Arthur takes out a new loan of $60 000 to pay for an overseas holiday. Interest on this loan compounds weekly. The balance of the loan, in dollars, after \(n\) weeks, \(V_n\), can be determined using a recurrence relation of the form \(V_0=60\ 000, \quad V_{n+1}=1.0015\,V_n-d\) --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, GEN1 2022 VCAA 4 MC
Consider the graph below.
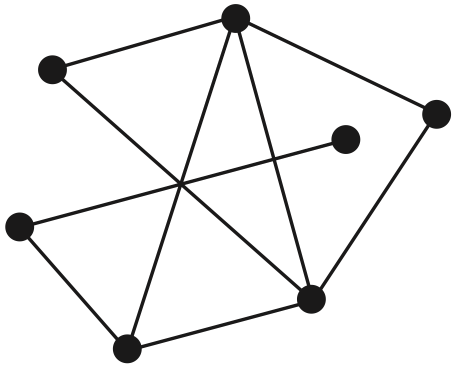
The number of edges that need to be removed for this graph to be planar is
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Matrices, GEN1 2022 VCAA 8 MC
Two types of computers - laptops `(L)` and desktops `(D)` - can be serviced by Henry `(H)`, Irvine `(I)` or Jean `(J)`.
Matrix `N` shows the time, in minutes, it takes each person to service a laptop and a desktop.
`{:(qquadqquadquad\ LquadqquadD),(N = [(18,8),(10,17),(12,9)]{:(H),(I),(J):}):}`
Matrix `Q` shows the number of laptops and desktops in four different departments: marketing `(M)`, advertising `(A)`, publishing `(P)` and editing `(E)`.
`{:(qquadqquadquad\ LquadqquadD),(Q = [(6,8),(4,7),(5,5),(10,12)]{:(M),(A),(P),(E):}):}`
A calculation that determines the total time that it would take each of Henry, Irvine or Jean, working alone, to service all the laptops and desktops in all four departments is
- `[1\ 1\ 1\ 1]×(Q×N^T)`
- `(Q×N^T)×[(1),(1),(1)]`
- `(N×Q^T)×Q`
- `[(1,0,0),(0,1,0),(0,0,1)]×N×Q^T`
- `[1\ 1\ 1\ 1]×Q×N^T×[(1),(1),(1)]`
CHEMISTRY, M7 2020 VCE 16 MC
Complex Numbers, EXT2 N2 2023 HSC 16c
The complex numbers \(w\) and \(z\) both have modulus 1, and \(\dfrac{\pi}{2} \lt \text{Arg} \Big{(}\dfrac{z}{w}\Big{)} \lt \pi\), where \(\text{Arg}\) denotes the principal argument.
For real numbers \(x\) and \(y\), consider the complex number \(\dfrac{xz+yw}{z}\).
On an \(xy\)-plane, clearly sketch the region that contains all points \((x,y)\) for which \(\dfrac{\pi}{2} \lt \text{Arg} \Big{(}\dfrac{xz+yw}{z}\Big{)} \lt \pi\).
Vectors, EXT2 V1 2023 HSC 10 MC
Consider any three-dimensional vectors \(\underset{\sim}{a}=\overrightarrow{O A}, \underset{\sim}{b}=\overrightarrow{O B}\) and \(\underset{\sim}{c}=\overrightarrow{O C}\) that satisfy these three conditions
\(\underset{\sim}{a} \cdot \underset{\sim}{b}=1\)
\(\underset{\sim}{b} \cdot \underset{\sim}{c}=2\)
\(\underset{\sim}{c} \cdot \underset{\sim}{a}=3\).
Which of the following statements about the vectors is true?
- Two of \(\underset{\sim}{a}, \underset{\sim}{b}\) and \(\underset{\sim}{c}\) could be unit vectors.
- The points \(A, B\) and \(C\) could lie on a sphere centred at \(O\).
- For any three-dimensional vector \(\underset{\sim}{a}\), vectors \(\underset{\sim}{b}\) and \(\underset{\sim}{c}\) can be found so that \(\underset{\sim}{a}, \underset{\sim}{b}\) and \(\underset{\sim}{c}\) satisfy these three conditions.
- \(\forall \ \underset{\sim}{a}, \underset{\sim}{b}\) and \(\underset{\sim}{c}\) satisfying the conditions, \(\exists \ r, s\) and \(t\) such that \(r, s\) and \(t\) are positive real numbers and \(r\underset{\sim}{a}+s \underset{\sim}{b}+t \underset{\sim}{c}=\underset{\sim}{0}\).
Networks, GEN1 2023 VCAA 38 MC
A particular building project has ten activities that must be completed.
These activities and their immediate predecessor(s) are shown in the table below.
\begin{array} {|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textbf{Activity} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \textbf{Immediate predecessor(s)} \\
\hline
A & - \\
\hline
B & - \\
\hline
C & A \\
\hline
D & A \\
\hline
E & B \\
\hline
F & D, E \\
\hline
G & C, F \\
\hline
H & F \\
\hline
I & D, E \\
\hline
J & H, I \\
\hline
\end{array}
A directed graph that could represent this project is
Complex Numbers, EXT2 N2 2023 HSC 16a
Let \(w\) be the complex number \(z=e^{\small{\dfrac{2i \pi}{3}}} \).
- Show that \(1+w+w^2=0\). (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The vertices of a triangle can be labelled \(A, B\) and \(C\) in anticlockwise or clockwise direction, as shown.
Three complex numbers \(a, b\) and \(c\) are represented in the complex plane by points \(A, B\) and \(C\) respectively.
- Show that if triangle \(A B C\) is anticlockwise and equilateral, then \(a+b w+c w^2=0\). (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- It can be shown that if triangle \(A B C\) is clockwise and equilateral, then \(a+b w^2+c w=0\). (Do NOT prove this.)
- Show that if \(A B C\) is an equilateral triangle, then
\(a^2+b^2+c^2=a b+b c+c a .\) (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, GEN1 2023 VCAA 23 MC
Tavi took out a loan of $20 000, with interest compounding quarterly. She makes quarterly repayments of $653.65.
The graph below represents the balance in dollars of Tavi's loan at the end of each quarter of the first year of the loan.
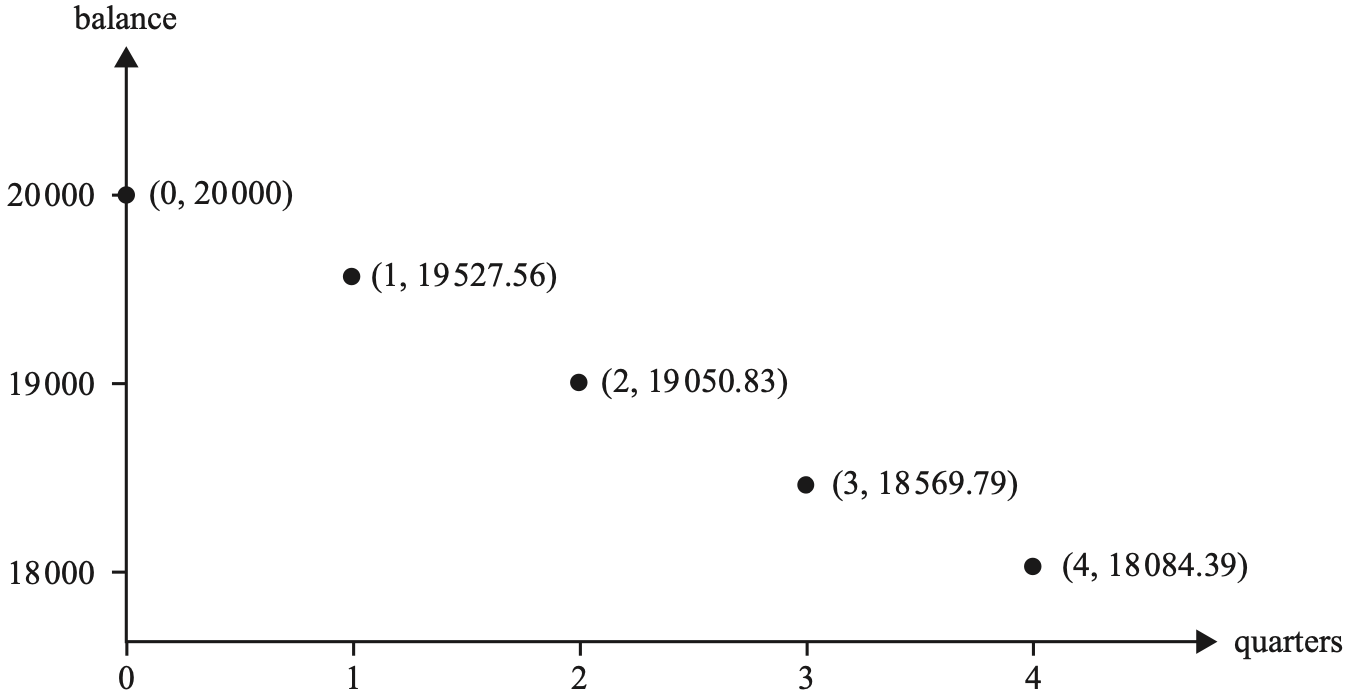
The effective interest rate for the first year of Tavi's loan is closest to
- 3.62%
- 3.65%
- 3.66%
- 3.67%
- 3.68%
PHYSICS, M2 2023 VCE 8
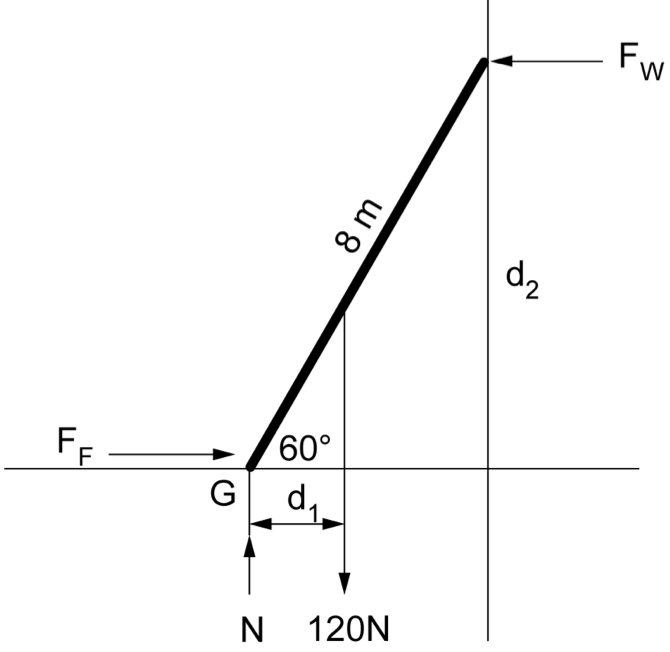
Maia is at a skatepark. She stands on her skateboard as it rolls in a straight line down a gentle slope at a constant speed of 3.0 m s\(^{-1}\), as shown in the figure below. The slope is 5° to the horizontal. The combined mass of Maia and the skateboard is 65 kg. --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Near the bottom of the ramp, Maia takes hold of a large pole and comes to a complete rest while still standing on the skateboard. Maia and the skateboard now have no momentum or kinetic energy. --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
ENGINEERING, PPT 2023 HSC 27b
A portion of a roller coaster wheel sub-assembly is shown. An exploded pictorial of the wheel sub-assembly is shown. Complete an assembled sectioned front view of the wheel sub-assembly at scale 1: 2. Apply AS 1100 drawing standards. Do NOT add dimensions. (6 marks) --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
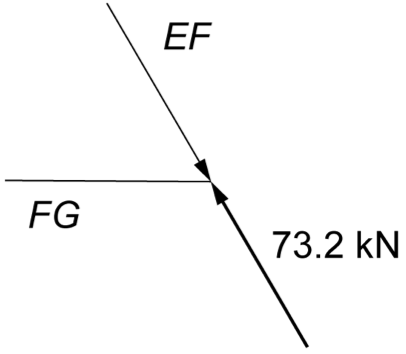
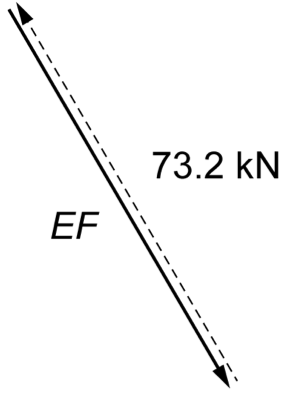
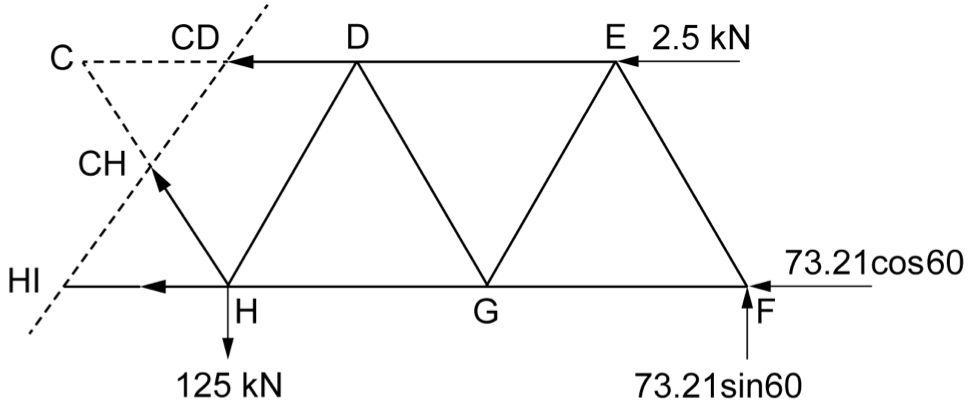
ENGINEERING, CS 2023 HSC 26c
A truss is loaded as shown.
Showing working, complete the table. (6 marks)
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \textit{Magnitude} & \textit{Nature of force}\\ & \text{(kN)} & \text{(T or C)} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{Internal reaction of member}\ EF \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & & \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{Internal reaction of member}\ CH \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & & \\
\hline
\end{array}
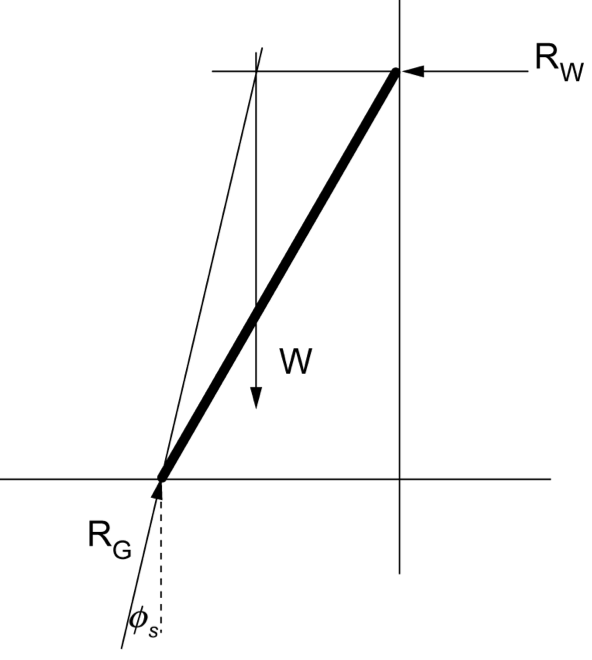
ENGINEERING, PPT 2023 HSC 25d
A uniform 8-metre ladder with a mass of 12 kg has been placed against a smooth wall. Determine the minimum coefficient of static friction between the ground and the ladder. Assume there is no friction between the ladder and the wall. (4 marks) --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
ENGINEERING, PPT 2023 HSC 24b
A roller coaster component is fabricated using cold rolled steel. Two webs are welded onto a base plate as shown. (2 marks) The diagram shows a partially completed microstructure of the parent and weld metals. Complete the microstructure by drawing and labelling the following grain types in the heat-affected zone for ONE of the webs:
BIOLOGY, M2 EQ-Bank 29
The countercurrent flow in the gills of fish allow for up to 95% of oxygen to be extracted from water.
Explain how the structure of fish gills and the countercurrent flow contribute to the efficiency of the gas exchange process. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M3 EQ-Bank 5
A 50 gram copper ball is placed into an insulated container containing 50 mL of water and immediately sealed. The initial temperature of the metal ball and water is 50°C and 10°C respectively.
A student hypothesises that since the water and copper ball both have the same mass, the temperature of the metal ball and water, once thermal equilibrium is established, would be 30°C.
When the student measured the temperature inside the container, it was 26°C.
Explain the results of the experiment and why the student's hypothesis is incorrect. (4 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M3 EQ-Bank 1
Jack enjoys drinking green tea at 60°C.
He pours 200 mL of 90°C green tea into a cup and then adds 4°C chilled water to the same cup to cool it down.
What is the minimum amount of chilled water, to the nearest mL, required to cool Jack's green tea to 60°C? (4 marks)
(Assume the green tea is essentially water and no energy is lost to the surroundings)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M1 EQ-Bank 5
Car A approaches an intersection at 10 ms\(^{-1}\) from the South as shown. As Car B approaches the intersection, it measures the velocity of Car A to be 22.36 ms\(^{-1}\) NW. Draw Car B on the diagram showing its direction and speed. Show all working. (3 marks) --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M3 2018 VCE 11
The diagram shows two speakers, \(\text{A}\) and \(\text{ B}\), facing each other. The speakers are connected to the same signal generator/amplifier and the speakers are simultaneously producing the same 340 Hz sound.
Take the speed of sound to be 340 ms\( ^{-1}\).
- Calculate the wavelength of the sound. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- A student stands in the centre, equidistant from speakers \(\text{A}\) and \(\text{B}\). He then moves towards speaker \(\text{B}\) and experiences a sequence of loud and quiet regions. He stops at the second region of quietness.
- How far has the student moved from the centre? Explain your reasoning. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M2 2014 VCE 11*
Consider the following unbalanced ionic equation.
\(\ce{Hg(l) + Cr2O7^2–(aq) + H+(aq)\rightarrow Hg^2+(aq) + Cr^3+(aq) + H2O(l)}\)
When this equation is completely balanced including the total charge on each side of the equation, find the coefficient of \(\ce{Hg(l)}\). (3 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M4 2020 VCE 18
Students are modelling the effect of the resistance of electrical cables, \(r\), on the transmission of electrical power. They model the cables using the circuit shown in Figure 18. The students investigate the effect of changing \(r\) by measuring the current in the electrical cables for a range of values. Their results are shown in Table 1 below. \begin{array} {|c|c|c|} --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{Resistance of cables,}\ r\ (\Omega) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \text{Current in cables},\ i\ (\text{A}) & \ \ \ \dfrac{1}{i} \Big{(}\text{A}^{-1}\Big{)}\ \ \ \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} 2.4 \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 2.4 & \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} 3.6 \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 2.0 & \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} 6.4 \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 1.7 & \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} 7.6 \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 1.5 & \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} 10.4 \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 1.3 & \\
\hline
\end{array}
PHYSICS, M3 2021 VCE 14
A distant fire truck travelling at 20 ms\(^{-1}\) to a fire has its siren emitting sound at a constant frequency of 500 Hz.
Chris is standing on the edge of the road. Assume that the fire truck is travelling directly towards him as it approaches and directly away from him as it goes past. The arrangement is shown in the diagram.
- On the diagram below, sketch the frequency that Chris will hear as the truck moves towards him and then moves away from him. The \(500 \text{ Hz}\) siren signal is shown as a dotted line for reference. No calculations are required. (2 marks)
- Name the physics principle involved in Chris’s experience. (1 mark)
PHYSICS, M2 2021 VCE 4
Liesel, a student of yoga, sits on the floor in the lotus pose, as shown in Figure 4. The action force, \(F_g\), on Liesel due to gravity is 500 N down.
Identify and explain what the reaction force is to the action force, \(F_{ g }\), shown in the diagram above. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M4 2022 VCE 4*
Two point charges, \(Q\) and \(4Q\), are placed 12 cm apart, as shown in the diagram below.
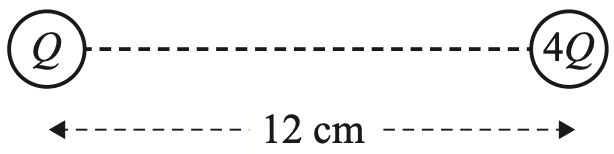
On the straight line between the charges \(Q\) and \(4Q\), find where the electric field is zero. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M1 2012 HSC 21
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Complex Numbers, EXT2 N1 2023 HSC 7 MC
Which of the following statements about complex numbers is true?
- For all real numbers \(x, y, \theta\) with \(x \neq 0\),
\(\tan \theta=\dfrac{y}{x} \ \Rightarrow \ x+i y=r e^{i \theta}\), for some real number \(r\).
- For all non-zero complex numbers \(z_1\) and \(z_2\),
\(\operatorname{Arg}\left(z_1\right)=\theta_1\) and \(\operatorname{Arg}\left(z_2\right)=\theta_2 \ \Rightarrow \ \operatorname{Arg}\left(z_1 z_2\right)=\theta_1+\theta_2,\)
where \(\operatorname{Arg}\) denotes the principal argument.
- For all real numbers \(r_1, r_2, \theta_1, \theta_2\) with \(r_1, r_2>0\),
\(r_1 e^{i \theta_1}=r_2 e^{i \theta_2} \ \Rightarrow \ r_1=r_2\) and \(\theta_1=\theta_2 \text {. }\)
- For all real numbers \(x, y, r, \theta\) with \(r>0\) and \(x \neq 0\),
\(x+i y=r e^{i \theta} \ \Rightarrow \ \theta=\arctan \Big(\dfrac{y}{x} \Big)\)
PHYSICS, M4 2017 HSC 8 MC
An electron is fired in a vacuum towards a screen. With no electric field being applied, the electron hits the screen at \(P\). A uniform electric field is turned on and another electron is fired towards the screen from the same location, at the same velocity, striking the screen at point \(Q\).
With the electric field still turned on, a proton is fired towards the screen from the same starting point as the electrons and with the same velocity.
At what point does the proton strike the screen?
- \(A\)
- \(B\)
- \(C\)
- \(D\)
CHEMISTRY, M8 2023 HSC 36
An organic reaction pathway involving compounds \(\text{A, B,}\) and \(\text{C}\) is shown in the flow chart.
The molar mass of \(\text{A}\) is 84.156 g mol\(^{-1}\).
A chemist obtained some spectral data for the compounds as shown.
| \( \text{Data from} \ ^{1} \text{H NMR spectrum of compound C} \) | ||
| \( Chemical \ Shift \ \text{(ppm)} \) | \( Relative \ peak \ area \) | \( Splitting \ pattern \) |
| \(1.01\) | \(3\) | \(\text{Triplet}\) |
| \(1.05\) | \(3\) | \(\text{Triplet}\) |
| \(1.65\) | \(2\) | \(\text{Multiplet}\) |
| \(2.42\) | \(2\) | \(\text{Triplet}\) |
| \(2.46\) | \(2\) | \(\text{Quartet}\) |
| \( ^{1} \text{H NMR chemical shift data}\) | |
| \( Type \ of \ proton \) | \( \text{δ/ppm} \) |
| \( \ce{R - C\textbf{H}3,R - C\textbf{H}2 - R}\) | \(0.7-1.7\) |
| \( \left.\begin{array}{l}\ce{\textbf{H}3C - CO - \\-C\textbf{H}2 - CO -}\end{array}\right\} \begin{aligned} & \text { (aldehydes, ketones,} \\ &\text{carboxylic acids or esters) }\end{aligned}\) | \(2.0-2.6\) |
| \( \ce{R - C\textbf{H}O} \) | \(9.4-10.00\) |
| \( \ce{R - COO\textbf{H}} \) | \(9.0-13.0\) |
Identify the functional group present in each of compounds \(\text{A}\) to \(\text{C}\) and draw the structure of each compound. Justify your answer with reference to the information provided. (9 marks)
--- 28 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M8 2023 HSC 20 MC
In 1995 , observational evidence showed that Hubble's description of the expansion of the universe was inaccurate.
It was discovered that the expansion of the universe was accelerating. This discovery was based on observations of light from galaxies whose distances from Earth could be accurately measured, and were significantly more distant than any observed by Hubble.
Which graph relating velocities of galaxies to their distances from Earth is consistent with an accelerating rate of expansion of the universe?
PHYSICS, M8 2023 HSC 33
Consider the following statement.
The interaction of subatomic particles with fields, as well as with other types of particles and matter, has increased our understanding of processes that occur in the physical world and of the properties of the subatomic particles themselves.
Justify this statement with reference to observations that have been made and experiments that scientists have carried out. (9 marks)
--- 22 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 2023 HSC 37
When performing industrial reductions with \(\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})\), the following equilibrium is of great importance.
\( \ce{2CO(g) \rightleftharpoons CO2(g) + C(s) \quad \quad $K$_{e q} = 10.00 at 1095 K } \)
A 1.00 L sealed vessel at a temperature of 1095 K contains \( \ce{CO(g)} \) at a concentration of 1.10 × 10\(^{-2}\) mol L\(^{-1}\), \(\ce{CO2(g)} \) at a concentration of 1.21 × 10\(^{-3}\) mol L\(^{-1}\), and excess solid carbon.
- Is the system at equilibrium? Support your answer with calculations. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
-
Carbon dioxide gas is added to the system above and the mixture comes to equilibrium. The equilibrium concentrations of \( \ce{CO(g)}\) and \(\ce{CO2(g)} \) are equal. Excess solid carbon is present and the temperature remains at 1095 K.
Calculate the amount (in mol) of carbon dioxide added to the system. (3 marks)
--- 14 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M5 2023 HSC 32
A horizontal disc rotates at 3 revolutions per second around its centre, with the top of the disc at ground level.
At 2 m from the centre of the disc, a ball is held in place at ground level on the top of the disc by a spring-loaded projectile launcher. At position \(X\), the launcher fires the ball vertically upward with a velocity of 5.72 m s\(^{-1}\).
Calculate the ball's position relative to the launcher's new position, at the instant the ball hits the ground. (7 marks)
--- 14 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M6 2023 HSC 31
A roller coaster uses a braking system represented by the diagrams. When the roller coaster car reaches the end of the ride, the two rows of permanent magnets on the car pass on either side of a thick aluminium conductor called a braking fin. The graph shows the acceleration of the roller coaster reaching the braking fin at two different speeds. Explain the similarities and differences between these two sets of data. (5 marks) --- 15 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M7 2023 HSC 6 MC
Liver fluke is a disease caused by parasites that infect grazing animals, including sheep. The life cycle of the liver fluke is shown.
How could the transmission of this disease to humans be prevented?
- Eradicating the snails
- Administering antibiotics to sheep
- Wearing gloves when handling sheep
- Regularly spraying fields with herbicides
Vectors, EXT2 V1 2023 HSC 15c
A curve \( \mathcal{C}\) spirals 3 times around the sphere centred at the origin and with radius 3, as shown.
A particle is initially at the point \((0,0,-3)\) and moves along the curve \(\mathcal{C}\) on the surface of the sphere, ending at the point \((0,0,3)\).
By using the diagram below, which shows the graphs of the functions \(f(x)=\cos (\pi x)\) and \(g(x)=\sqrt{9-x^2}\), and considering the graph \(y=f(x)g(x)\), give a possible set of parametric equations that describe the curve \( \mathcal{C}\). (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD1 M5 2023 HSC 31
Measurement, STD1 M3 2023 HSC 29
The diagram shows the location of three places \(X\), \(Y\) and \(C\).
\(Y\) is on a bearing of 120° and 15 km from \(X\).
\(C\) is 40 km from \(X\) and lies due west of \(Y\).
\(P\) lies on the line joining \(C\) and \(Y\) and is due south of \(X\).
- Find the distance from \(X\) to \(P\). (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the bearing of \(C\) from \(X\), to the nearest degree? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Vectors, EXT1 V1 2023 HSC 14c
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- The point \(P\) lies on the circle centred at \(I(r, 0)\) with radius \(r>0\), such that \(\overrightarrow{I P}\) makes an angle of \(t\) to the horizontal. The point \(Q\) lies on the circle centred at \(J(-R, 0)\) with radius \(R>0\), such that \(\overrightarrow{J Q}\) makes an angle of \(2 t\) to the horizontal. --- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Combinatorics, EXT1 A1 2023 HSC 10 MC
A group with 5 students and 3 teachers is to be arranged in a circle.
In how many ways can this be done if no more than 2 students can sit together?
- \(4 ! \times 3!\)
- \(5 ! \times 3!\)
- \(2 ! \times 5 ! \times 3!\)
- \(2 ! \times 2 ! \times 2 ! \times 3!\)
Functions, EXT1 F2 2023 HSC 14b
Consider the hyperbola \(y=\dfrac{1}{x}\) and the circle \((x-c)^2+y^2=c^2\), where \(c\) is a constant. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1 C3 2023 HSC 13a
A hemispherical water tank has radius \(R\) cm. The tank has a hole at the bottom which allows water to drain out. Initially the tank is empty. Water is poured into the tank at a constant rate of \(2 k R\) cm³ s\(^{-1}\), where \(k\) is a positive constant. After \(t\) seconds, the height of the water in the tank is \(h\) cm, as shown in the diagram, and the volume of water in the tank is \(V\) cm³. It is known that \(V= \pi \Big{(} R h^2-\dfrac{h^3}{3}\Big{)}. \) (Do NOT prove this.) While water flows into the tank and also drains out of the bottom, the rate of change of the volume of water in the tank is given by \(\dfrac{d V}{d t}=k(2 R-h)\). --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, STD1 S1 2023 HSC 20
Consider the following dataset.
22, 27, 29, 32, 36, 37, 39, 45, 47, 58
Is 58 an outlier in this dataset? Justify your answer with working. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD1 N1 2023 HSC 18
A network of running tracks connects the points \(A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H\), as shown. The number on each edge represents the time, in minutes, that a typical runner should take to run along each track. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, STD1 S1 2023 HSC 13
Statistics, STD1 S1 2023 HSC 11
A company employs 50 people. The annual income of the employees is shown in the grouped frequency distribution table. \begin{array} {|c|c|c|c|} --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\hline
\textit{Annual income} & \textit{Class centre} & \textit{Number of} & fx \\ \text{(\$)} & (x) & \textit{employees}\ (f) & \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{40 000 – 49 999} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 45\ 000 & 12 & 540\ 000 \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{50 000 – 59 999} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 55\ 000 & 13 & 715\ 000 \\
\hline\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{60 000 – 69 999} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 65\ 000 & 15 & A \\
\hline\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{70 000 – 79 999} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 75\ 000 & 7 & 525\ 000 \\
\hline\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{80 000 – 89 999} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 85\ 000 & 3 & 255\ 000 \\
\hline
\hline\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & & \textit{Total}\ = 50 & \textit{Total = B} \\
\hline
\end{array}
Financial Maths, STD1 F1 2023 HSC 7 MC
An item was purchased for a price of \($880\), including \(10\%\) GST.
What is the amount of GST included in the price?
- \($8.00\)
- \($8.80\)
- \($80.00\)
- \($88.00\)
Functions, 2ADV F1 2023 HSC 10 MC
The graph \(y = x^2\) meets the line \(y = k\) (where \(k>0\)) at points \(P\) and \(Q\) as shown in the diagram. The length of the interval \(PQ\) is \(L\).
Let \(a\) be a positive number. The graph \(y=\dfrac{x^2}{a^2}\) meets the line \(y=k\) at points \(S\) and \(T\).
What is the length of \(ST\)?
- \(\dfrac{L}{a}\)
- \(\dfrac{L}{a^2}\)
- \(aL\)
- \(a^2L\)
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2023 HSC 32
The curves \(y=e^{-2 x}\) and \(y=e^{-x}-\dfrac{1}{4}\) intersect at exactly one point as shown in the diagram. The point of intersection has coordinates \(\left(\ln 2, \dfrac{1}{4}\right)\). (Do NOT prove this.) --- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, 2ADV S1 2023 HSC 31
Four Year 12 students want to organise a graduation party. All four students have the same probability, \(P(F)\), of being available next Friday. All four students have the same probability, \(P(S)\), of being available next Saturday. It is given that \(P(F)=\dfrac{3}{10}, P(S\mid F)=\dfrac{1}{3}\), and \(P(F\mid S)=\dfrac{1}{8}\). Kim is one of the four students. --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, 2ADV S3 2023 HSC 29
A continuous random variable \(X\) has probability density function \(f(x)\) given by \(f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl} 12 x^2(1-x), & \text { for } 0 \leq x \leq 1 \\ 0, & \text { for all other values of } x \end{array}\right.\) --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, 2ADV F2 2023 HSC 27
The graph of \(y=f(x)\), where \(f(x)=a|x-b|+c\), passes through the points \((3,-5), (6,7)\) and \((9,-5)\) as shown in the diagram. --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, 2ADV F1 2023 HSC 9 MC
Let \(f(x)\) be any function with domain all real numbers.
Which of the following is an even function, regardless of the choice of \(f(x)\)?
- \(2 f(x)\)
- \(f(f(x))\)
- \((f(-x))^2\)
- \(f(x) f(-x)\)
Statistics, STD2 S4 2023 HSC 34
A university uses gas to heat its buildings. Over a period of 10 weekdays during winter, the gas used each day was measured in megawatts (MW) and the average outside temperature each day was recorded in degrees Celsius (°C). Using `x` as the average daily outside temperature and `y` as the total daily gas usage, the equation of the least-squares regression line was found. The equation of the regression line predicts that when the temperature is 0°C, the daily gas usage is 236 MW. The ten temperatures measured were: 0°, 0°, 0°, 2°, 5°, 7°, 8°, 9°, 9°, 10°, The total gas usage for the ten weekdays was 1840 MW. In any bivariate dataset, the least-squares regression line passes through the point `(bar x,bar y)`, where `bar x` is the sample mean of the `x`-values and `bary` is the sample mean of the `y`-values. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, STD2 F4 2023 HSC 29
The table shows monthly repayments for each $1000 borrowed.
- A couple borrows $520 000 to buy a house at 8% per annum over 25 years.
- How much does the couple repay in total for this loan? (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Chris borrows some money at 7% per annum. Chris will repay the loan over 15 years, paying $3596 per month.
- How much money does Chris borrow? (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD2 M1 2023 HSC 9 MC
The length and width of a rectangle are measured to be 8 cm and 5 cm respectively, to the nearest centimetre.
What are the lower and upper bounds for the area of the rectangle?
- `text{28 cm}^2\ text{and 54 cm}^2`
- `text{36 cm}^2\ text{and 42 cm}^2`
- `text{38.25 cm}^2\ text{and 41.25 cm}^2`
- `text{33.75 cm}^2\ text{and 46.75 cm}^2`
BIOLOGY, M1 2014 HSC 19 MC
What is the best explanation for the fish surviving gradual temperature change but not a rapid temperature change?
- It takes time for each gene to be expressed.
- Enzyme activity is decreased at low temperatures.
- The fish produce different enzymes at different temperatures.
- Some enzymes will not denature if the temperature change is gradual.
BIOLOGY, M2 2015 HSC 36e
'Science has been used to solve problems in the investigation of photosynthesis, and so has provided information of benefit to society.'
Justify this statement with reference to the scientific knowledge behind radioactive tracers for the study of photosynthesis. (7 marks)
--- 20 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M2 2018 HSC 18 MC
The micrograph shows normal-sized human red blood cells.
Within three of these red blood cells, an infection known as Plasmodium falciparum appears under the microscope view as a dark ring shape.
Which of the following is the best estimate of the diameter of the Plasmodium?
- \(0.002\ \text{mm}\)
- \(0.8\ \mu \text{m}\)
- \(2\ \text{mm}\)
- \(8\ \mu \text{m}\)
BIOLOGY, M1 2015 HSC 18 MC
Students conducted a large first-hand investigation into enzyme activity.
The aim in the report is shown.
Aim: To determine the optimum pH of four different enzymes.
How many independent variables were in this first-hand investigation?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 5
BIOLOGY, M1 2017 HSC 36e
Analyse the impact of the development of the electron microscope on the understanding of chloroplast structure and function. (7 marks)
--- 14 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- …
- 28
- Next Page »