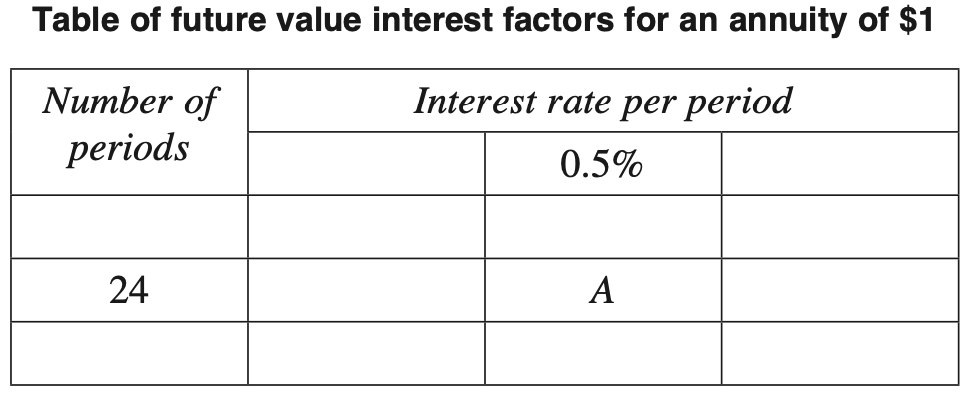
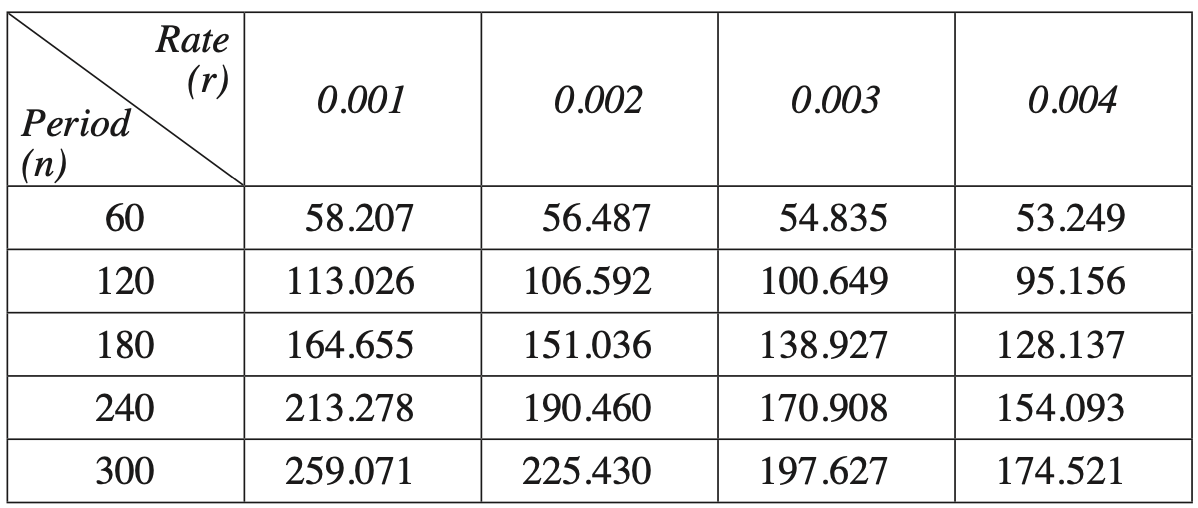
André invested $18 000 in an account for five years, with interest compounding monthly.
He adds an extra payment into the account each month immediately after the interest is calculated.
For the first two years, the balance of the account, in dollars, after \(n\) months, \(A_n\), can be modelled by the recurrence relation
\(A_0=18\,000, \quad A_{n+1}=1.002 A_n+100\)
After two years, André decides he would like the account to reach a balance of $30 000 at the end of the five years.
He must increase the value of the monthly extra payment to achieve this.
The minimum value of the new payment for the last three years is closest to
- $189.55
- $195.45
- $202.35
- $246.55