Number and Algebra, NAP-J2-08
Emily has 85 cents in 5-cent pieces.
How many 5-cent pieces does she have?
| `17` | `80` | `40` | `425` |
|
|
|
|
|
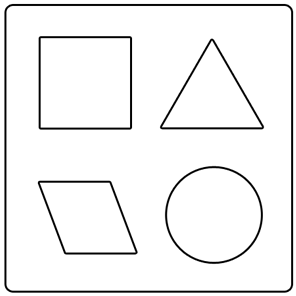
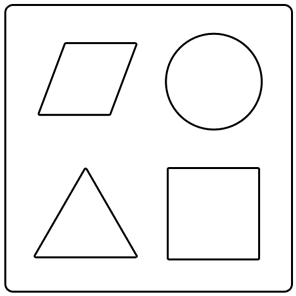
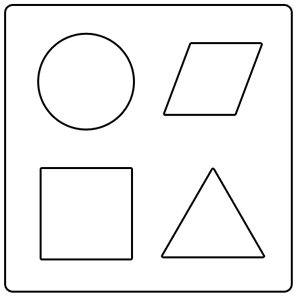
Geometry, NAP-J2-06
Measurement, NAP-J2-05
How many days are there in 4 weeks?
| 7 days | 11 days | 20 days | 28 days |
|
|
|
|
|
Statistics, NAP-J2-04
CHEMISTRY, M4 2009 HSC 20
- Calculate the mass of ethanol \(\ce{C2H6O}\) that must be burnt to increase the temperature of 210 g of water by 65°C, if exactly half of the heat released by this combustion is lost to the surroundings.
- The heat of combustion of ethanol is 1367 kJ mol −1. (3 marks)
--- 12 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- What are TWO ways to limit heat loss from the apparatus when performing a first-hand investigation to determine and compare heat of combustion of different liquid alkanols? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M4 2013 HSC 27
A 0.259 g sample of ethanol is burnt to raise the temperature of 120 g of an oily liquid, as shown in the graph. There is no loss of heat to the surroundings.
Using the information shown on the graph, calculate the specific heat capacity of the oily liquid. The heat of combustion of ethanol is 1367 kJ mol–1. (4 marks)
--- 14 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Number, NAP-J3-CA03
Four students did a standing long jump and the results were recorded.
Which student had the longest jump?
| Leigh 2.01 m | Sam 0.70 m | Job 0.80 m | Ronan 1.05 m |
|
|
|
|
|
Statistics, NAP-J3-CA01
L&E, 2ADV E1 SM-Bank 9
Solve `log_2(6-x)-log_2(4-x) = 2` for `x`, where `x < 4`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
L&E, 2ADV E1 SM-Bank 7
Solve the equation `2 log_3(5)-log_3 (2) + log_3 (x) = 2` for `x.` (2 marks)
L&E, 2ADV E1 SM-Bank 4 MC
If `f(x) = 3 log_e (2x),` and `f(5x) = log_e (y),`
then `y` is equal to
- `30x`
- `6x`
- `125x^3`
- `1000x^3`
L&E, 2ADV E1 SM-Bank 2 MC
If `y = log_a (7x - b) + 3`, then `x` is equal to
- `1/7 a^(y - 3) + b`
- `(y - 3)/(log_a(7 - b))`
- `1/7 (a^(y - 3) + b)`
- `a^(y - 3) - b/7`
L&E, 2ADV E1 SM-Bank 10
Solve the equation `2^(3x-3) = 8^(2-x)` for `x`. (2 marks)
GEOMETRY, FUR1 SM-Bank 32 MC
Makoua and Macapá are two towns on the equator.
The longitude of Makoua is 16°E and the longitude of Macapá is 52°W.
How far apart are these two towns if the radius of Earth is approximately 6400 km?
A. `4000\ text(km)`
B. `7600\ text(km)`
C. `1\ 367\ 200\ text(km)`
D. `1\ 447\ 600\ text(km)`
E. `2\ 734\ 400\ text(km)`
GEOMETRY, FUR1 SM-Bank 18 MC
Stockholm is located at 59°N 18°E and Darwin is located at 13°S 131°E.
What is the time difference between Stockholm and Darwin? (Ignore time zones and daylight saving.)
- 184 minutes
- 188 minutes
- 288 minutes
- 452 minutes
- 596 minutes
GEOMETRY, FUR1 SM-Bank 15 MC
Which expression will give the shortest distance, in kilometres, between Mount Isa (20°S 140°E) and Tokyo (35°N 140°E)?
- `15/360 xx 2 xx pi xx 6400`
- `55/360 xx 2 xx pi xx 6400`
- `125/360 xx 2 xx pi xx 6400`
- `140/360 xx 2 xx pi xx 6400`
- `305/360 xx 2 xx pi xx 6400`
GEOMETRY, FUR2 SM-Bank 25
A ship sails due South from Channel-Port-aux-Basques, Canada, 47°N 59°W to Barbados, 13°N 59°W.
How far did the ship sail, to the nearest kilometre? Assume that the radius of Earth is 6400 km. (2 marks)
GEOMETRY, FUR2 SM-Bank 15
Osaka is at 34°N, 135°E, and Denver is at 40°N, 105°W.
- Show that there is a 16-hour time difference between the two cities.
(Ignore time zones.) (1 mark) - John lives in Denver and wants to ring a friend in Osaka. In Denver it is 9 pm Monday.
What time and day is it in Osaka then? (1 mark)
- John’s friend in Osaka sent him a text message which happened to take 14 hours to reach him. It was sent at 10 am Thursday, Osaka time.
What was the time and day in Denver when John received the text? (1 mark)
GEOMETRY, FUR2 SM-Bank 14
Pontianak has a longitude of 109°E, and Jarvis Island has a longitude of 160°W.
Both places lie on the Equator
- Find the shortest great circle distance between these two places, to the nearest kilometre. You may assume that the radius of the Earth is 6400 km. (2 marks)
- The position of Rabaul is 4° to the south and 48° to the west of Jarvis Island. What is the latitude and longitude of Rabaul? (1 mark)
GEOMETRY, FUR2 SM-Bank 13
Melbourne is located at (38°S, 145°E) and Dubai is located at (24°N, 55°E).
- Calculate the difference in longitude between Melbourne and Dubai. (1 mark)
- Show that the time difference between Melbourne and Dubai is 6 hours. (1 mark)
- A plane leaves Melbourne on Friday at 11.30 pm. The flight time to Dubai is 15 hours.
What will be the time and the day in Dubai when the plane is due to land? (1 marks)
GEOMETRY, FUR2 SM-Bank 12
Probability, MET1 2012 VCAA 8b
The probability density function `f` of a random variable `X` is given by
`qquad qquad f(x) = {((x + 1)/12, 0 <= x <= 4), (\ \ 0, text{otherwise}):}`
Find the value of `b` such that `text(Pr) (X <= b) = 5/8.` (3 marks)
Calculus, MET1 2006 VCAA 3a
Let `y = x tan(x)`. Evaluate `(dy)/(dx)` when `x = pi/6`. (3 mark)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2009 VCAA 1b
For `f(x) = (cos(x))/(2x + 2)` find `f prime (pi)`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 5
The function with rule `f(x)` has derivative `f^{prime}(x) = cos\ 3x`.
If `f(pi/6) = 1,` find `f(x).` (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2007 VCAA 20 MC
The average value of the function `y = tan (2x)` over the interval `[0, pi/8]` is
- `2/pi log_e (2)`
- `pi/4`
- `1/2`
- `4/pi log_e 2`
- `8/pi`
Probability, MET2 2007 VCAA 18 MC
The heights of the children in a queue for an amusement park ride are normally distributed with mean 130 cm and standard deviation 2.7 cm. 35% of the children are not allowed to go on the ride because they are too short.
The minimum acceptable height correct to the nearest centimetre is
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
Probability, MET2 2007 VCAA 16 MC
If a random variable `X` has probability density function
`f(x) = {(x/2, if x in[0,2]), (0,\ \ \ text(otherwise)):}`
then `text(E) (X)` is equal to
- `1/2`
- `1`
- `4/3`
- `2/3`
- `2`
Calculus, MET2 2007 VCAA 13 MC
For the graph of `y = 4x^3 + 27x^2-30x + 10` the subset of `R` for which the gradient is negative is given by the interval
- `(0.5, 5.0)`
- `(-4.99, 0.51)`
- `(-oo, 1/2)`
- `(-5, 1/2)`
- `(2.25, oo)`
Calculus, MET2 2007 VCAA 12 MC
Let `f: R -> R` be a differentiable function such that
- `f prime(3) = 0`
- `f prime(x) < 0` when `x < 3` and when `x > 3`
When `x = 3`, the graph of `f` has a
- local minimum
- local maximum
- stationary point of inflection
- point of discontinuity
- gradient of 3
L&E, 2ADV E1 SM-Bank 11 MC
Solve the equation `e^(4x) - 5e^(2x) + 4 = 0` for `x`
- `x= 1, 4`
- `x= – 4, – 1`
- `x= 0, log_e 2`
- `x= – log_e 2, 0, log_e 2 `
Graphs, MET2 2007 VCAA 10 MC
The graph of `y = kx-3` intersects the graph of `y = x^2 + 8x` at two distinct points for
- `k = 11`
- `k > 8 + 2 sqrt 3 or k < 8-2 sqrt 3`
- `5 <= k <= 6`
- `8-2 sqrt 3 <= k <= 8 + 2 sqrt 3`
- `k = 5`
Calculus, MET2 2007 VCAA 9 MC
Let `k = int_-2^-1 1/x\ dx`, then `e^k` is equal to
- `log_e(2)`
- `1`
- `2`
- `e`
- `1/2`
Calculus, MET2 2007 VCAA 4 MC
The average rate of change of the function with rule `f(x) = x^3 - sqrt (x + 1)` between `x = 0` and `x = 3` is
A. `0`
B. `12`
C. `26/3`
D. `25/3`
E. `8`
Graphs, MET2 2007 VCAA 1 MC
The linear function `f: D -> R,\ f(x) = 6 - 2x` has range `text([−4, 12]).`
The domain `D` is
- `[– 3, 5]`
- `[– 5, 3]`
- `R`
- `[– 14, 18]`
- `[– 18, 14]`
Algebra, MET1 SM-Bank 24
The polynomial `p(x) = x^3-ax + b` has a remainder of 2 when divided by `(x-1)` and a remainder of 5 when divided by `(x + 2)`.
Find the values of `a` and `b`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, MET1 SM-Bank 23
The graph of `P(x) = x^2 + ax + b` cuts the `x`-axis when `x=2.` When `P(x)` is divided by `x + 1`, the remainder is 18.
Find the values of `a` and `b`. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Graphs, MET2 2008 VCAA 22 MC
The graph of the function `f` with domain `[0, 6]` is shown below.
Which one of the following is not true?
- The function is not continuous at `x = 2` and `x = 4.`
- The function exists for all values of `x` between `0` and `6.`
- `f(x) = 0` for `x = 2` and `x = 5.`
- The function is positive for `x ∈ [0, 5).`
- The gradient of the function is not defined at `x = 4.`
Probability, MET2 2008 VCAA 14 MC
The minimum number of times that a fair coin can be tossed so that the probability of obtaining a head on each trial is less than 0.0005 is
A. `8`
B. `9`
C. `10`
D. `11`
E. `12`
Probability, MET2 2008 VCAA 13 MC
According to a survey, 30% of employed women have never been married.
If 10 employed women are selected at random, the probability (correct to four decimal places) that at least 7 have never been married is
A. `0.0016`
B. `0.0090`
C. `0.0106`
D. `0.9894`
E. `0.9984`
Probability, MET2 2008 VCAA 5 MC
Let `X` be a discrete random variable with a binomial distribution. The mean of `X` is 1.2 and the variance of `X` is 0.72
The values of `n` (the number of independent trials) and `p` (the probability of success in each trial) are
A. `n = 4,\ \ \ \ \ p = 0.3`
B. `n = 3,\ \ \ \ \ p = 0.6`
C. `n = 2,\ \ \ \ \ p = 0.6`
D. `n = 2,\ \ \ \ \ p = 0.4`
E. `n = 3,\ \ \ \ \ p = 0.4`
Calculus, MET2 2008 VCAA 3 MC
The average value of the function with rule `f(x) = log_e (3x + 1)` over the interval `[0, 2]` is
- `(log_e(7))/2`
- `log_e(7)`
- `(7 log_e (7))/3 - 2`
- `(7 log_e (7) - 6)/6`
- `(35 log_e(7) - 12)/18`
Calculus, MET2 2008 VCAA 1 MC
Algebra, 2UG AM3 SM-Bank 06
Solve these simultaneous equations to find the values of `x` and `y`.
`4x - 2y = 18`
`3x + 2y = 10` (3 marks)
Algebra, MET1 SM-Bank 25
Solve these simultaneous equations to find the values of `x` and `y`. (3 marks)
`y = 2x + 1`
`x-2y-4 = 0`
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 28
The function `f` has the rule `f(x) = 1 + 2 cos x`.
- Show that the graph of `y = f(x)` cuts the `x`-axis at `x = (2 pi)/3`. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the graph `y = f(x)` for `x in [-pi,pi]` showing where the graph cuts each of the axes. (2 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the area under the curve `y = f(x)` between `x = -pi/2` and `x = (2 pi)/3`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Graphs, MET1 SM-Bank 27
The graph shown is `y = A sin bx`.
- Write down the value of `A`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `b`. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Copy or trace the graph into your writing booklet.
On the same set of axes, draw the graph `y = 3 sin x + 1` for `0 <= x <= pi`. (2 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 25
Evaluate `int_0^(pi/4) cos 2x\ dx`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 21
Find the equation of the tangent to the curve `y = cos 2x` at the point whose `x`-coordinate is `pi/6.` (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 20
If `f(x)= 2 sin 3x - 3 tan x`, find `f^{prime}(0)`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, MET1 SM-Bank 24
The rule for `f` is `f(x) = e^x-e^(-x)`.
Show that the inverse function is given by
`f^(-1)(x) = log_e((x + sqrt(x^2 + 4))/2)` (3 marks)
--- 14 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, MET1 SM-Bank 23
The function `f: [0,oo) → R` with rule `f(x) = 1/(1 + x^2)` is drawn below.
- Copy or trace this diagram into your writing booklet.
- On the same set of axes, sketch `y=f^(-1)(x)` where `f^(-1)` is the inverse function of `f(x)`. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
- Find the domain of the inverse `f^(-1)`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find an expression for `y = f^(-1)(x)` in terms of `x`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The graphs of `y = f(x)` and `y = f^(-1)(x)` meet at exactly one point `P`.Let `α` be the `x`-coordinate of `P`. Explain why `α` is a root of the equation
- `x^3 + x-1 = 0`. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 SM-Bank 21
The rule for function `f` is `f(x) = e^(-x^2)`. The diagram shows the graph `y = f(x)`.
The graph has two points of inflection.
- Find the `x` coordinates of these points. (2 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain why the domain of `f(x)` must be restricted if `f(x)` is to have an inverse function. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the rule for the inverse function `f^(-1)` if the domain of `f(x)` is restricted to `x ≥ 0.` (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the domain for `f^(-1)`. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Sketch the curve `y = f^(-1) (x)`. (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=blank) ---
Graphs, MET1 SM-Bank 20
The rule for `f` is `f(x) = x-1/2 x^2` for `x <= 1`. This function has an inverse, `f^(-1) (x)`.
- Sketch the graphs of `y = f(x)` and `y = f^(-1) (x)` on the same set of axes. (Use the same scale on both axes.) (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the rule for the inverse function `f^(-1) (x)`. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Evaluate `f^(-1) (3/8)`. (1 mark)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, MET1 SM-Bank 11
Let `f: R→R` where `f(x)= x^3-2`.
Evaluate `f^(-1)(25),` where `f^(-1)` is the inverse function of `f`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2006 ADV 2bi
If `f^{prime}(x)= (x^2)/(x^3 + 1)` and `f(1)= log_e 2,` find `f(x)`. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2011 ADV 4b
Find the value of `int_e^(e^3) 5/x` with respect to `x`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2008 ADV 3b
- Differentiate `log_e(cos x)` with respect to `x`. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, or otherwise, evaluate `int_0^(pi/4) tan x\ dx`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2016 ADV 12d
- Differentiate `y = xe^(3x)`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence find the exact value of `int_0^2 e^(3x) (3 + 9x)\ dx`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- …
- 114
- Next Page »