SM-Bank 8
Let `(tantheta - 1) (sin theta - sqrt 3 cos theta) (sin theta + sqrt 3 costheta) = 0`.
- State all possible values of `tan theta`. (1 mark)
- Hence, find all possible solutions for `(tan theta - 1) (sin^2 theta - 3 cos^2 theta) = 0`,
where `0 <= theta <= pi`. (2 marks)
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- …
- 82
- Next Page »