- Show that `3-sqrt3 i = 2sqrt3 text(cis)(-pi/6)`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find `(3-sqrt3 i)^3`, expressing your answer in the form `x + iy`, where `x`, `y ∈ R`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the integer values of `n` for which `(3-sqrt3 i)^n` is real. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the integer values of `n` for which `(3-sqrt3 i)^n = ai`, where `a` is a real number. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, SPEC1 2019 VCAA 5
The graph of `f(x) = cos^2(x) + cos(x) + 1` over the domain `0 <= x <= 2pi` is shown below.
- i. Find `f^{′}(x)`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- ii. Hence, find the coordinates of the turning points of the graph in the interval `(0, 2pi)`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the graph of `y = 1/(f(x))` on the set of axes above. Clearly label the turning points and endpoints of this graph with their coordinates. (3 marks)
Calculus, MET2 2019 VCAA 1
Let `f: R -> R,\ \ f(x) = x^2e^(-x^2)`. --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, SPEC1 2019 VCAA 3
A machine produces chocolate in the form of a continuous cylinder of radius 0.5 cm. Smaller cylindrical pieces are cut parallel to its end, as shown in the diagram below.
The lengths of the pieces vary with a mean of 3 cm and a standard deviation of 0.1 cm.
- Find the expected volume of a piece of chocolate in cm³. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the variance of the volume of a piece of chocolate in cm6. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the expected surface area of a piece of chocolate in cm². (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, 2ADV F2 SM-Bank 35
- Sketch the function `y = f(x)` where `f(x) = (x - 1)^3` on a number plane, labelling all intercepts. (1 mark)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- On the same graph, sketch `y = −f(−x)`. Label all intercepts. (2 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, 2ADV F1 SM-Bank 37
Find all values of `x` for which `|\ x - 4\ | = x/2 + 7`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, SPEC1 2019 VCAA 2
Find all values of `x` for which `|x - 4| = x/2 + 7`. (3 marks)
Functions, 2ADV F1 SM-Bank 36
Consider the function `f(x) = 1/(x + 2)`.
- Sketch the graph `y = f(−x)`. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- On the same graph, sketch `y = −f(x)`. (2 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, MET2 2019 VCAA 7 MC
The discrete random variable `X` has the following probability distribution.
| `qquad x` | `qquad 0 qquad` | `qquad 1 qquad` | `qquad 2 qquad` | `qquad 3 qquad` | |
| `qquad Pr(X = x) qquad` | `a` | `3a` | `5a` | `7a` |
The mean of `X` is
- `1/16`
- `1`
- `35/16`
- `17/8`
- `2`
Calculus, MET2 2019 VCAA 5 MC
Let `f prime(x) = 3x^2 - 2x` such that `f(4) = 0`.
The rule of `f` is
A. `f(x) = x^3 - x^2`
B. `f(x) = x^3 - x^2 + 48`
C. `f(x) = x^3 - x^2 - 48`
D. `f(x) = 6x - 2`
E. `f(x) = 6x - 24`
Statistics, 2ADV S2 SM-Bank 14
A probability density function `f(x)` is given by
`f(x) = {(px(3 - x), \ text(if)\ \ 0 <= x <= 3),(0, \ text(if)\ \ x < 0\ \ text(or if)\ \ x > 3):}`
where `p` is a positive constant.
- Find the value of `p`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the mode of `f(x)`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, 2ADV S3 EQ-Bank 17
The diastolic measurement for blood pressure in 35-year-old people is normally distributed, with a mean of 75 and a standard deviation of 12.
- A person is considered to have low blood pressure if their diastolic measurement is 63 or less.What percentage of 35-year-olds have low blood pressure? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Calculate the `z`-score for a diastolic measurement of 57. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The probability that a 35-year-old person has a diastolic measurement for blood pressure between 57 and 63 can be found by evaluating
`qquad qquad int_a^b f(x)\ dx`
where `a` and `b` are constants and where
`qquad qquad f(x) = 1/(sqrt(2pi)) e^((−x^2)/2)`
is the normal probability density function with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
By first finding the values `a` and `b`, calculate an approximate value for this probability by using the trapezoidal rule with 3 function values. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, find the approximate probability that a 35-year-old person chosen at random has a diastolic measurement of 57 or less. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, MET2 2019 VCAA 2 MC
The set of values of `k` for which `x^2 + 2x-k = 0` has two real solutions is
- `{-1, 1}`
- `(-1, oo)`
- `(-oo, -1)`
- `{-1}`
- `[-1, oo)`
Graphs, MET2 2019 VCAA 1 MC
Let `f: R -> R,\ \ f(x) = 3 sin ((2x)/5) - 2`.
The period and range of `f` are respectively
- `5 pi` and `[-3, 3]`
- `5 pi` and `[-5, 1]`
- `5 pi` and `[-1, 5]`
- `(5 pi)/2` and `[-5, 1]`
- `(5 pi)/2` and `[-3, 3]`
Calculus, MET1 2019 VCAA 7
The graph of the relation `y = sqrt (1-x^2)` is shown on the axes below. `P` is a point on the graph of this relation, `A` is the point `(-1, 0)` and `B` is the point `(x, 0)`.
- Find an expression for the length `PB` in terms of `x` only. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the maximum area of the triangle `ABP`. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, MET1 2019 VCAA 6
Fred owns a company that produces thousands of pegs each day. He randomly selects 41 pegs that are produced on one day and finds eight faulty pegs. --- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2019 VCAA 5
Let `f: R\ text(\{1}) -> R, \ f(x) = 2/(x-1)^2 + 1`.
- Find the area bounded by the graph of `f`, the `x`-axis, the line `x = -1` and the line `x = 0`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2019 VCAA 1aii
Let `f: (1/3, oo) -> R,\ \ f(x) = 1/(3x-1)`.
Find an antiderivative of `f(x)`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2019 VCAA 1ai
Let `f: (1/3, oo) -> R,\ \ f(x) = 1/(3x-1)`.
Find `f ^{′}(x)`. (1 mark)
L&E, 2ADV E1 SM-Bank 14
The spread of a highly contagious virus can be modelled by the function
`f(x) = 8000/(1 + 1000e^(−0.12x))`
Where `x` is the number of days after the first case of sickness due to the virus is diagnosed and `f(x)` is the total number of people who are infected by the virus in the first `x` days.
- Calculate `f(0)`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `f(365)` and interpret it result. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C2 EQ-Bank 2
Differentiate with respect to `x`:
`10^(5x^2 - 3x)`. (2 marks)
Calculus, 2ADV C2 EQ-Bank 1
Differentiate `log_2 x^2` with respect to `x`. (2 marks)
Vectors, EXT1 V1 SM-Bank 20
Consider the vector `underset~a = underset~i + sqrt3underset~j`, where `underset~i` and `underset~j` are unit vectors in the positive direction of the `x` and `y` axes respectively.
- Find the unit vector in the direction of `underset~a`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the acute angle that `underset~a` makes with the positive direction of the `x`-axis. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The vector `underset~b = m underset~i - 2underset~j`.
Given that `underset~b` is perpendicular to `underset~a`, find the value of `underset~m`. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Vectors, EXT1 V1 SM-Bank 19
Consider the following vectors
`overset(->)(OA) = 2underset~i + 2underset~j,\ \ overset(->)(OB) = 3underset~i - underset~j,\ \ overset(->)(OC) = 5underset~i + 3underset~j`
- Find `overset(->)(AB)`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The points `A`, `B` and `C` are vertices of a triangle. Prove that the triangle has a right angle at `A`. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Vectors, EXT1 V1 SM-Bank 16 MC
The vectors `underset~a = 2underset~i + m underset~j` and `underset~b = m^2underset~i - underset~j` are perpendicular for
A. `m = −2` and `m = 0`
B. `m = 2` and `m = 0`
C. `m = -1/2` and `m = 0`
D. `m = 1/2` and `m = 0`
Vectors, EXT1 V1 SM-Bank 15
Consider the vectors
`underset~a = 6underset~i + 2underset~j,\ \ underset~b = 2underset~i - m underset~j`
- Calculate `2underset~a - 3underset~b`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the values of `m` for which `|underset~b| = 3sqrt2`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `m` such that `underset~a` is perpendicular to `underset~b`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Vectors, EXT1 V1 SM-Bank 12
Find the projection of `underset~a` onto `underset~b` given `underset~a = 2underset~i + underset~j` and `b = 3underset~i - 2underset~j`. (2 marks)
Vectors, EXT1 V1 SM-Bank 10
In the quadrilateral `PQRS`, `T` lies on `SR` such that `ST : TR = 3 : 1`.
- Find `overset(->)(TS)` in terms of `underset~u`, `underset~v` and `underset~w`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, find `overset(->)(TP)` in terms of `underset~u`, `underset~v` and `underset~w`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT2 C1 2019 HSC 15c
- Show that `int_0^1 x/(x + 1)^2\ dx = ln 2 - 1/2`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Let `I_n = int_0^1 x^n/(x + 1)^2\ dx`.
Show that `I_n = 1/(2(n - 1)) - n/(n - 1) I_(n - 1)\ \ text(for)\ \ n >= 2`. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Evaluate `I_3`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Proof, EXT2 P2 2019 HSC 14c
- Show that `cot x - cot 2x = text(cosec)\ 2x`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Use mathematical induction to prove that, for all `n >= 1`,
`sum_(r = 1)^n\ text(cosec)(2^r x) = cot x - cot(2^n x)`. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Mechanics, EXT2 M1 2019 HSC 14b
A parachutist jumps from a plane, falls freely for a short time and then opens the parachute. Let t be the time in seconds after the parachute opens, `x(t)` be the distance in metres travelled after the parachute opens, and `v(t)` be the velocity of the parachutist in `text(ms)^(-1)`.
The acceleration of the parachutist after the parachute opens is given by
`ddot x = g - kv,`
where `g\ text(ms)^(-2)` is the acceleration due to gravity and `k` is a positive constant.
- With an open parachute the parachutist has a terminal velocity of `w\ text(ms)^(-1)`.
Show that `w = g/k`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
At the time the parachute opens, the speed of descent is `1.6 w\ text(ms)^(-1)`.
- Show that it takes `1/k log_e 6` seconds to slow down to a speed of `1.1w\ text(ms)^(-1)`. (4 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Let `D` be the distance the parachutist travels between opening the parachute and reaching the speed `1.1w\ text(ms)^(-1)`.
Show that `D = g/k^2 (1/2 + log_e 6)`. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Mechanics, EXT2* M1 2019 HSC 13c
Two objects are projected from the same point on a horizontal surface. Object 1 is projected with an initial velocity of `20\ text(ms)^(-1)` directed at an angle of `pi/3` to the horizontal. Object 2 is projected 2 seconds later.
The equations of motion of an object projected from the origin with initial velocity `v` at an angle `theta` to the `x`-axis are
`x = vt cos theta`
`y = -4.9t^2 + vt sin theta`,
where `t` is the time after the projection of the object. Do NOT prove these equations.
- Show that Object 1 will land at a distance `(100 sqrt 3)/4.9` m from the point of projection. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The two objects hit the horizontal plane at the same place and time.
Find the initial speed and the angle of projection of Object 2, giving your answer correct to 1 decimal place. (3 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, EXT1′ F1 2019 HSC 12d
Consider the function `f(x) = x^3 - 1`.
- Sketch the graph `y = |\ f(x)\ |`. (1 mark)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the graph `y = 1/(f(x))`. (2 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Without using calculus, sketch the graph `y = x/(f(x))`. (2 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1′ C3 2019 HSC 12b
The diagram shows two straight railway tracks that meet at an angle of `(2 pi)/3` at the point `P`.
Trains `A` and `B` are joined by a cable which is 70 m long.
At time `t` seconds, train `A` is `x` metres from `P` and train `B` is `y` metres from `P`.
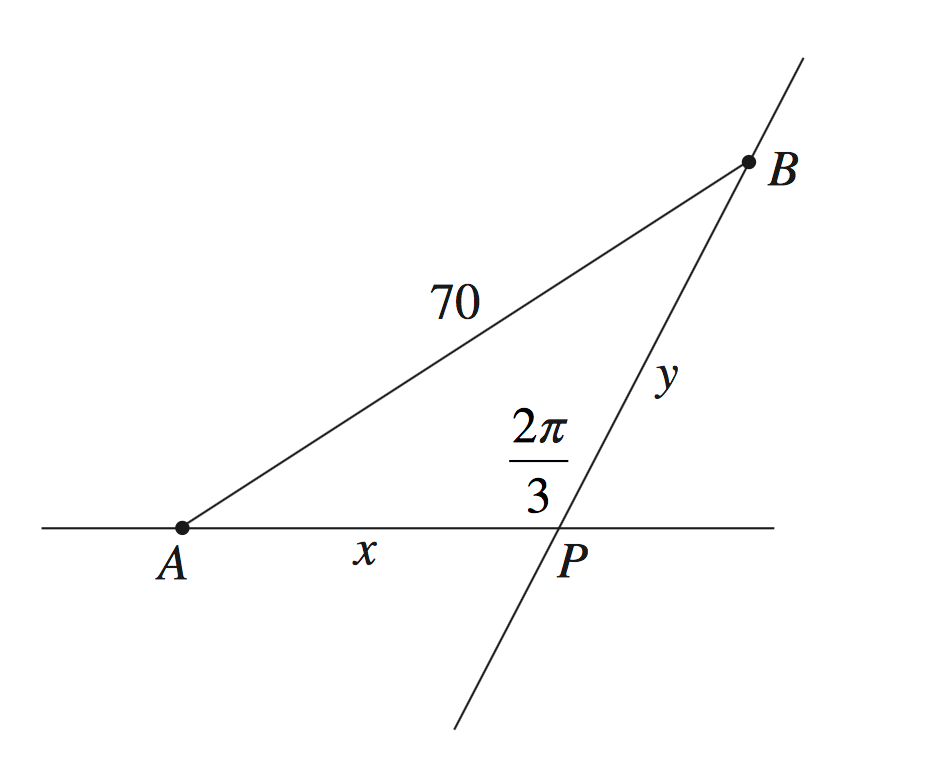
Train `B` is towing train `A` and is moving at a constant speed of `4\ text(ms)^(-1)` away from `P`.
- Show that `x^2 + xy + y^2 = 70^2`. (1 mark)
- What is the value of `(dx)/(dt)` when train `A` is 30 metres from `P` and train `B` is 50 metres from `P`? (3 marks)
Complex Numbers, EXT2 N1 2019 HSC 11e
Let `z = -1 + i sqrt 3`.
- Write `z` in modulus-argument form. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find `z^3`, giving your answer in the form `x + iy`, where `x` and `y` are real numbers. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT2 C1 2019 HSC 11c
Find `int (dx)/(x^2 + 10x + 29)` (2 marks)
Calculus, EXT2 C1 2019 HSC 3 MC
Which expression is equal to `int x cos x\ dx`?
- `-x sin x + cos x + C`
- `-x sin x - cos x + C`
- `x sin x + cos x + C`
- `x sin x - cos x + C`
Financial Maths, STD1 F2 2019 HSC 35
A bank offers two different savings accounts.
Account `X` offers simple interest of 7% per annum.
Account `Y` offers compound interest of 6% per annum compounded yearly.
The table displays the future values of $20 000 invested in each account for the first 2 years.
- How much more money is there in Account `X` than in Account `Y` at the end of 2 years? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show that there would be more money in Account `Y` than in Account `X` at the end of 8 years. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, STD1 A3 2019 HSC 23
Five rabbits were introduced onto a farm at the start of 2018. At the start of 2019 there were 10 rabbits on the farm. It is predicted that the number of rabbits on the farm will continue to double each year.
Measurement, STD1 M5 2019 HSC 20
Proof, EXT1 P1 2019 HSC 14a
Prove by mathematical induction that, for all integers `n >= 1`,
`1(1!) + 2(2!) + 3(3!) + … + n(n!) = (n + 1)! - 1`. (3 marks)
--- 14 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, STD1 S3 2019 HSC 22
Measurement, STD1 M4 2019 HSC 6 MC
When blood pressure is measured, two numbers are recorded: systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. If the measurements recorded are 130 systolic and 85 diastolic, then the blood pressure is written as '130 over 85'.
The bars on the graph indicate the healthy ranges of blood pressure for people of various ages.
Which person has both blood pressure measurements in the healthy range for their age?
- Stella aged 23 with blood pressure 120 over 72
- Shane aged 35 with blood pressure 124 over 90
- Jon aged 54 with blood pressure 137 over 94
- Annie aged 61 with blood pressure 142 over 88
Measurement, STD1 M1 2019 HSC 4 MC
Which compass bearing is the same as a true bearing of 110°?
- S20°E
- S20°W
- S70°E
- S70°W
Measurement, STD1 M4 2019 HSC 3 MC
Sugar is sold in four different sized packets.
Which is the best buy?
- 100 g for $0.40
- 500 g for $1.65
- 1 kg for $3.50
- 2 kg for $6.90
Calculus, EXT1 C1 2019 HSC 12d
A refrigerator has a constant temperature of 3°C. A can of drink with temperature 30°C is placed in the refrigerator.
After being in the refrigerator for 15 minutes, the temperature of the can of drink is 28°C.
The change in the temperature of the can of drink can be modelled by `(dT)/(dt) = k(T - 3)`, where `T` is the temperature of the can of drink, `t` is the time in minutes after the can is placed in the refrigerator and `k` is a constant.
- Show that `T = 3 + Ae^(kt)`, where `A` is a constant, satisfies
`qquad(dT)/(dt) = k(T - 3)`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- After 60 minutes, at what rate is the temperature of the can of drink changing? (3 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1 C1 2019 HSC 12a
Distance `A` is inversely proportional to distance `B`, such that `A = 9/B` where `A` and `B` are measured in metres. The two distances vary with respect to time. Distance `B` is increasing at a rate of `0.2\ text(ms)^(-1)`.
What is the value of `(dA)/(dt)` when `A = 12`? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, EXT1 S1 2019 HSC 11f
Prize-winning symbols are printed on 5% of ice-cream sticks. The ice-creams are randomly packed into boxes of 8.
- What is the probability that a box contains no prize-winning symbols? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the probability that a box contains at least 2 prize-winning symbols? (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1 C2 2019 HSC 11e
Find `int 2 sin^2 4x\ dx`. (2 marks)
Functions, EXT1 F2 2019 HSC 11d
Find the polynomial `Q(x)` that satisfies `x^3 + 2x^2-3x-7 = (x-2) Q(x) + 3`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, EXT1 F1 2019 HSC 11b
For what values of `x` is `x/(x + 1) < 2`? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, 2ADV’ F2 2019 HSC 4 MC
Functions, 2ADV 2019 HSC 1 MC
What is the domain of the function `f(x) = ln(4-x)`?
- `x < 4`
- `x <= 4`
- `x > 4`
- `x >= 4`
Algebra, STD2 A4 2019 HSC 36
A small business makes and sells bird houses.
Technology was used to draw straight-line graphs to represent the cost of making the bird houses `(C)` and the revenue from selling bird houses `(R)`. The `x`-axis displays the number of bird houses and the `y`-axis displays the cost/revenue in dollars.
- How many bird houses need to sold to break even? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- By first forming equations for cost `(C)` and revenue `(R)`, determine how many bird houses need to be sold to earn a profit of $1900. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, STD2 A4 2019 HSC 33
The time taken for a car to travel between two towns at a constant speed varies inversely with its speed.
It takes 1.5 hours for the car to travel between the two towns at a constant speed of 80 km/h.
- Calculate the distance between the two towns. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- By first plotting four points, draw the curve that shows the time taken to travel between the two towns at different constant speeds. (3 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2019 HSC 14b
The derivative of a function `y = f(x)` is given by `f^{′}(x) = 3x^2 + 2x-1`.
- Find the `x`-values of the two stationary points of `y = f(x)`, and determine the nature of the stationary points. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The curve passes through the point `(0, 4)`.
Find an expression for `f(x)`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence sketch the curve, clearly indicating the stationary points. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For what values of `x` is the curve concave down? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2019 HSC 13c
- Differentiate `(ln x)^2`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, or otherwise, find `int(ln x)/x\ dx`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1* C1 2019 HSC 12c
The number of leaves, `L(t)`, on a tree `t` days after the start of autumn can be modelled by
`L(t) = 200\ 000e^(-0.14t)`
- What is the number of leaves on the tree when `t = 31`? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What is the rate of change of the number of leaves on the tree when `t = 31`? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- For what value of `t` are there 100 leaves on the tree? (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, 2ADV M1 2019 HSC 12b
In an arithmetic series, the fourth term is 6 and the sum of the first 16 terms is 120.
Find the common difference. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, 2ADV S1 2019 HSC 11f
A bag contains 5 green beads and 7 purple beads. Two beads are selected at random, without replacement.
What is the probability that the two beads are the same colour? (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- …
- 57
- Next Page »