Identify the TWO types of nucleon and state ONE difference between them. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Aussie Maths & Science Teachers: Save your time with SmarterEd
Identify the TWO types of nucleon and state ONE difference between them. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. Cornea and lens
ii. Differences in visual perception at `A` and `B`.
i. Cornea and lens
ii. Differences in visual perception at `A` and `B`.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Vasoconstriction and shivering.
b. Body temperature maintenance in endotherms:
a. Vasoconstriction and shivering.
b. Body temperature maintenance in endotherms:
A zebronkey hybrid is the result of crossing a male zebra which has 44 chromosomes with a female donkey which has 62 chromosomes.
How many chromosomes will the zebronkey have?
`A`
`=>A`
What is the probability of producing a tall pea plant when a heterozygous tall pea plant is crossed with a homozygous short pea plant?
`B`
`=>B`
Which waste product does renal dialysis remove?
`A`
`=>A`
What name is given to the process whereby a white blood cell engulfs a microorganism?
`C`
`=>C`
What is the role of lymphocytes in the body?
`A`
`=>A`
Which row of the table correctly matches the polymer with its structural feature and property?
`A`
`=>A`
Students conducted preliminary experiments across different species to analyse their DNA base composition.
The table shows the experimental data collected.
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{Species} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \textit{% Adenine} & \textit{% Guanine} \\
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{A} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& 38 & 12 \\
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{B} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& 26 & 22 \\
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{C} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& 8 & 40 \\
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{D} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& 20 & 32 \\
\hline \rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{E} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& 33 & 18 \\
\hline
\end{array}
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a.
b. As % Adenine increases, the % Guanine decreases.
c. Explanation of data relationship:
a.
b. As % Adenine increases, the % Guanine decreases.
c. Explanation of data relationship:
Name an infectious disease and explain how ONE host response is a defence adaptation. (3 marks)
Exemplar solution:
Which row of the table correctly matches the reaction type with the reactant(s), catalyst and product(s)?
`D`
`=>D`
Which diagram represents ionisation of a weak acid?

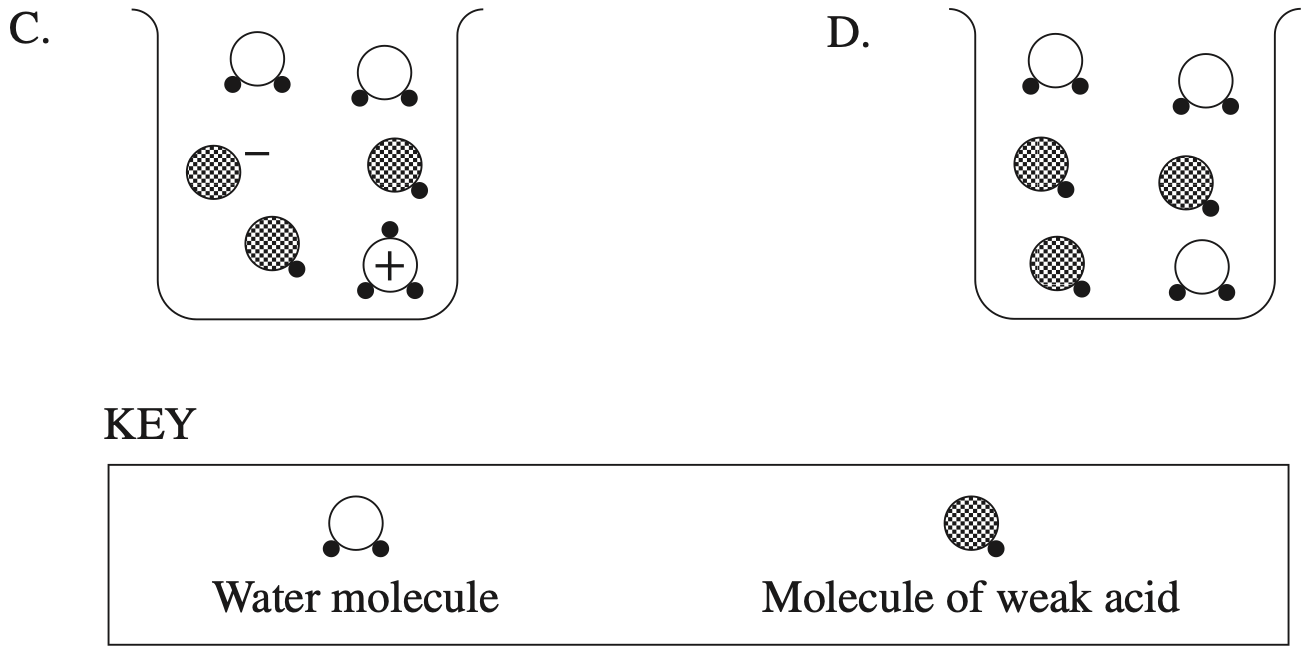
`C`
`=>C`
A camp stove using butane as a fuel was used to heat a pot of water inside a small tent. Poisonous carbon monoxide `(text{CO})` gas can be released from these stoves.
An investigation was carried out to determine the carbon monoxide concentration in the tent when the clearance height of the pot above the flame was altered. The results are shown in the table.
\begin{array} {|l|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \text{Clearance height (mm)} & 35 & 40 & 45 & 50 \\
\hline \text{CO concentration (ppm)} & 120 & 87 & 50 & 18\\
\hline \end{array}
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\begin{array} {|l|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \text{Clearance height (mm)} & 35 & 40 & 45 & 50 \\
\hline \text{Efficiency (%)} & 90 & 70 & 50 & 30\\
\hline \end{array}
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
b. From the graph, the minimum height above the flame is 48 mm.
c. Highest temperature of water:
| `q` | `=mC DeltaT` | |
| `297\ 000` | `=1.0 xx 4.18 xx 10^3 xx Delta T` | |
| `Delta T` | `=(297\ 000)/(4.18 xx 10^3)=71.1°text{C}` |
`:.` Highest temperature of water = 20.0 + 71.1 = 91.1°C
Ethylene can be readily transformed into many useful products.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Cracking
b. Vinyl chloride:
Polyvinyl chloride:
a. Cracking
b. Vinyl chloride:
Polyvinyl chloride:
The following plants were presented to a quarantine office in Australia as part of a shipment of plants entering Australia for the plant nursery trade.

Which of the following is a decision that the quarantine office is likely to make?
`D`
`=>D`
The image shows a laminated veneer lumber (LVL) beam that is used to span long distances in buildings.
Give reasons for using LVL instead of a steel beam as the supporting member in a building. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Possible reasons include:
Possible reasons include:
A mixture of carbon monoxide, chlorine and phosgene \(\ce{(COCl_2)}\) gases was placed in a closed container. The concentrations of the gases were monitored over time.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. At two minutes (where the concentrations stop changing)
b. \(\ce{CO(g) + Cl2(g) \rightleftharpoons COCl2(g)}\)
a. At two minutes (where the concentrations stop changing)
b. \(\ce{CO(g) + Cl2(g) \rightleftharpoons COCl2(g)}\)
This apparatus was set up to produce methyl butanoate.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Flame could ignite one of reagents which is flammable.
b.
c. Esterification is a relatively slow reaction.
a. Flame could ignite one of reagents which is flammable.
b.
c. Esterification is a relatively slow reaction.
A polymer has the following structure.
Which of the following represents the monomer from which this polymer can be produced?
`D`
`=>D`
What is the name of this compound?
`D`
`=>D`
It is appropriate to produce a half development of a transition piece when the piece
`B`
`=>B`
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Methodology:
b. Testing a natural indicator:
a. Methodology:
b. Testing a natural indicator:
Question 18
How could the reliability of the analysis of the pond water be improved?
Question 19
What was the concentration of lead ions in the sample?
`18. A`
`19. C`
Question 18
`=>A`
Question 19
\[\ce{n(PbCl2) = \frac{0.13}{207.2 + 2 \times 35.45} = \frac{0.13}{278.1} = 4.67 \times 10^{-4} mol}\]
\(\ce{n(Pb^2+) = n(PbCl2) = 4.67 \times 10^{-4} mol}\)
\[\ce{[Pb^2+] = \frac{4.67 \times 10^{-4}}{0.050} = 9.3 \times 10^{-3} mol L^{-1}}\]
`=>C`
A group of students wanted to test whether water purifying tablets were effective in making creek water free from bacteria.
They conducted an experiment using a water sample collected from the creek and found that the tablets were effective.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Refer to the following information to answer Questions 19 and 20 .
The intestinal tract of a human foetus is sterile.
After birth, microflora from the mother are transferred to the baby's mouth through close contact. After a year, the microflora of the baby is similar to the mother's, with the baby's immune system ignoring these microbes.
Also during the first year of life, breast milk from the mother provides antibodies to the baby for any disease the mother has already experienced. When breastfeeding ceases, these antibody levels in the baby start to fall.
After the first year, any new species of invading bacteria is treated as a pathogen by the baby's immune system.
Question 19
A medical consequence for six-month-old babies that have only been bottle-fed with formula milk and not breastfed is that
Question 20
Strict hygiene practices are followed in the care of newborns, whereas hygiene practices in the care of older babies are less emphasised.
Which of the following is the best reason for this difference?
Question 19: `D`
Question 20: `B`
Question 19
`=>D`
Question 20
`=>B`
The table shows the base triplets in mRNA for amino acids.
From the table, the amino acid Serine (Ser) can be coded for by the base triplet UCG.
Which base triplet could code for the amino acid Tyrosine (Tyr)?
`D`
`=>D`
Refer to the following information to answer Questions 12 and 13.
Question 12
Which reason best explains why the corresponding control measure reduces this problem?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\textbf{}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\textbf{}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\textbf{}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{Control measure}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \textit{Reason} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Release of infertile flies}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&\text{Infertile flies do not eat the fruit}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Release of infertile flies}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{The number of flies in the next}\\
\text{}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{generation is decreased}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Boiling fruit and feeding to}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{Chickens are unaffected by the} \\
\text{chickens}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{damaged fruit} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{Boiling fruit and feeding to}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{The amount of waste for landfill is} \\
\text{chickens}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{reduced} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
Question 13
The following measures could be used to prevent the spread of this fruit fly across Australia.
To prevent the spread of this fruit fly across Australia, which combination of measures would be most practical to use?
Question 12: \(B\)
Question 13: \(D\)
Question 12
\(\Rightarrow B\)
Question 13
\(\Rightarrow D\)
Environment can affect phenotype by altering the sequence of bases in DNA.
Which of the following is an example of this?
`D`
`=>D`
Refer to the following information to answer Questions 7 and 8 .
The diagram shows a homeostatic mechanism in a mammal.
Question 7
What does `text{X}` represent in the diagram?
Question 8
Which of the following describes what happens to the muscles and the arteriole walls in the skin when the core body temperature is below normal?
Q7. `B`
Q8. `B`
Q7. `text{X}` = the brain
`=>B`
Q8. When body temperature is below normal:
`=>B`
Which adaptation would decrease water loss from a plant in a region with low rainfall?
`C`
`=>C`
Atomic absorption spectroscopy was used to determine the concentration of zinc in a water sample. The absorbance of a series of standard solutions of known concentration of zinc was measured. The results are shown in the table.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
What are alternative forms of genes called?
`A`
By Elimination:
`=>A`
The oxides `\text{CaO}, \text{CO}_2, \text{Na}_2\text{O}` and `\text{N}_2\text{O}_4` are placed in water to form four separate solutions.
Which row of the table correctly indicates the solutions with pH less than 7 and the solutions with pH greater than 7?
`A`
`=>A`
What flame colour do copper ions produce when heated?
`B`
`=>B`
Which type of glassware is used in a titration to deliver an accurate volume of a solution to a known volume of another solution?
`D`
`=>D`
The following equipment was set up to measure the heat of combustion of an alkanol.
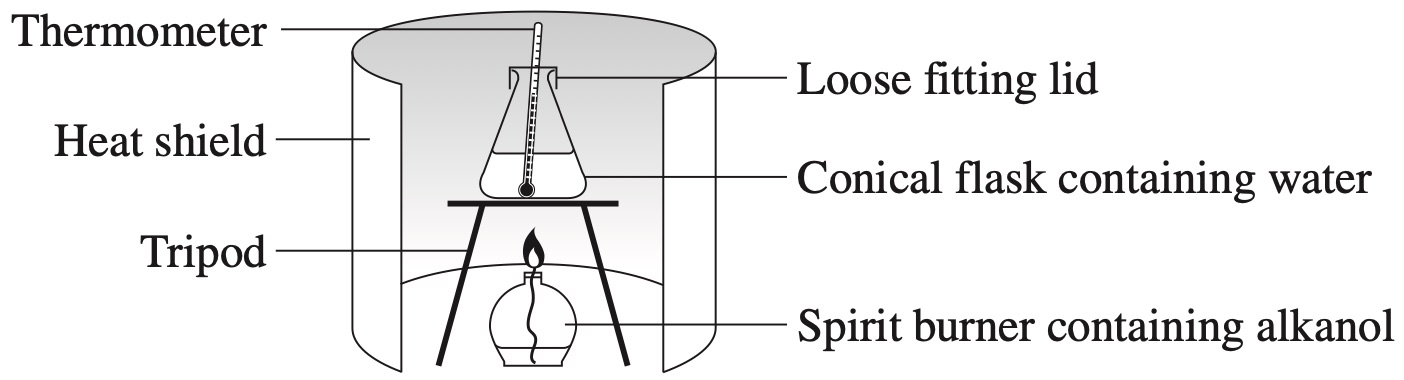
Black deposits were observed on the bottom of the conical flask and the heat of combustion measured was lower than the theoretical value.
Which of the following equations could account for these observations?
`D`
The black deposit is carbon (soot).
By Elimination:
A: Ethane is not an alkanol (eliminate A).
B: No soot is formed in this reaction (eliminate B).
C: This reaction is incorrect as no hydrogen gas is produced (eliminate C).
`=>D`
Esterification can be carried out in a school laboratory using the equipment shown.
How could the safety of the process shown be improved?
`D`
By elimination
A: Resulting pressure build up is dangerous (incorrect)
B: Adds to the catalytic effect but not a safety reduction measure (incorrect)
C: Direction is optimal as water flow is coolest where vapours are hottest (incorrect)
D: Heating mantle reduces the chance of vapours igniting (correct)
`=>D`
`D`
Consider each option:
`=>D`
A projectile is launched from a cliff top. The dots show the position of the projectile at equal time intervals.
Assuming negligible air resistance, which diagram best shows the path of the projectile?
`D`
`=>D`
When an alternating current is passed through coil `A`, a voltage is observed on the oscilloscope connected to coil `B`.
How could a bar magnet be used, instead of coil A, to produce a similar pattern on the oscilloscope? (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Answers could include one of the following:
Answers could include one of the following:
Which movement of the magnet(s) will produce the greatest deflection of the galvanometer?
`D`
`=>D`
The diagram shows two parallel charged plates `5 × 10^(-3) text{m}` apart.
What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates in `text{V m}^(-1)` ?
`D`
`E=(V)/(d)=(15)/(0.005)=3000\ text{V m}^(-1)`
`=>D`
Some mobile phones are recharged at a power point using a charger that contains a transformer.
What is the purpose of the transformer?
`D`
`=>D`
The escape velocity from a planet is given by `v = sqrt((2GM)/(r))`.
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `v=5010 text{m s}^(-1)`
b. Applying the law of conservation of energy:
| `KE_(i)+U_(i)` | `=0` | |
| `(1)/(2)mv^(2)-(GMm)/(r)` | `=0` | |
| `mv^(2)` | `=(2GMm)/(r)` | |
| `∴ v_(esc)` | `=sqrt((2GM)/(r))` |
| a. | `v` | `=sqrt((2xx6.67 xx10^(-11)xx6.39 xx10^(23))/(3.39 xx10^(6)))` |
| `=5014.5 text{m s}^(-1)` | ||
| `=5015 text{m s}^(-1)\ \ text{(to 0 d.p.)}` |
b. Applying the law of conservation of energy:
| `KE_(i)+U_(i)` | `=0` | |
| `(1)/(2)mv^(2)-(GMm)/(r)` | `=0` | |
| `mv^(2)` | `=(2GMm)/(r)` | |
| `∴ v_(esc)` | `=sqrt((2GM)/(r))` |
A satellite orbits Earth with an elliptical orbit that passes through positions `X` and `Y`.
Which row of the table correctly identifies the position at which the satellite has greater kinetic energy and the position at which it has greater potential energy?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{} & \textit{} \\
\textit{}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \textit{} \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{Greater} & \textit{Greater} \\
\quad \textit{kinetic energy}\quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \quad \textit{potential energy} \quad \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}X\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}&X\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}X\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& Y\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}Y\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& X \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}Y\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& Y \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
`B`
`=>B`
Which of the following is an inertial frame of reference?
`B`
`=>B`
The radius of the moon is 1740 km. The moon's mass is `7.35 × 10^(22)` kg. In this question, ignore the moon's rotational and orbital motion.
A 20 kg mass is launched vertically from the moon's surface at a velocity of `1200 \ text{m s}^(-1)`.
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Proof (See Worked Solutions)
b. `424 text{m s}^-1`
| a. | `U_(i)` | `=-(GMm)/(r)` |
| `=(-6.67 xx10^(-11)xx7.35 xx10^(22)xx20)/(1.74 xx10^(6))` | ||
| `=-5.64 xx10^(7)\ text{J}` | ||
| `U_(f)` | `=(-6.67 xx10^(-11)xx7.35 xx10^(22)xx20)/(2.24 xx10^(6))` | |
| `=-4.38 xx10^(7)\ text{J}` |
`:.Delta U=U_(f)-U_(i)=1.26 xx10^(7)\ text{J}`
b. `KE_(i)=(1)/(2)m u^(2)=(1)/(2)xx20 xx1200^(2)=1.44 xx10^(7) text{J}`
`KE_(f)=KE_(i)-DeltaE_(p)\ \ text{(by LCE)}=1.44 xx10^(7)-1.26 xx10^(7)=1.8 xx10^(6) text{J}`
| `(1)/(2)mv^(2)` | `=1.8 xx10^(6)` | |
| `v^2` | `=(2xx1.8 xx10^(6))/(20)` | |
| `:.v` | `=sqrt((2xx1.8 xx10^(6))/(20))= 424 text{m s}^-1` |
Contemporary aircraft construction includes the use of alloys and composite materials.
Which of the following statements is NOT true for composite materials used in aircraft?
`D`
`=>D`
The table below shows the distances, in kilometres, between a number of towns.
Each number from 1 to 30 is written on a separate card. The 30 cards are shuffled. A game is played where one of these cards is selected at random. Each card is equally likely to be selected.
Ezra is playing the game, and wins if the card selected shows an odd number between 20 and 30.
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `21, 23, 25, 27, 29`
| b. | `Ptext{(not win)}` | `=1-Ptext{(win)}` |
| `=1-5/30` | ||
| `=25/30` | ||
| `=5/6` |
Yeast is a single-celled fungus that can reproduce by budding.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Asexual.
b. Steps of procedure:
a. Asexual.
b. Steps of procedure:
The floor plan of a home unit has been drawn to scale.
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `5`
b. `text{Conversion: 1000 mm = 1 metre}`
`text{Calculate area by splitting into 2 rectangles}`
| `text{Area}` | `= 5.5 × 5 + (4.5 +2.5) xx 4` | |
| `= 55.5\ text{m²}` |
A water tank holds 6000 litres when full.
The tank is full when water starts to flow out of it at a constant rate of 3 litres per minute until the tank is empty.
Which expression represents the volume (`V` litres) of water in the tank after `t` minutes?
`A`
`text{When}\ \ t=0, \ V=6000-0 xx 3 =6000`
`text{When}\ \ t=1, \ V=6000-1 xx 3 =5997`
`vdots`
`text{After}\ t\ text{minutes}, \ V=6000-t xx 3 =6000-3t`
`=> A`
A direction field is to be drawn for the differential equation
`(dy)/(dx)=(x-2y)/(x^(2)+y^(2)). `
On the diagram, clearly draw the correct slopes of the direction field at the points `P, Q` and `R`. (2 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
`text{At (–1, 1):}\ \ dy/dx=(-1-2)/(1+1)=-3/2`
`text{At (1, 1):}\ \ dy/dx=(1-2)/(1+1)=-1/2`
`text{At (2, 1):}\ \ dy/dx=(2-2)/(4+1)=0`
Let `J_(n)=int_(0)^(1)x^(n)e^(-x)\ dx`, where "n" is a non-negative integer.
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
| i. | `J_0` | `=int_0^1 e^(-x)\ dx` |
| `=[-e^(-x)]_0^1` | ||
| `=-e^(-1)+1` | ||
| `=1-1/e` |
ii. `text{Show}\ \ J_n<=1/(n+1)`
`text{Note:}\ e^(-x)<1\ \ text{for}\ \ x in [0,1]`
| `J_n` | `=int_0^1 x^n e^(-x)\ dx` | |
| `leq int_0^1 x^n \ dx` | ||
| `leq 1/(n+1)[x^(n+1)]_0^1` | ||
| `leq 1/(n+1)(1^(n+1)-0)` | ||
| `leq 1/(n+1)\ \ text{… as required}` |
iii. `text{Show}\ \ J_n=nJ_(n-1)-1/e`
| `u` | `=x^n` | `v′` | `=e^(-x)` |
| `u′` | `=nx^(n-1)` | `v` | `=-e^(-x)` |
| `J_n` | `=[-x^n * e^(-x)]_0^1-int_0^1 nx^(n-1)*-e^(-x)\ dx` | |
| `=(-1^n * e^(-1)+0^n e^0)+nint_0^1 x^(n-1)*e^(-x)\ dx` | ||
| `=nJ_(n-1)-1/e` |
iv. `text{Prove}\ \ J_(n)=n!-(n!)/(e)sum_(r=0)^(n)(1)/(r!)\ \ text{for}\ \ n >= 0`
`text{If}\ \ n=0:`
`text{LHS} = 1-1/e\ \ text{(see part (i))}`
`text{RHS} = 0!-0!/e (1/(0!)) = 1-1/e(1)=\ text{LHS}`
`:.\ text{True for}\ \ n=0.`
`text{Assume true for}\ \ n=k:`
`J_(k)=k!-(k!)/(e)sum_(r=0)^(k)(1)/(r!)`
`text{Prove true for}\ \ n=k+1:`
`text{i.e.}\ \ J_(k+1)=(k+1)!-((k+1!))/(e)sum_(r=0)^(k+1)(1)/(r!)`
| `J_(k+1)` | `=(k+1)J_k-1/e\ \ text{(using part (iii))}` | |
| `=(k+1)(k!-(k!)/(e)sum_(r=0)^(k)(1)/(r!))-1/e` | ||
| `=(k+1)!-((k+1)!)/(e)sum_(r=0)^(k)(1)/(r!)-1/e xx ((k+1)!)/((k+1)!)` | ||
| `=(k+1)!-((k+1)!)/e(\ sum_(\ r=0)^(k)(1)/(r!)+1/((k+1)!))` | ||
| `=(k+1)!-((k+1)!)/e(\ sum_(\ r=0)^(k+1)(1)/(r!))` |
`=>\ text{True for}\ \ n=k+1`
`:.\ text{S}text{ince true for}\ n=1,\ text{by PMI, true for integers}\ n>=1`
v. `0<=J_n<= 1/(n+1)\ \ \ text{(part (ii))}`
`lim_(n->oo) 1/(n+1)=0\ \ => \ lim_(n->oo) J_n=0`
`text{Using part (iv):}`
| `J_n/(n!)` | `=1-1/e sum_(r=0)^(n)(1)/(r!)` | |
| `1/e sum_(r=0)^(n)(1)/(r!)` | `=1-J_n/(n!)` | |
| `sum_(r=0)^(n)(1)/(r!)` | `=e-(eJ_n)/(n!)` | |
| `lim_(n->oo)(\ sum_(\ r=0)^(n)(1)/(r!))` | `=lim_(n->oo)(e-(eJ_n)/(n!))` | |
| `=e-0` | ||
| `=e` |
The following DNA base sequence is used to code for a sequence of four amino acids.
`text{CGC ATC ATG CTA}`
Which of the following correctly represents the anticodons on the transfer RNA during synthesis of this string of amino acids?
`B` or `A`
By Elimination:
`=>B`
*Note: `A` also considered an acceptable answer due to confusion as to whether the segment above was DNA or RNA.
The following apparatus was used in an experiment to determine the molar enthalpy of combustion of ethanol.
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. `-628\ text{kJ mol}^(-1)`
b. Improvement to experiment accuracy (one of many possible answers):
| a. | `text{n(ethanol)}` | `= text{m}/text{MM}` |
| `=0.370/46.068` | ||
| `=0.008032\ text{mol}` |
`q=mC DeltaT = 105\ text{g} xx 4.18\ text{J g}^(-1)\ text{K}^(-1) xx (30-18.5)\ text{K} = 5047.35\ text{J}`
| `(Delta_(c) H)` | `=-q/n` | |
| `=- 5047.35/0.008032` | ||
| `=-628\ 405\ text{J mol}^(-1)` | ||
| `=-628\ text{kJ mol}^(-1)\ \ text{(3 sig fig)}` |
b. Improvement to experiment accuracy (one of many possible answers):
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
a. Successful answers should have one of the following:
b. Functional Group isomers
c. Tollens’ Test:
a. Successful answers should have one of the following:
b. Functional Group isomers
c. Tollens’ Test: