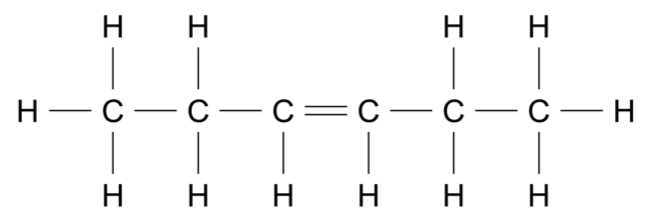
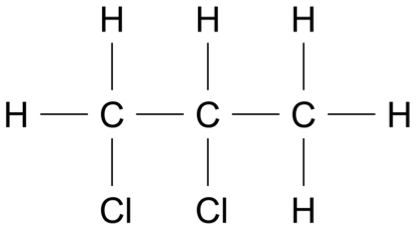
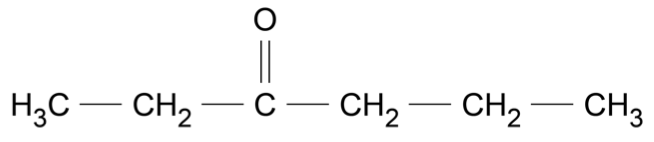Which of the following is correct about the forces acting during a rocket launch?
- Equal and opposite forces act on the rocket. This enables it to continue to accelerate even in the vacuum of space.
- The engines exert an upward thrust on the rocket. This thrust exceeds the downward force of the engines on the air.
- The rocket engines exert a downward force on the gases being expelled. These gases exert an upward force on the engines.
- The expelled gases exert a force against the launch pad. The launch pad then exerts an equal and opposite force on the rocket causing it to accelerate.