The network diagram shows a series of water channels and ponds in a garden. The vertices `A`, `B`, `C`, `D`, `E`, and `F` represent six ponds. The edges represent the water channels which connect the ponds. The numbers on the edges indicate the maximum capacity of the channels.
Combinatorics, EXT1 A1 2020 HSC 14a
- Use the identity `(1 + x)^(2n) = (1 + x)^n(1 + x)^n`
to show that
`((2n),(n)) = ((n),(0))^2 + ((n),(1))^2 + … + ((n),(n))^2`,
where `n` is a positive integer. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- A club has `2n` members, with `n` women and `n` men.
A group consisting of an even number `(0, 2, 4, …, 2n)` of members is chosen, with the number of men equal to the number of women.
Show, giving reasons, that the number of ways to do this is `((2n),(n))`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- From the group chosen in part (ii), one of the men and one of the women are selected as leaders.
Show, giving reasons, that the number of ways to choose the even number of people and then the leaders is
`1^2 ((n),(1))^2 + 2^2((n),(2))^2 + … + n^2((n),(n))^2`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The process is now reversed so that the leaders, one man and one woman, are chosen first. The rest of the group is then selected, still made up of an equal number of women and men.
By considering this reversed process and using part (ii), find a simple expression for the sum in part (iii). (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, STD2 N3 2020 HSC 26
The preparation of a meal requires the completion of all activities `A` to `J`. The network diagram shows the activities and their completion times in minutes.
- What is the minimum time needed to prepare the meal? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- List the activities which make up the critical path for this network. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Complete the table below, showing the earliest start time and float time for activities `A` and `G` (2 marks)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, STD2 F4 2020 HSC 29
Statistics, STD2 S2 2020 HSC 28
Consider the following dataset.
`1 5 9 10 15`
Suppose a new value, `x`, is added to this dataset, giving the following.
`1 5 9 10 15 x`
It is known that `x` is greater than 15. It is also known that the difference between the means of the two datasets is equal to ten times the difference between the medians of the two datasets.
Calculate the value of `x`. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD2 M1 2020 HSC 27
The shaded region on the diagram represents a garden. Each grid represents 5 m × 5 m.
- Use two applications of the trapezoidal rule to calculate the approximate area of the garden. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Should the answer to part (a) be more than, equal to or less than the actual area of the garden? Referring to the diagram above, briefly explain your answer. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, EXT1 C3 2020 HSC 12e
Find the curve which satisfies the differential equation `(dy)/(dx) = -x/y` and passes through the point `(1, 0)`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, STD2 A4 2020 HSC 24
There are two tanks on a property, Tank A and Tank B. Initially, Tank A holds 1000 litres of water and Tank B is empty.
- Tank A begins to lose water at a constant rate of 20 litres per minute.
The volume of water in Tank A is modelled by `V = 1000 - 20t` where `V` is the volume in litres and `t` is the time in minutes from when the tank begins to lose water.
On the grid below, draw the graph of this model and label it as Tank A. (1 mark)
- Tank B remains empty until `t=15` when water is added to it at a constant rate of 30 litres per minute.
By drawing a line on the grid (above), or otherwise, find the value of `t` when the two tanks contain the same volume of water. (2 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Using the graphs drawn, or otherwise, find the value of `t` (where `t > 0`) when the total volume of water in the two tanks is 1000 litres. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Trigonometry, 2ADV T3 2020 HSC 31
The population of mice on an isolated island can be modelled by the function.
`m(t) = a sin (pi/26 t) + b`,
where `t` is the time in weeks and `0 <= t <= 52`. The population of mice reaches a maximum of 35 000 when `t=13` and a minimum of 5000 when `t = 39`. The graph of `m(t)` is shown.
- What are the values of `a` and `b`? (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- On the same island, the population of cats can be modelled by the function
`\ \ \ \ \ c(t) = −80cos(pi/26 (t - 10)) + 120`
Consider the graph of `m(t)` and the graph of `c(t)`.
Find the values of `t, \ 0 <= t <= 52`, for which both populations are increasing. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the rate of change of the mice population when the cat population reaches a maximum. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Measurement, STD2 M7 2020 HSC 23
In a tropical drink, the ratio of pineapple juice to mango juice to orange juice is 15 : 9 : 4 .
- How much orange juice is needed if the tropical drink is to contain 3 litres of pineapple juice? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The internal dimensions of a drink container, in the shape of a rectangular prism, are shown.
To completely fill the container with the tropical drink, how many litres of mango juice are required. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, 2ADV S2 2020 HSC 27
A cricket is an insect. The male cricket produces a chirping sound.
A scientist wants to explore the relationship between the temperature in degrees Celsius and the number of cricket chirps heard in a 15-second time interval.
Once a day for 20 days, the scientist collects data. Based on the 20 data points, the scientist provides the information below.
- A box-plot of the temperature data is shown.
- The mean temperature in the dataset is 0.525°C below the median temperature in the dataset.
- A total of 684 chirps was counted when collecting the 20 data points.
The scientist fits a least-squares regression line using the data `(x, y)`, where `x` is the temperature in degrees Celsius and `y` is the number of chirps heard in a 15-second time interval. The equation of this line is
`y = −10.6063 + bx`,
where `b` is the slope of the regression,
The least-squares regression line passes through the point `(barx, bary)`, where `barx` is the sample mean of the temperature data and `bary` is the sample mean of the chirp data.
Calculate the number of chirps expected in a 15-second interval when the temperature is 19° Celsius. Give your answer correct to the nearest whole number. (5 marks)
Statistics, 2ADV S3 2020 HSC 28
In a particular country, the hourly rate of pay for adults who work is normally distributed with a mean of $25 and a standard deviation of $5.
- Two adults who both work are chosen at random.
Find the probability that at least one of them earns between $15 and $30 per hour. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The number of adults who work is equal to three times the number of adults who do not work.
One adult is chosen at random.
Find the probability that the chosen adult works and earn more than $25 per hour. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, 2ADV F1 2020 HSC 24
The circle of `x^2-6x + y^2 + 4y-3 = 0` is reflected in the `x`-axis.
Sketch the reflected circle, showing the coordinates of the centre and the radius. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2020 HSC 30
The diagram shows two parabolas `y = 4x - x^2` and `y = ax^2`, where `a > 0`. The two parabolas intersect at the origin, `O`, and at `A`.
- Show that the `x`-coordinate of `A` is `4/(a + 1)`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `a` such that the shaded area is `16/3`. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2020 HSC 29
The diagram shows the graph of `y = c ln x, \ c > 0`.
- Show that the equation of the tangent to `y = c ln x` at `x = p`, where `p > 0`, is
`\ \ \ \ \ y = c/p x - c + c ln p`. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `c` such that the tangent from part (a) has a gradient of 1 and passes through the origin. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, STD2 F5 2020 HSC 34
Tina inherits $60 000 and invests it in an account earning interest at a rate of 0.5% per month. Each month, immediately after the interest has been paid, Tina withdraws $800.
The amount in the account immediately after the `n`th withdrawal can be determined using the recurrence relation
`A_n = A_(n - 1)(1.005) - 800`,
where `n = 1, 2, 3, …` and `A_0 = 60\ 000`
- Use the recurrence relation to find the amount of money in the account immediately after the third withdrawal. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Calculate the amount of interest earned in the first three months. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, 2ADV M1 2020 HSC 26
Tina inherits $60 000 and invests it in an account earning interest at a rate of 0.5% per month. Each month, immediately after the interest has been paid, Tina withdraws $800.
The amount in the account immediately after the `n`th withdrawal can be determined using the recurrence relation
`A_n = A_(n - 1)(1.005) - 800`,
where `n = 1, 2, 3, …` and `A_0 = 60\ 000`
- Use the recurrence relation to find the amount of money in the account immediately after the third withdrawal. (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Calculate the amount of interest earned in the first three months. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Calculate the amount of money in the account immediately after the 94th withdrawal. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Algebra, STD2 A4 2020 HSC 19
A fence is to be built around the outside of a rectangular paddock. An internal fence is also to be built.
The side lengths of the paddock are `x` metres and `y` metres, as shown in the diagram.
A total of 900 metres of fencing is to be used. Therefore `3x + 2y = 900`.
The area, `A`, in square metres, of the rectangular paddock is given by `A =450x - 1.5x^2`.
The graph of this equation is shown.
- If the area of the paddock is `30 \ 000\ text(m)^2`, what is the largest possible value of `x`? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the values of `x` and `y` so that the area of the paddock is as large as possible. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Using your value from part (b), find the largest possible area of the paddock. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, 2ADV S1 2020 HSC 14
History and Geography are two of the subjects students may decide to study. For a group of 40 students, the following is known.
-
- 7 students study neither History nor Geography
- 20 students study History
- 18 students study Geography
- A student is chosen at random. By a using a Venn diagram, or otherwise, find the probability that the student studies both History and Geography. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- A students is chosen at random. Given that the student studies Geography, what is the probability that the student does NOT study History? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Two different students are chosen at random, one after the other. What is the probability that the first student studies History and the second student does NOT study History? (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2020 HSC 25
A landscape gardener wants to build a garden in the shape of a rectangle attached to a quarter-circle. Let `x` and `y` be the dimensions of the rectangle in metres, as shown in the diagram.
The garden bed is required to have an area of 36 m² and to have a perimeter which is as small as possible. Let `P` metres be the perimeter of the garden bed.
- Show that `P = 2x + 72/x`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the smallest possible perimeter of the garden bed, showing why this is the minimum perimeter. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, 2ADV S3 2020 HSC 23
A continuous random variable, `X`, has the following probability density function.
`f(x) = {(sin x, text(for)\ \ 0 <= x <= k),(0, text(for all other values of)\ x):}`
- Find the value of `k`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find `P(X <= 1)`. Give your answer correct to four decimal places. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2020 HSC 21
Hot tea is poured into a cup. The temperature of tea can be modelled by `T = 25 + 70(1.5)^(−0.4t)`, where `T` is the temperature of the tea, in degrees Celsius, `t` minutes after it is poured.
- What is the temperature of the tea 4 minutes after it has been poured? (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- At what rate is the tea cooling 4 minutes after it has been poured? (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- How long after the tea is poured will it take for its temperature to reach 55°C? (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, STD2 S2 2020 HSC 15 MC
The top of a rectangular table is divided into 8 equal sections as shown.
A standard die with faces labelled 1 to 6 is rolled onto the table. The die is equally likely to land in any of the 8 sections of the table. If the die does not land entirely in one section of the table, it is rolled again.
A score is calculated by multiplying the value shown on the top face of the die by the number shown in the section of the table where the die lands.
What is the probability of getting a score of 6?
- `frac{1}{48}`
- `frac{1}{12}`
- `frac{1}{8}`
- `frac{1}{6}`
Financial Maths, STD2 F5 2020 HSC 14 MC
An annuity consists of ten payments, each equal to $1000. Each payment is made on 30 June each year from 2021 through to 2030 inclusive.
The rate of compound interest is 5% per annum.
The present value of the annuity is calculated at 30 June 2020.
The future value of the annuity is calculated at 30 June 2030.
Without performing any calculations, which of the following statements is true?
- Present value of the annuity < $10 000 < future value of the annuity
- $10 000 < present value of the annuity < future value of the annuity
- Future value of the annuity < $10 000 < present value of the annuity
- $10 000 < future value of the annuity < present value of the annuity
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2020 HSC 18
- Differentiate `e^(2x) (2x + 1)`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Hence, find `int(x + 1)e^(2x)\ dx`. (1 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C3 2020 HSC 8 MC
Calculus, 2ADV C4 2020 HSC 7 MC
Financial Maths, STD2 F4 2020 HSC 11 MC
An asset is depreciated using the declining-balance method with a rate of depreciation of 8% per half year. The asset was bought for $10 000.
What is the salvage value of the asset after 5 years?
- $1749.01
- $4182.12
- $4343.88
- $6590.82
Algebra, STD2 A2 2020 HSC 10 MC
A plumber charges a call-out fee of $90 as well as $2 per minute while working.
Suppose the plumber works for `t` hours.
Which equation expresses the amount the plumber charges ($`C`) as a function of time (`t` hours)?
- `C = 2 + 90t`
- `C = 90 + 2t`
- `C = 120 + 90t`
- `C = 90 + 120t`
Networks, STD2 N2 2020 HSC 9 MC
Team `A` and Team `B` have entered a chess competition.
Team `A` and `B` have three members each. Each member of Team `A` must play each member of Team `B` once.
Which of the following network diagrams could represent the chess games to be played?
|
|
Statistics, STD2 S1 2020 HSC 7 MC
Which histogram best represents a dataset that is positively skewed?
Measurement, STD2 M1 2020 HSC 5 MC
A plant stem is measured to be 16.0 cm, correct to one decimal place.
What is the percentage error in this measurement?
- 0.3125%
- 0.625%
- 3.125%
- 6.25%
Measurement, STD2 M1 2020 HSC 2 MC
What is 0.002073 expressed in standard form with two significant figures?
- `2.07 xx 10^(-2)`
- `2.1 xx 10^(-2)`
- `2.07 xx 10^(-3)`
- `2.1 xx 10^(-3)`
Mechanics, EXT2 M1 EQ-Bank 4
A torpedo with a mass of 80 kilograms has a propeller system that delivers a force of `F` on the torpedo, at maximum power. The water exerts a resistance on the torpedo proportional to the square of the torpedo's velocity `v`.
- Explain why `(dv)/(dt) = 1/80 (F - kv^2)`
where `k` is a positive constant. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- If the torpedo increases its velocity from `text(10 ms)\ ^(−1)` to `text(20 ms)\ ^(−1)`, show that the distance it travels in this time, `d`, is given by
`d = 40/k log_e((F - 100k)/(F - 400k))` (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Mechanics, EXT2 M1 EQ-Bank 2
A particle with mass `m` moves horizontally against a resistance force `F`, equal to `mv(1 + v^2)` where `v` is the particle's velocity.
Initially, the particle is travelling in a positive direction from the origin at velocity `T`.
- Show that the particle's displacement from the origin, `x`, can be expressed as
`x = tan^(-1)((T - v)/(1 + Tv))` (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show that the time, `t`, when the particle is travelling at velocity `v`, is given by
`t = 1/2 log_e ((T^2(1 + v^2))/(v^2(1 + T^2)))` (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Express `v^2` as a function of `t`, and hence find the limiting values of `x` and `v`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Mechanics, EXT2 M1 EQ-Bank 1
A canon ball of mass 9 kilograms is dropped from the top of a castle at a height of `h` metres above the ground.
The canon ball experiences a resistance force due to air resistance equivalent to `(v^2)/500`, where `v` is the speed of the canon ball in metres per second. Let `g=9.8\ text(ms)^-2` and the displacement, `x` metres at time `t` seconds, be measured in a downward direction.
- Show the equation of motion is given by
`ddotx = g - (v^2)/4500` (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Show, by integrating using partial fractions, that
`v = 210((e^(7/75 t) - 1)/(e^(7/75 t) + 1))` (5 marks)
--- 12 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- If the canon hits the ground after 4 seconds, calculate the height of the castle, to the nearest metre. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, 2ADV F2 EQ-Bank 13
The curve `y = kx^2 + c` is subject to the following transformations
-
- Translated 2 units in the positive `x`-direction
- Dilated in the positive `y`-direction by a factor of 4
- Reflected in the `y`-axis
The final equation of the curve is `y = 8x^2 + 32x - 8`.
- Find the equation of the graph after the dilation. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the values of `k` and `c`. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Trigonometry, 2ADV T3 EQ-Bank 3
By drawing graphs on the number plane, show how many solutions exist for the equation `cosx = |(x - pi)/4|` in the domain `(−∞, ∞)` (3 marks)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, 2ADV C4 EQ-Bank 5
The velocity of a particle moving along the `x`-axis at `v` metres per second at `t` seconds, is shown in the graph below.
Initially, the displacement `x` is equal to 12 metres.
- Write an equation that describes the displacement, `x`, at time `t` seconds. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Draw a graph that shows the displacement of the particle, `x` metres from the origin, at a time `t` seconds between `t= 0` and `t = 5`. Label the coordinates of the endpoints of your graph. (2 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, 2ADV S3 EQ-Bank 1
A probability density function can be used to model the lifespan of a termite, `X`, in weeks, is given by
`f(x) = {(k(36 - x^2)),(0):}\ \ \ {:(3 <= x <= 6),(text(otherwise)):}`
- Show that the value of `k` is `1/45`. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the cumulative distribution function. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the probability that a termite's lifespan is greater than 5 weeks. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
NETWORKS, FUR2-NHT 2019 VCAA 3
The zoo’s management requests quotes for parts of the new building works.
Four businesses each submit quotes for four different tasks.
Each business will be offered only one task.
The quoted cost, in $100 000, of providing the work is shown in Table 1 below.
The zoo’s management wants to complete the new building works at minimum cost.
The Hungarian algorithm is used to determine the allocation of tasks to businesses.
The first step of the Hungarian algorithm involves row reduction; that is, subtracting the smallest element in each row of Table 1 from each of the elements in that row.
The result of the first step is shown in Table 2 below.
The second step of the Hungarian algorithm involves column reduction; that is, subtracting the smallest element in each column of Table 2 from each of the elements in that column.
The results of the second step of the Hungarian algorithm are shown in Table 3 below. The values of Task 1 are given as `A, B, C` and `D`.
- Write down the values of `A, B, C` and `D`. (1 mark)
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The next step of the Hungarian algorithm involves covering all the zero elements with horizontal or vertical lines. The minimum number of lines required to cover the zeros is three.
Draw these three lines on Table 3 above. (1 mark)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- An allocation for minimum cost is not yet possible.
When all steps of the Hungarian algorithm are complete, a bipartite graph can show the allocation for minimum cost.
Complete the bipartite graph below to show this allocation for minimum cost. (1 mark)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Business 4 has changed its quote for the construction of the pathways. The new cost is $1 000 000. The overall minimum cost of the building works is now reduced by reallocating the tasks.
How much is this reduction? (1 mark)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, GEN1 2019 NHT 22-23 MC
Armand borrowed $12 000 to pay for a holiday.
He will be charged interest at the rate of 6.12% per annum, compounding monthly.
This loan will be repaid with monthly repayments of $500.
Part 1
After four months, the total interest that Armand will have paid is closest to
- $231
- $245
- $255
- $734
- $1796
Part 2
After eight repayments, Armand decided to increase the value of his monthly repayments.
He will make a number of monthly repayments of $850 and then one final repayment that will have a smaller value.
This final repayment has a value closest to
- $168
- $169
- $180
- $586
- $681
GEOMETRY, FUR1-NHT 2019 VCAA 7 MC
GEOMETRY, FUR1-NHT 2019 VCAA 4 MC
MATRICES, FUR2-NHT 2019 VCAA 4
After 5.00 pm, tourists will start to arrive in Gillen and they will stay overnight.
As a result, the number of people in Gillen will increase and the television viewing habits of the tourists will also be monitored.
Assume that 50 tourists arrive every hour.
It is expected that 80% of arriving tourists will watch only `C_2` during the hour that they arrive.
The remaining 20% of arriving tourists will not watch television during the hour that they arrive.
Let `W_m` be the state matrix that shows the number of people in each category `m` hours after 5.00 pm on this day.
The recurrence relation that models the change in the television viewing habits of this increasing number of people in Gillen `m` hours after 5.00 pm on this day is shown below.
`W_(m + 1) = TW_m + V`
where
`{:(quad qquad qquad qquadqquadqquadquadtext(this hour)),(qquadqquadqquad quad \ C_1 qquad quad C_2 qquad \ C_3 quad \ NoTV),(T = [(quad 0.50, 0.05, 0.10, 0.20 quad),(quad 0.10, 0.60, 0.20, 0.20 quad),(quad 0.25, 0.10, 0.50, 0.10 quad),(quad 0.15, 0.25, 0.20, 0.50 quad)]{:(C_1),(C_2),(C_3),(NoTV):}\ text(next hour,) qquad and qquad W_0 = [(400), (600), (300),(700)]):}`
- Write down matrix `V`. (1 mark)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- How many people in Gillen are expected to watch `C_2` at 7.00 pm on this day? (2 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
L&E, 2ADV E1 2019 NHT 4
Solve `log_3(t)-log_3(t^2-4) = -1` for `t`. (3 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1-NHT 2018 VCAA 9
Let diagram below shows a trapezium with vertices at `(0, 0), (0, 2), (3, 2)` and `(b, 0)`, where `b` is a real number and `0 < b < 2`
On the same axes as the trapezium, part of the graph of a cubic polynomial function is drawn. It has the rule `y = ax(x-b)^2`, where `a` is a non-zero real number and `0 ≤ x ≤ b`.
- At the local maximum of the graph, `y = b`.
- Find `a` in terms of `b`. (3 marks)
--- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
The area between the graph of the function and the `x`-axis is removed from the trapezium, as shown in the diagram.
- Show that the expression for the area of the shaded region is `b + 3-(9b^2)/(16)` square units. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Find the value of `b` for which the area of the shaded region is a maximum and find this maximum area. (2 marks)
--- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, MET1-NHT 2018 VCAA 8
Let `overset^p` be the random variable that represents the sample proportions of customers who bring their own shopping bags to a large shopping centre. From a sample consisting of all customers on a particular day, an approximate 95% confidence interval for the proportion `p` of customers who bring their own shopping bags to this large shopping centre was determined to be `((4853)/(50\ 000) , (5147)/(50\ 000))`. --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Statistics, MET1-NHT 2018 VCAA 6
The discrete random variable `X` has the probability mass function `text(Pr)(X = x) = {(kx), (k), (0):} qquad {:(x∈{1, 4, 6}), (x = 3), (text(otherwise)):}` --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, GEN1 2019 NHT 21 MC
Statistics, EXT1 S1 EQ-Bank 14
It is known that 65% of adults over the age of 60 have been tested for bowel cancer.
A random sample of 140 adults aged over 60 years is surveyed.
Using a normal approximation to the binomial distribution and the probability table attached, calculate the probability that at least 85 of the adults chosen have been tested for bowel cancer. (3 marks)
--- 9 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, GEN2 2019 NHT 8
A record producer gave the band $50 000 to write and record an album of songs.
This $50 000 was invested in an annuity that provides a monthly payment to the band.
The annuity pays interest at the rate of 3.12% per annum, compounding monthly.
After six months of writing and recording, the band has $32 667.68 remaining in the annuity.
- What is the value, in dollars, of the monthly payment to the band? (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- After six months of writing and recording, the band decided that it needs more time to finish the album.
To extend the time that the annuity will last, the band will work for three more months without withdrawing a payment.
After this, the band will receive monthly payments of $3800 for as long as possible.
The annuity will end with one final monthly payment that will be smaller than all of the others.
Calculate the total number of months that this annuity will last. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Financial Maths, GEN2 2019 NHT 7
Tisha plays drums in the same band as Marlon.
She would like to buy a new drum kit and has saved $2500.
- Tisha could invest this money in an account that pays interest compounding monthly.
The balance of this investment after `n` months, `T_n` could be determined using the recurrence relation below
`T_0 = 2500, \ \ \ \ T_(n+1) = 1.0036 xx T_n`
Calculate the total interest that would be earned by Tisha's investment in the first five months.Round your answer to the nearest cent. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Tisha could invest the $2500 in a different account that pays interest at the rate of 4.08% per annum, compounding monthly. She would make a payment of $150 into this account every month.
- Let `V_n` be the value of Tisha's investment after `n` months.
Write down a recurrence relation, in terms of `V_0`, `V_n` and `V_(n + 1)`, that would model the change in the value of this investment. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Tisha would like to have a balance of $4500, to the nearest dollar, after 12 months.
What annual interest rate would Tisha require?
Round your answer to two decimal places. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Data Analysis, GEN2 2019 NHT 5
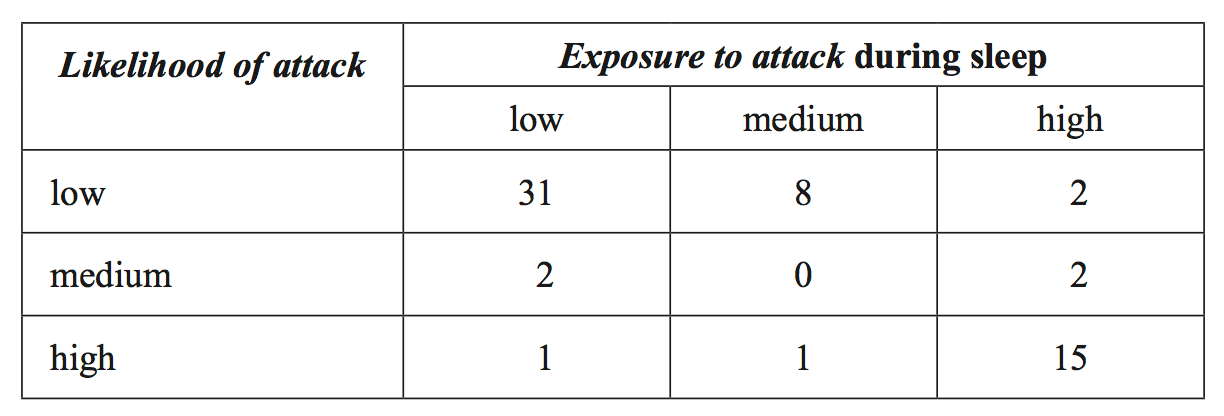
A random sample of 12 mammals drawn from a population of 62 types of mammals was categorized according to two variables. likelihood of attack (1 = low, 2 = medium, 3 = high) exposure to attack during sleep (1 = low, 2 = medium, 3 = high) The data is shown in the following table. --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- The following two-way frequency table was formed from the data generated when the entire population of 62 types of mammals was similarly categorized. --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Data Analysis, GEN2 2019 NHT 4
The scatterplot below plots the variable life span, in years, against the variable sleep time, in hours, for a sample of 19 types of mammals.
On the assumption that the association between sleep time and life span is linear, a least squares line is fitted to this data with sleep time as the explanatory variable.
The equation of this least squares line is
life span = 42.1 – 1.90 × sleep time
The coefficient of determination is 0.416
- Draw the graph of the least squares line on the scatterplot above. (1 mark)
--- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Describe the linear association between life span and sleep time in terms of strength and direction. (2 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Interpret the slope of the least squares line in terms of life span and sleep time. (2 marks)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Interpret the coefficient of determination in terms of life span and sleep time. (1 mark)
--- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- The life of the mammal with a sleep time of 12 hours is 39.2 years.
- Show that, when the least squares line is used to predict the life span of this mammal, the residual is 19.9 years. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
MATRICES, FUR1-NHT 2019 VCAA 7-8 MC
A farm contains four water sources, `P`, `Q`, `R` and `S`.
Part 1
Cows on the farm are free to move between the four water sources.
The change in the number of cows at each of these water sources from week to week is shown in the transition diagram below.
Let `C_n` be the state matrix for the location of the cows in week `n` of 2019.
The state matrix for the location of the cows in week 23 of 2019 is `C_23 = [(180),(200),(240),(180)]{:(P),(Q),(R),(S):}`
The state matrix for the location of the cows in week 24 of 2019 is `C_24 = [(160),(222),(203),(215)]{:(P),(Q),(R),(S):}`
Of the cows expected to be at `Q` in week 24 of 2019, the percentage of these cows at `R` in week 23 of 2019 is closest to
- 8%
- 9%
- 20%
- 22%
- 25%
Part 2
Sheep on the farm are also free to move between the four water sources.
The change in the number of sheep at each water source from week to week is shown in matrix `T` below.
`{:(),(),(T=):}{:(qquadqquadqquadtext(this week)),((qquadP,quadQ,quadR,quadS)),([(0.4,0.3,0.2,0.1),(0.2,0.1,0.5,0.3),(0.1,0.3,0.1,0.2),(0.3,0.3,0.2,0.4)]):}{:(),(),({:(P),(Q),(R),(S):}):}{:(),(),(text(next week)):}`
In the long term, 635 sheep are expected to be at `S` each week.
In the long term, the number of sheep expected to be at `Q` each week is closest to
- 371
- 493
- 527
- 607
- 635
GRAPHS, FUR1-NHT 2019 VCAA 7 MC
The shaded area in the graph below represents the feasible region for a linear programming problem.
The maximum value of the objective function `Z = -2x - 2y` occurs at
- point `C` only.
- any point along line segment `BC`.
- any point along line segment `AD`.
- any point along line segment `AB`.
- any point along line segment `DC`.
GRAPHS, FUR1-NHT 2019 VCAA 4 MC
A farm has `x` cows and `y` sheep.
On this farm there are always at least twice as many sheep as cows.
The relationship between the number of cows and the number of sheep on this farm can be represented by the inequality
- `x <= y/2`
- `y <= x/2`
- `2x >= y`
- `2y >= x`
- `xy >= 2`
MATRICES, FUR1-NHT 2019 VCAA 5 MC
A population of birds feeds at two different locations, `A` and `B`, on an island.
The change in the percentage of the birds at each location from year to year can be determined from the transition matrix `T` shown below.
`{:(),(),(T=):}{:(qquadtext(this year)),((qquadA,\ B)),([(0.8,0.4),(0.2,0.6)]):}{:(),(),({:(A),(B):}):}{:(),(),(text(next year)):}`
In 2018, 55% of the birds fed at location `B`.
In 2019, the percentage of the birds that are expected to feed at location `A` is
- 32%
- 42%
- 48%
- 58%
- 62%
NETWORKS, FUR1-NHT 2019 VCAA 7 MC
A graph has five vertices, `A, B, C, D` and `E`.
The adjacency matrix for this graph is shown below.
`{:(qquad qquad A quad B quad C quad D quad E), ({:(A), (B), (C), (D), (E):} [(0, 1, 0, 1, 2),(1, 0, 1, 0, 1),(0, 1, 1, 0, 1),(1, 0, 0, 0, 1),(2, 1, 1, 1, 0)]):}`
Which one of the following statements about this graph is not true?
- The graph is connected.
- The graph contains an Eulerian trail.
- The graph contains an Eulerian circuit.
- The graph contains a Hamiltonian cycle.
- The graph contains a loop and multiple edges.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- …
- 81
- Next Page »