There are two unlabelled solutions. One is barium nitrate and the other lead nitrate.
Which of the following could be added to the two unlabelled solutions to distinguish between them?
- Sodium sulfate
- Sodium nitrate
- Sodium chloride
- Sodium carbonate
Aussie Maths & Science Teachers: Save your time with SmarterEd
There are two unlabelled solutions. One is barium nitrate and the other lead nitrate.
Which of the following could be added to the two unlabelled solutions to distinguish between them?
`C`
`=>C`
Three test tubes were set up as shown.
Bromine water was added to `X` and `Y` in the absence of UV light.
Which of the following best represents the changes in test tubes `X` and `Y` ?
`C`
By Elimination:
`=>C`
Which defence adaptation in the table is correctly matched with one of its features?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\ \text{Defence adaptation}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \text{Feature} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Inflammation }\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&\text{Constriction of blood vessels}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Phagocytosis}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Production of antibodies by white blood cells}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Lymph system}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Transportation of blood to help fight pathogens} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Cell death}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Formation of a barrier around the pathogen} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
\(D\)
\(\Rightarrow D\)
In the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), protons travel in a circular path at a speed greater than 0.9999 `c`.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Advantages:
b. Applications of special relativity:
Other answers could include:
a. Advantages:
b. Applications of special relativity:
Other answers could include:
Consider the following two models used to calculate the work done when a 300 kg satellite is taken from Earth's surface to an altitude of 200 km.
You may assume that the calculations are correct.
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Model `X`:
Model `Y`:
b. Similarity of results due to:
c. `v=7797 text{ms}^(-1)`
a. Model `X`:
Model `Y`:
b. Similarity of results due to:
c. Centripetal force = force due to gravity:
| `F_(c)` | `=F_(g)` | |
| `(mv^2)/(r)` | `=(GMm)/(r^2)` | |
| `:.v` | `=sqrt((GM)/(r))=sqrt((6.67 xx10^(-11)xx6xx10^(24))/(6.58 xx10^(6)))=7797 text{ms}^(-1)` |
The diagram shows a label on a transformer used in an appliance.
Explain why the information provided on the label is not correct. Support your answer with calculations. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculating the input power:
`P=VI=240 xx5=1200\ text{W}`
Calculating the output power:
`P=VI=2000 xx 1=2000\ text{W}`
Calculating the input power:
`P=VI=240 xx5=1200\ text{W}`
Calculating the output power:
`P=VI=2000 xx 1=2000\ text{W}`
A projectile was launched from the ground. It had a range of 70 metres and was in the air for 3.5 seconds.
At what angle to the horizontal was it launched?
`B`
Find `u_(x):`
| `s_(x)` | `=u_(x)t` | |
| `u_(x)` | `=(70)/(3.5)=20 text{ms}^(-1)` |
Find `u_(y)` (projectile has a vertical velocity of zero at its maximum height):
| `v_(y)` | `=u_(y)+a_(y)t` | |
| `0` | `=u_(y)-9.8xx1.75` | |
| `u_(y)` | `=17.15 text{ms}^(-1)` |
Find launch angle:
| `tan theta` | `=(u_(y))/(u_(x))` | |
| `theta` | `=tan^(-1)((17.15)/(20))=40^(@)` |
`=>B`
The diagram shows an ideal transformer.
When the switch is closed, the pointer on the galvanometer deflects.
How could the size of the deflection be increased?
`B`
`=>B`
A circular loop of wire is stationary in a magnetic field. The sides are then pushed together to change the shape, as shown in the diagram.
As the loop is compressed, a current is induced.
Which row of the table shows the direction of the current and explains why it is induced?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{Current Direction}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \textit{Why the current is induced} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Clockwise}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&\text{Change in magnetic flux}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Anticlockwise}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Change in magnetic flux}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Clockwise}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Change in magnetic flux density} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Anticlockwise}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Change in magnetic flux density} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
\(A\)
\(\Rightarrow A\)
A simple AC generator was connected to a cathode ray oscilloscope and the coil was rotated at a constant rate. The output is shown on this graph.
Which of the following graphs best represents the output if the rate of rotation is decreased to half of the original value?
`D`
Halving the rate of rotation of the bar magnet:
`=>D`
`P`, `Q` and `R` are straight, current-carrying conductors. They all carry currents of the same magnitude `(I)`. Conductors `P` and `Q` are fixed in place. The magnitude of the force between conductors `Q` and `R` is `F` newtons.
What is the net force on conductor `R` when it is in the position shown?
`B`
`=>B`
A current-carrying wire is placed perpendicular to a magnetic field.
Which graph correctly shows the relationship between magnetic field strength `(B)` and current `(I)` if the force is to remain constant?
`C`
`F=IlB sin theta \ \ =>\ \ I=(F)/(lB sin theta)`
`=>C`
Which of the following is a true statement about scientific theories, such as Einstein's theory of special relativity?
`B`
By Elimination:
`=>B`
The following makeshift device was made to provide lighting for a stranded astronaut on Mars.
The mass of Mars is `6.39 ×10^(23) \ text {kg}`.
The 2 kg mass falls, turning the DC generator, which supplies energy to the light bulb. The mass falls from a point that is 3 376 204 m from the centre of Mars.
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. 7.48 J
b. When switch is opened:
a. `DeltaE=U_(f)-U_(i)`
`=((-Gm_(1)m_(2))/(r_(f)))-((-Gm_(1)m_(2))/(r_(i)))`
`=(-6.67 xx10^(-11)xx6.39 xx10^(23)xx2)/(3\ 376\ 203)-((-6.67 xx10^(-11)xx6.39 xx10^(23)xx2))/(3\ 376\ 204)`
`=-7.48\ text{J}`
b. When switch is opened:
The following diagram shows the acceleration of a rocket during the first stage of its launch.
Explain the acceleration of the rocket with reference to the law of conservation of momentum. (5 marks)
Muons are subatomic particles which at rest have a lifetime of 2.2 microseconds `(mus)`. When they are produced in Earth's upper atmosphere, they travel at 0.9999 `c`.
Using classical physics, the distance travelled by a muon in its lifetime can be calculated as follows:
`x=vt=660\ text{m}`
Which row of the table correctly summarises the behaviour of these muons?
`A`
`=>A`
A projectile was launched horizontally inside a lift in a building. The diagram shows the path of the projectile when the lift was stationary.
The projectile was launched again with the same velocity. At this time, the lift was slowing down as it approached the top floor of the building.
Which diagram correctly shows the new path of the projectile (dotted line) relative to the path created in the stationary lift (solid line)?
`C`
`=>C`
A satellite orbits Earth with period `T`. An identical satellite orbits the planet Xerus which has a mass four times that of Earth. Both satellites have the same orbital radius `r`.
What is the period of the satellite orbiting Xerus?
`B`
Applying Kepler’s Third Law:
| `(r^(3))/(T^(2))` | `=(GM)/(4pi^(2))` | |
| `r^3` | `=(GMT^(2))/(4pi^(2))` |
Since satellites have the same orbital radius:
| `(G(M_(E))(T_E)^(2))/(4pi^(2))` | `=(G(M_(X))(T_(X))^(2))/(4pi^(2))` | |
| `(M_(E))(T_E)^(2)` | `=(M_(X))(T_(X))^(2)` | |
| `((T_(X))^(2))/((T_E)^(2))` | `=(M_(E))/(M_(X))` | |
| `=1/4\ \ (M_X=4xxM_E\ text{(given)})` | ||
| `(T_(X))/(T_E)` | `=(1)/(2)` | |
| `T_X` | `=(T_E)/2` |
`=>B`
Which diagram correctly shows the deflection of a cathode ray by a bar magnet?
`B`
`=>B`
A region of space contains a constant magnetic field and a constant electric field.
How will these fields affect an electron that is stationary in this region?
`C`
`=>C`
In a thought experiment, a proton is travelling at a constant velocity in a vacuum with no field present. An electric field and a magnetic field are then turned on at the same time.
The fields are uniform in magnitude and direction and can be considered to extend infinitely. The velocity of the proton at the instant the fields were turned on is perpendicular to the fields.
Analyse the motion of the proton after the fields have been turned on. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Contrast the design of transformers and magnetic braking systems in terms of the effects that eddy currents have in these devices. (6 marks)
--- 15 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Transformers:
Magnetic Braking Systems:
Transformers:
Magnetic Braking Systems:
The diagram shows an electric circuit in a magnetic field directed into the page. The graph shows how the flux through the conductive loop changes over a period of 12 seconds.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `2.1\ text{T}`
b. `0.3 text{V}`
| a. | `Phi` | `=BA` |
| `B` | `=(Phi)/(A)=(Phi)/(pir^(2))` | |
| `B_max` | `=(0.6)/(pi xx(0.3)^(2))=2.1\ text{T}` |
b. Voltage (emf) = time rate of flux
The escape velocity from a planet is given by `v = sqrt((2GM)/(r))`.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `v=5010 text{m s}^(-1)`
b. Applying the law of conservation of energy:
| `KE_(i)+U_(i)` | `=0` | |
| `(1)/(2)mv^(2)-(GMm)/(r)` | `=0` | |
| `mv^(2)` | `=(2GMm)/(r)` | |
| `∴ v_(esc)` | `=sqrt((2GM)/(r))` |
| a. | `v` | `=sqrt((2xx6.67 xx10^(-11)xx6.39 xx10^(23))/(3.39 xx10^(6)))` |
| `=5014.5 text{m s}^(-1)` | ||
| `=5015 text{m s}^(-1)\ \ text{(to 0 d.p.)}` |
b. Applying the law of conservation of energy:
| `KE_(i)+U_(i)` | `=0` | |
| `(1)/(2)mv^(2)-(GMm)/(r)` | `=0` | |
| `mv^(2)` | `=(2GMm)/(r)` | |
| `∴ v_(esc)` | `=sqrt((2GM)/(r))` |
Using examples from special relativity, explain how theories in science are validated in different ways. (5 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A particle of mass \(m\) and charge \(q\) travelling at velocity \(v\) enters a magnetic field of magnitude \(B\) and follows the path shown.
A second particle enters a magnetic field of magnitude \(2B\) with a velocity of \(\dfrac{1}{2}v\) and follows an identical path.
What is the mass and charge of the second particle?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\quad \textit{Mass}\quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \quad \textit{Charge} \quad \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}m\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&q\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\frac{1}{2} m\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& 2q\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}4m\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& q \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}m\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \frac{1}{2}q \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
\(C\)
| \(F_c\) | \(=F_b\) | |
| \(\dfrac{m v^2}{r}\) | \(=q v B\) | |
| \(r\) | \(=\dfrac{m v}{q B}\) |
\(\text{Given} \ B=2 B \ \text{and} \ v=\dfrac{1}{2} v:\)
\(r=\dfrac{m \frac{1}{2} v}{q(2 B)}=\dfrac{m v}{4 q B}\)
\(\Rightarrow C\)
An AC supply is connected to a light bulb by two long parallel conductors as shown.
Which graph shows the variation over time of the magnetic force between the two conductors?
`D`
`=>D`
A car travelling at a constant speed follows the path shown.
An accelerometer that measures acceleration along the `X - X^’` direction is fixed in the car.
Which graph shows the measurements recorded by the accelerometer over the 20-second interval?
`B`
`=>B`
The diagram shows a model of a system used to distribute energy from a power station through transmission lines and transformers to houses.
During the evening peak period there is an increase in the number of electrical appliances being turned on in houses.
Explain the effects of this increased demand on the components of the system, with reference to voltage, current and energy. (6 marks)
--- 18 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Current and voltage:
Energy losses:
Current and voltage:
Energy losses:
The radius of the moon is 1740 km. The moon's mass is `7.35 × 10^(22)` kg. In this question, ignore the moon's rotational and orbital motion.
A 20 kg mass is launched vertically from the moon's surface at a velocity of `1200 \ text{m s}^(-1)`.
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Proof (See Worked Solutions)
b. `424 text{m s}^-1`
| a. | `U_(i)` | `=-(GMm)/(r)` |
| `=(-6.67 xx10^(-11)xx7.35 xx10^(22)xx20)/(1.74 xx10^(6))` | ||
| `=-5.64 xx10^(7)\ text{J}` | ||
| `U_(f)` | `=(-6.67 xx10^(-11)xx7.35 xx10^(22)xx20)/(2.24 xx10^(6))` | |
| `=-4.38 xx10^(7)\ text{J}` |
`:.Delta U=U_(f)-U_(i)=1.26 xx10^(7)\ text{J}`
b. `KE_(i)=(1)/(2)m u^(2)=(1)/(2)xx20 xx1200^(2)=1.44 xx10^(7) text{J}`
`KE_(f)=KE_(i)-DeltaE_(p)\ \ text{(by LCE)}=1.44 xx10^(7)-1.26 xx10^(7)=1.8 xx10^(6) text{J}`
| `(1)/(2)mv^(2)` | `=1.8 xx10^(6)` | |
| `v^2` | `=(2xx1.8 xx10^(6))/(20)` | |
| `:.v` | `=sqrt((2xx1.8 xx10^(6))/(20))= 424 text{m s}^-1` |
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Using the graphs, describe the velocity and acceleration of the ball quantitatively and qualitatively. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Experimental error:
Other errors include:
b. Velocity and acceleration of ball:
a. Experimental error:
Other errors include:
b. Velocity and acceleration of ball:
Which of the following is the AS 1100 standard for drawing a break line?
`C`
`=>C`
A watch is currently worth $6100. It has appreciated by 5.8% per annum since purchase.
What was its value 10 years ago? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`$3471.15`
`FV=$6100`
`text{Find}\ PV\ text{given}\ n=10, \ r=5.8text{%}=0.058:`
| `FV` | `=PV(1+r)^n` | |
| `6100` | `=(PV)(1+0.058)^10` | |
| `PV` | `=6100/(1.058)^10` | |
| `=$3471.148…` | ||
| `=$3471.15\ \ text{(nearest cent)}` |
A car is purchased for $15 000. The graph shows the value of the car, `$V`, at time `t` years since it was purchased, using the declining-balance method of depreciation.
When using the straight-line method of depreciation, the value of the car depreciates at a rate of $2500 per year.
By first completing the table, plot on the grid above the value of the car for the first three years based on the straight-line method of depreciation. (2 marks)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a.
b.
Values are equal when graphs intersect
→ after 4 years
a.
b.
Values are equal when graphs intersect
→ after 4 years
Julie has a gross annual salary of $67 000. During the year she also received an income of $780 from investments and had tax deductions totalling $1000.
The table below shows the income tax rates for the 2021–2022 financial year.
Calculate the tax payable on Julie's taxable income, ignoring the Medicare levy. (3 marks)
`$12 170.50`
| `text{Taxable Income}` | `=\ text{Total Income – Deductions}` | |
| `=67\ 000 + 780-1000` | ||
| `=$66\ 780` |
| `:.\ text{Tax Payable}` | `=5092+0.325(66\ 780-45\ 000)` | |
| `=5092+7078.50` | ||
| `=$12\ 170.50` |
Shan is interested in buying a block of bushland. The price per hectare is $500. The land he wishes to purchase is in the shape of a right-angled triangle as shown.
The length of side `A B` is 7800 metres and the length of side `B C` is 3000 metres. The right angle of the triangle is angle `A C B`.
Note: 1 hectare =10 000 m2
What is the cost of the block of bushland? (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
$540 000
`text{Using Pythagoras:}`
| `AC^2` | `=7800^2-3000^2` | |
| `=51\ 840\ 000` | ||
| `:.AC` | `=7200` |
| `text{Area}\ DeltaABC` | `=(BC xx AC)/2` | |
| `=3000 xx 7200` | ||
| `=108\ 000\ 000\ text{m}^2` | ||
| `=1080\ text{hectares (1 hectare = 10 000 m}^(2))` |
| `:.\ text{Cost}` | `=$500 xx 1080` | |
| `=$540\ 000` |
A family uses a credit card to purchase a lounge during the month of November.
The credit card has no interest-free period. Interest is charged at a rate of 21% per annum, compounded daily, from and including the date of purchase to the last day of the month.
The table shows the only purchases and payments on the credit card during the month of November.
What is the closing balance owing on the credit card on 30 November? (3 marks)
`$5569.34`
`text{Interest calculation:}`
`text{Days = 16 (15th November – 30th November)}`
`text{Daily interest rate} = 21/365 %`
| `text{Card Balance (30 Nov)}` | `=7500(1+21/(365 xx100))^16-2000` | |
| `=7569.339…- 2000` | ||
| `=$5569.34` |
Peta has the choice of investing $7000 in two different investment funds.
Fund A: 5.2% per annum simple interest
Fund B: 5% per annum interest, compounded annually
What is the difference between the amounts of interest earned in the two investment funds over 3 years? (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`$11.38`
`text{Fund A}`:
| `text{Simple Interest}` | `= 7000xx 5.2text{%}xx 3` | |
| `= 7000xx 0.052xx 3` | ||
| `= $1092` |
`text{Fund B}`:
| `FV` | `=PV (1+r)^n` | |
| `= 7000 (1+0.05)^3` | ||
| `=$8103.38\ \ text{(nearest cent)}` |
| `text{Interest}` | `= FV-PV` | |
| `=8103.38-7000` | ||
| ` = $1103.38` |
| `:.\ text{Difference}` | `= 1103.38-1092` | |
| `=$11.38` |
A 2500-watt air-conditioning system is turned on for 3 hours each day. Electricity is charged at 27 cents per kWh.
What is the cost of electricity for using the air-conditioning system over a seven-day period? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`$14.18`
| `text{Daily usage}` | `=2500 xx 3` |
| `= 7500\ text{W}` | |
| `=7.5\ text{kW (1000 W = 1 kW)}` |
| `text{Cost}` | `= 2.5 xx 7.5 xx 0.27` | |
| `= 14.175` | ||
| `=$14.18\ \ text{(nearest cent)}` |
Fried's formula is used to calculate the dosage of medication for children aged 1-2 years based on the adult dosage. The formula is
`text{Dosage}=(text{age (in months)} xx\ text{adult dosage})/(150)`.
The adult dosage of a particular medication is 200 mg.
Betty's dosage is calculated to be 24 mg.
How old is Betty in months? (2 marks)
18 months
`text{Substituting into the formula:}`
| `24` | `=( \ text{age} xx 200)/150` | |
| `text{age}` | `=(24 xx 150)/200` | |
| `=360/20` | ||
| `= 18\ text(months)` |
Singapore is 8 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC +8) and New York is 5 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time (UTC –5).
What is the time and day in Singapore when it is 9 pm Monday in New York? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
10 am Tuesday
New York → UTC – 5 hours
Singapore → UTC + 8 hours
Singapore is 5 + 8 = 13 hours ahead of New York
| `∴` Time and day in Singapore | = Monday 9 pm + 13 hours | |
| = Tuesday 9 am + 1 hour | ||
| = Tuesday 10 am |
Each number from 1 to 30 is written on a separate card. The 30 cards are shuffled. A game is played where one of these cards is selected at random. Each card is equally likely to be selected.
Ezra is playing the game, and wins if the card selected shows an odd number between 20 and 30.
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `21, 23, 25, 27, 29`
| b. | `Ptext{(not win)}` | `=1-Ptext{(win)}` |
| `=1-5/30` | ||
| `=25/30` | ||
| `=5/6` |
A concert organiser is interested in the relationship between the distance from the stage, in metres, and the loudness of the sound measured in decibels.
The data the concert organiser collected is shown on the graph.
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. The graph is not a straight line, therefore, non-linear.
b. Distance = 6 metres.
→ Intersection of line of best fit and horizontal line at decibels (y-axis) = 90
Discuss methods for increasing the signal strength of a receiving antenna. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A H–R diagram is shown. Star `X` is a main sequence star of 12 solar masses.

Describe how star `X` will change physically and chemically as it continues to evolve. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Use the following data to answer parts (a) and (b).
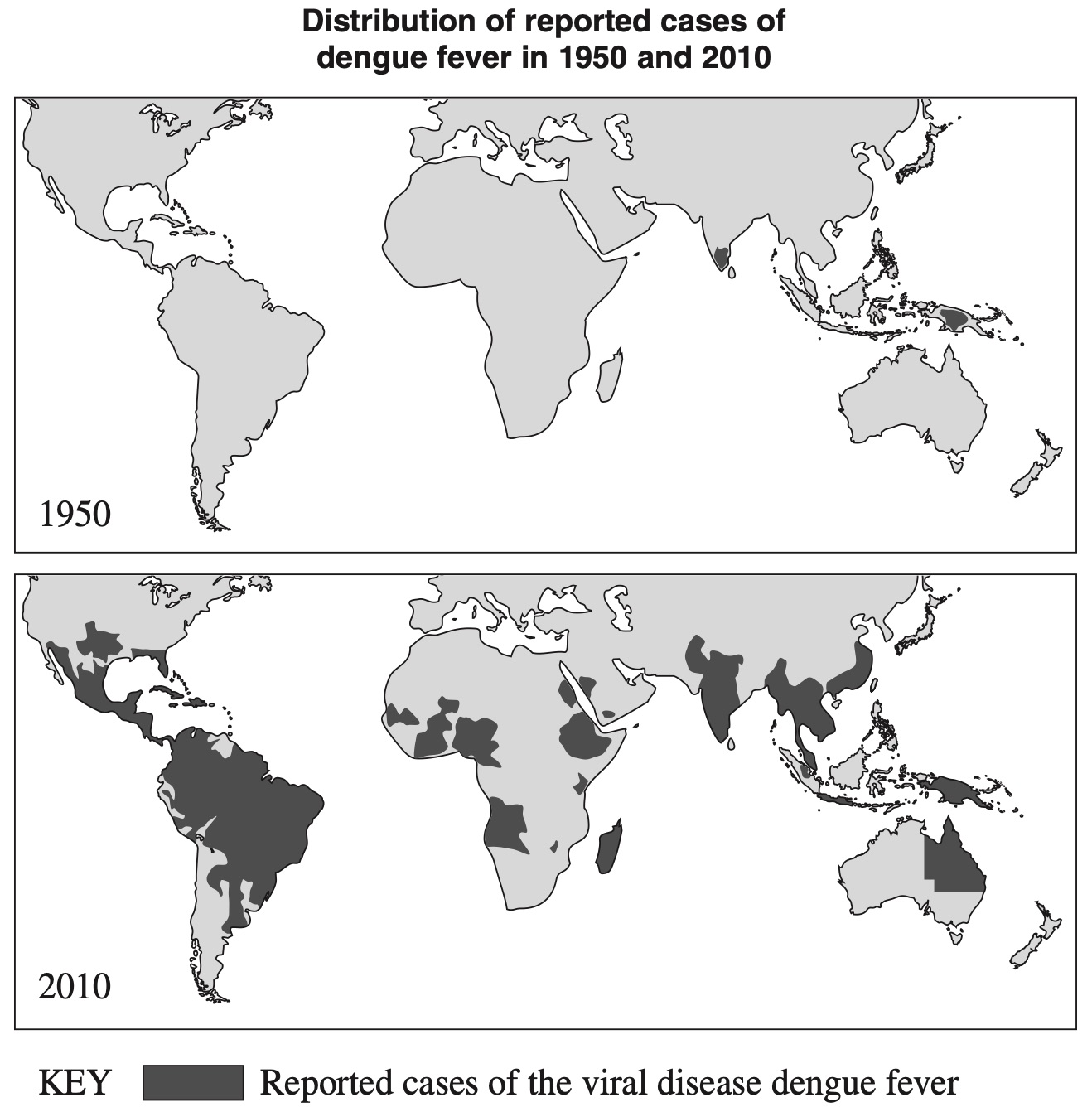
Dengue fever and malaria are examples of infectious diseases transmitted between humans by mosquitoes. Dengue fever is caused by a virus transmitted by mosquitoes of the genus Aedes. Malaria is caused by a single-celled organism transmitted by mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles.
The following data provide information about the global incidence of these two diseases over time.
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 16 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Trends in global disease burden:
b. Analysis of factors that could have contributed to the change in global distribution of both dengue fever and malaria
Both diseases are transmitted by a mosquito vector. The prevalence of mosquitoes in each area would therefore have a large influence on the number of infected individuals.
These factors can be associated with the distribution seen on the Dengue Fever map, however the countries with reported cases of Malaria has shrunk.
Medical advances such as vaccines also have the potential to be an effective measure of containing diseases.
a. Trends in global disease burden:
b. Analysis of factors that could have contributed to the change in global distribution of both dengue fever and malaria
Both diseases are transmitted by a mosquito vector. The prevalence of mosquitoes in each area would therefore have a large influence on the number of infected individuals.
These factors can be associated with the distribution seen on the Dengue Fever map, however the countries with reported cases of Malaria has shrunk.
Medical advances such as vaccines also have the potential to be an effective measure of containing diseases.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Helicobacter pylori is a bacteria that causes stomach ulcers.
Other answers could include:
b. Diseases will be able to spread faster and easier with certain modes of transmission.
Other answers could include the effectiveness of modes such as
a. Helicobacter pylori is a bacteria that causes stomach ulcers.
Other answers could include:
b. Diseases will be able to spread faster and easier with certain modes of transmission.
Other answers could include the effectiveness of modes such as
Experiments were conducted to obtain data on the traits 'seed shape' in plants and 'feather colour' in chickens. In each case, the original parents were pure breeding and produced the first generation (F1). The frequency data diagrams below relate to the second generation offspring (F2), produced when the F1 generations were bred together.
Explain the phenotypic ratios of the F2 generation in both the plant and chicken breeding experiments. Include Punnett squares and a key to support your answer. (5 marks)
--- 12 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\begin{array} {|c|c|c|}\hline & \text{R} & \text{r} \\ \hline \text{R} & \text{RR} & \text{Rr} \\ \hline \text{r} & \text{Rr} & \text{rr} \\ \hline \end{array}
Key: R = Round r = wrinkled
\begin{array} {|c|c|c|}\hline & \text{B} & \text{W} \\ \hline \text{B} & \text{BB} & \text{BW} \\ \hline \text{W} & \text{BW} & \text{WW} \\ \hline \end{array}
Key: B = Black Feathers W= White Feathers
\begin{array} {|c|c|c|}\hline & \text{R} & \text{r} \\ \hline \text{R} & \text{RR} & \text{Rr} \\ \hline \text{r} & \text{Rr} & \text{rr} \\ \hline \end{array}
Key: R = Round r = wrinkled
\begin{array} {|c|c|c|}\hline & \text{B} & \text{W} \\ \hline \text{B} & \text{BB} & \text{BW} \\ \hline \text{W} & \text{BW} & \text{WW} \\ \hline \end{array}
Key: B = Black Feathers W= White Feathers
Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant condition caused by a mutation of a gene on chromosome 4. It causes nerve cells to break down.
Stargardt disease is an autosomal recessive condition caused by a mutation of a different gene on chromosome 4 . It causes damage to the retina.
A patient is heterozygous for both Huntington's (Hh) and Stargardt disease (Rr). His father's extended family has numerous cases of both of these diseases. His mother does not have either disease and is homozygous for both genes.
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The travel graph displays Jamie's trip which began at town `M` at 8 am and finished at town `N`.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `140\ text{km}`
b. `text{James arrives back at town when he is 140 km away (2nd time)}`
`:. 10\ text{am}`
| c. | `text{Total distance}` | `=40 + 40 + 60+ 80` |
| `=220\ text{km}` |
d. `text{Fastest speed → graph is the steepest}`
`:.\ text{Fastest speed between 11 – 11:30 am}`
a. `140\ text{km}`
b. `text{James arrives back at town when he is 140 km away (2nd time)}` `:. 10\ text{am}` d. `text{Fastest speed → graph is the steepest}` `:.\ text{Fastest speed between 11 – 11:30 am}`
c.
`text{Total distance}`
`=40 + 40 + 60+ 80`
`=220\ text{km}`
♦♦ Mean mark part (c) 35%.
♦♦ Mean mark part (d) 32%.
Yeast is a single-celled fungus that can reproduce by budding.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Asexual.
b. Steps of procedure:
a. Asexual.
b. Steps of procedure:
The map shows the percentage of adult indigenous populations able to digest lactose.
The ability to digest lactose is due to the presence of an enzyme (lactase) which can metabolise the sugar (lactose) present in milk. The gene responsible for producing lactase is usually permanently switched off at some time between the ages of 2 and 5 years. However, some people remain able to digest lactose throughout their lives.
With reference to evolution and DNA, provide possible reasons for the distribution shown in the map. (5 marks)
The floor plan of a home unit has been drawn to scale.
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `5`
b. `text{Conversion: 1000 mm = 1 metre}`
`text{Calculate area by splitting into 2 rectangles}`
| `text{Area}` | `= 5.5 × 5 + (4.5 +2.5) xx 4` | |
| `= 55.5\ text{m²}` |
The area `(A)` of a circle is given by the formula `A=\pi r^2`, where `r` is the radius.
What is the value of `A`, correct to three significant figures, if `r=3.55` ?
`B`
| `A` | `=pi\r^2` | |
| `=pi xx3.55^2` | ||
| `=39.591…` | ||
| `=39.6\ \ text{(3 sig fig)}` |
`=>B`
Alzheimer's disease causes destruction of brain tissue, dementia and eventually death.
The diagram shows the effect of Alzheimer's disease on the brain.
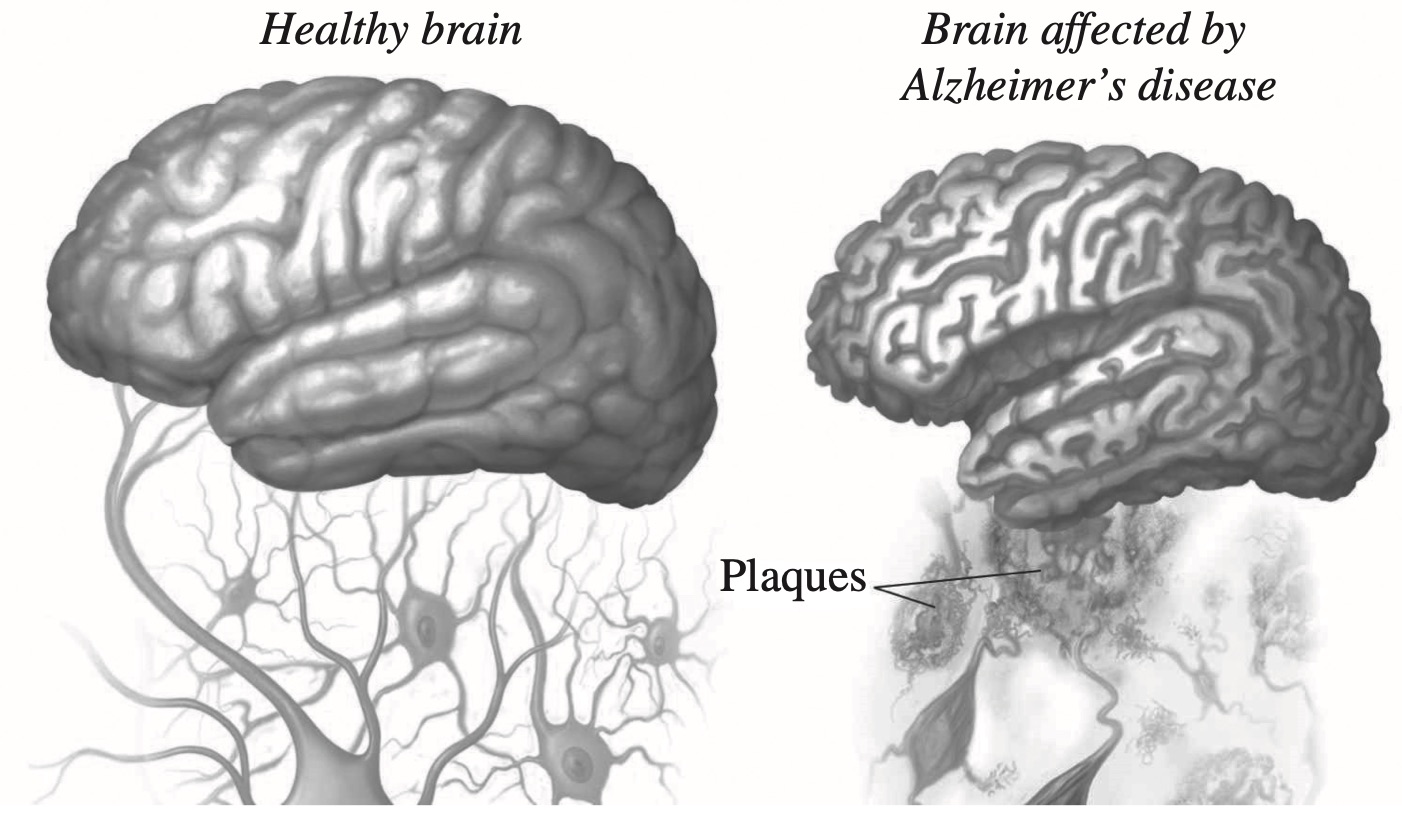
Amyloid beta protein is produced in the human brain throughout life. In people with Alzheimer's disease, it accumulates in excessive amounts.
The gene with the greatest known effect on the risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer's disease is called APOE. It is found on chromosome 19.
The APOE gene has multiple alleles, including e2, e3 and e4 .
The table shows the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease for various APOE genotypes compared to average risk in the population.
A large epidemiological study was conducted. It used historical data to investigate the association between Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection and dementia. Dementia is caused by a variety of brain illnesses. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia.
The study used the records of 8362 patients with HSV infection and 25086 randomly selected sex- and age-matched control patients without HSV infection. Some of the patients with HSV had been treated with antiviral medication.
The graph below shows some results of the study.
Diseases are classified as infectious or non-infectious.
Evaluate whether Alzheimer's disease should be classified as an infectious disease or a non-infectious disease. In your answer, include reference to the information and data provided above. (8 marks)
--- 18 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Infectious vs non-infection disease classification
Conclusion
Infectious vs non-infection disease classification
Conclusion
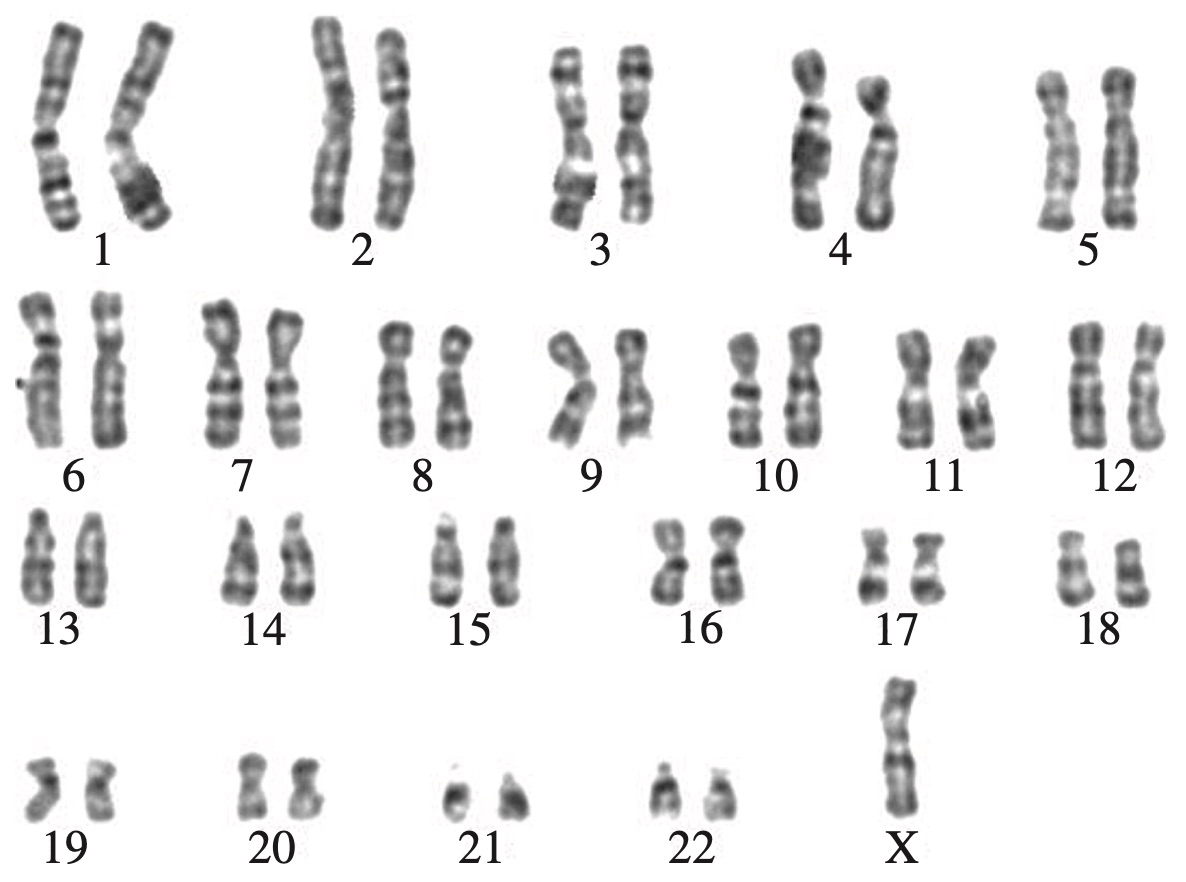
A human karyotype that shows evidence of chromosomal mutation is shown.
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. There is only one copy of the sex chromosome (Monosomy, Turner Syndrome).
b. Process of producing karyotype:
a. There is only one copy of the sex chromosome (Monosomy, Turner Syndrome).
b. Process of producing karyotype:
Complete the table to show the differences between somatic and germ-line mutations. (3 marks)
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \quad \quad \textit{Somatic mutation} \quad \quad & \quad \quad\textit{Germ-line mutation}\quad \quad \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{5ex}\text { Location } \rule[-4.5ex]{0pt}{0pt}& & \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{4ex}\text {Effect on} \\
\rule[-4ex]{0pt}{0pt}\text {offspring} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{5ex}\text {Example } \rule[-4.5ex]{0pt}{0pt}& & \\
\hline
\end{array}
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
A particle is moving vertically in a resistive medium under the influence of gravity. The resistive force is proportional to the velocity of the particle.
The initial speed of the particle is NOT zero.
Which of the following statements about the motion of the particle is always true?
`C`
`text{Case 1: particle moving downwards}`
`ddotx=g-kv\ \ (k>0)`
`text{Terminal velocity occurs when}\ \ ddotx=0\ \ =>\ \ v=g/k`
`text{Whether the particle’s speed increases, decreases or stays}`
`text{constant depends on whether}\ \ v_o<=g/k.`
`→\ text{Eliminate A and B.}`
`text{Case 2: particle moving upwards}`
`ddotx=-g-kv\ \ (k>0)`
`text{→ Acceleration of gravity and resistance against motion}`
`text{→ Particle will eventually hit a peak and then move downwards}`
`text{→ Once moving downwards}\ \ ddotx=g-kv\ \ (k>0)`
`text{→ Particle will hit terminal velocity (see Case 1)}`
`=>C`