The simplified model below shows the reactants and products of a proton-antiproton reaction which produces three particles called pions, each having a different charge. \(\text{p}+\overline{\text{p}} \rightarrow \pi^{+}+\pi^0+\pi^{-}\) There are no other products in this process, which involves only the rearrangement of quarks. No electromagnetic radiation is produced. Assume that the initial kinetic energy of the proton and antiproton is negligible. Protons consist of two up quarks \(\text{(u)}\) and a down quark \(\text{(d)}\) . Antiprotons consist of two up antiquarks \((\overline{\text{u}})\) and a down antiquark \((\overline{\text{d}})\). Each of the pions consists of two quarks. The following tables provide information about hadrons and quarks. Table 1: Hadron Information \begin{array} {|l|c|c|} \begin{array} {|l|c|} --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \quad \quad \ \ \textit{Particle} & \ \ \textit{Rest mass} \ \ & \quad \textit{Charge} \quad \\
& \left(\text{MeV/c}^2\right)&\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text {proton (p)} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 940 & +1 \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text {antiproton}(\overline{\text{p}}) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 940 & -1 \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text {neutral pion }\left(\pi^0\right) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 140 & \text{zero} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{positive pion }\left(\pi^{+}\right) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 140 & +1 \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text {negative pion }\left(\pi^{-}\right) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 140 & -1\\
\hline
\end{array}
Table 2: Quark charges
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \quad \quad \ \ \textit{Particle} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad \textit{Charge} \quad \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text {down quark (d)} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & -\dfrac{1}{3} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text {up quark (u)} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & +\dfrac{2}{3}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text {down antiquark}(\overline{\text{d}}) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & +\dfrac{1}{3}\\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{up antiquark }(\overline{\text{u}}) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & -\dfrac{2}{3} \\
\hline
\end{array}
Calculus, MET1 2024 VCAA 8
Let \(g: R \rightarrow R, \ g(x)=\sqrt[3]{x-k}+m\), where \(k \in R \backslash\{0\}\) and \(m \in R\). Let the point \(P\) be the \(y\)-intercept of the graph of \(y=g(x)\). --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2024 VCAA 7
Part of the graph of \(f:[-\pi, \pi] \rightarrow R, f(x)=x \sin (x)\) is shown below. --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
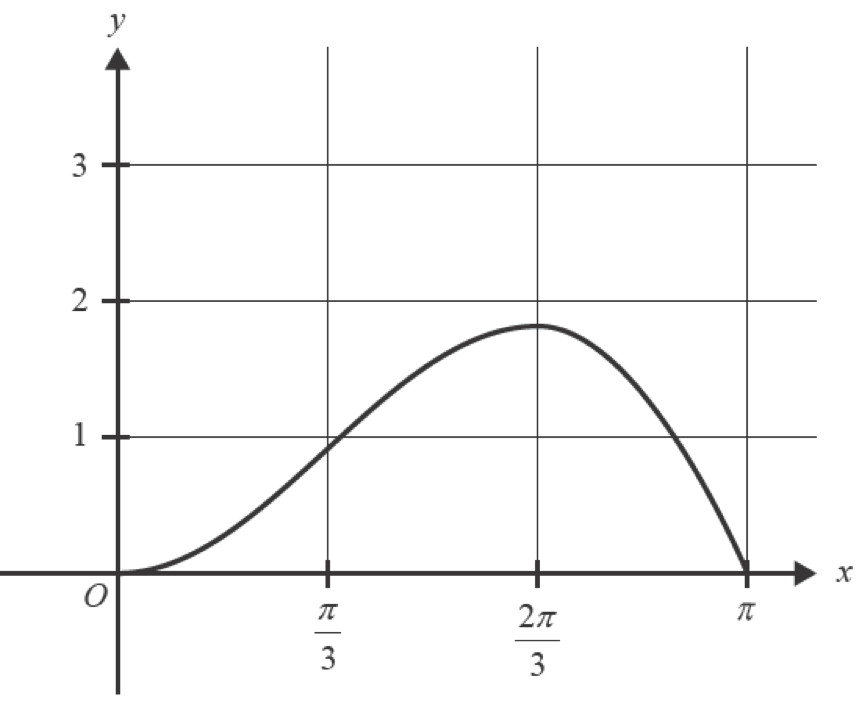
Functions, MET1 2024 VCAA 5
The function \(h:[0, \infty) \rightarrow R, \ h(t)=\dfrac{3000}{t+1}\) models the population of a town after \(t\) years. --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, MET1 2024 VCAA 4
Let \(X\) be a binomial random variable where \(X \sim \operatorname{Bi}\left(4, \dfrac{9}{10}\right)\). --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2024 VCAA 3
Let \(g: R \backslash\{-3\} \rightarrow R, \ g(x)=\dfrac{1}{(x+3)^2}-2\). --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Functions, MET1 2024 VCAA 2
Consider the simultaneous linear equations \(\begin{aligned} 3 k x-2 y & =k+4 \\ (k-4) x+k y & =-k\end{aligned}\) where \(x, y \in R\) and \(k\) is a real constant. Determine the value of \(k\) for which the system of equations has no real solution. (3 marks) --- 13 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET1 2024 VCAA 1b
Let \(f(x)=\log _e\left(x^3-3 x+2\right)\). Find \(f^{\prime}(3)\) (2 marks) --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Calculus, MET2 2024 VCAA 3
The points shown on the chart below represent monthly online sales in Australia. The variable \(y\) represents sales in millions of dollars. The variable \(t\) represents the month when the sales were made, where \(t=1\) corresponds to January 2021, \(t=2\) corresponds to February 2021 and so on. The graph of \(y=p(f)\) is shown as a dashed curve on the set of axes above. It has a local minimum at (2,2500) and a local maximum at (11,4400). --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- ii. Let \(q:(12,24] \rightarrow R, q(t)=p(t-h)+k\) be a cubic function obtained by translating \(p\), which can be used to model monthly online sales in 2022. Find the values of \(h\) and \(k\) such that the graph of \(y=q(t)\) has a local maximum at \((23,4750)\). (2 marks) --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Part of the graph of \(f\) is shown on the axes below. --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Find the value of \(n\). (1 mark) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. Find, correct to two decimal places, the values of \(a, b, c\) and \(d\). (3 mark)
\(f:(0,36] \rightarrow R, f(t)=3000+30 t+700 \cos \left(\dfrac{\pi t}{6}\right)+400 \cos \left(\dfrac{\pi t}{3}\right)\)
Calculus, MET2 2024 VCAA 2
A model for the temperature in a room, in degrees Celsius, is given by \(f(t)=\left\{ where \(t\) represents time in hours after a heater is switched on. --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- \(p(t)=\left\{ The amount of energy used by the heater, in kilowatt hours, can be estimated by evaluating the area between the graph of \(y=p(t)\) and the \(t\)-axis. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\begin{array}{cc}12+30 t & \quad \quad 0 \leq t \leq \dfrac{1}{3} \\
22 & t>\dfrac{1}{3}
\end{array}\right.\)
\begin{array}{cl}1.5 & 0 \leq t \leq 0.4 \\
0.3+A e^{-10 t} & t>0.4
\end{array}\right.\)
Functions, MET2 2024 VCAA 1
Consider the function \( f: R \rightarrow R, f(x)=(x+1)(x+a)(x-2)(x-2 a) \text { where } a \in R \text {. } \) --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- ii. exactly four \(x\)-intercepts. (1 mark) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- ii. Find the coordinates of the local maximum of \(g\). (1 mark) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- iii. Find the values of \(x\) for which \(g^{\prime}(x)>0\). (1 mark) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- iv. Consider the two tangent lines to the graph of \(y=g(x)\) at the points where --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Let \(h\) be the function \(h: R \rightarrow R, h(x)=(x+1)(x-1)(x+2)(x-2)\), which is the function \(f\) where \(a=-1\). --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- ii. Using a dilation and translations, describe a different sequence of transformations of \(h\), for which its image would have both local minimums at the same coordinates as that of \(g\). (2 marks) --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
i. exactly three \(x\)-intercepts. (2 marks)
i. Find \(g^{\prime}(x)\) (1 mark)
\(x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\) and \(x=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2}\). Determine the coordinates of the point of intersection of these two tangent lines. (2 marks)
i. Using translations only, describe a sequence of transformations of \(h\), for which its image would have a local maximum at the same coordinates as that of \(g\). (1 mark)
Probability, MET2 2024 VCAA 19 MC
Consider the normal random variable \(X\) that satisfies \( \text{Pr} (X < 10) = 0.2\) and \(\text{Pr}(X > 18) = 0.2 \).
The value of \(\text{Pr}(X<12)\) is closest to
- 0.134
- 0.297
- 0.337
- 0.365
Calculus, MET2 2024 VCAA 18 MC
Calculus, MET2 2024 VCAA 16 MC
Suppose that a differentiable function \( f: R \rightarrow R \) and its derivative \(f^{\prime}: R \rightarrow R\) satisfy \(f(4)=25\) and \(f^{\prime}(4)=15\).
Determine the gradient of the tangent line to the graph of \( {\displaystyle y=\sqrt{f(x)} } \) at \( x=4 \).
- \(\sqrt{15}\)
- \(\dfrac{1}{10}\)
- \(\dfrac{15}{2}\)
- \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)
PHYSICS, M5 2024 HSC 25
The mathematical model below shows the relationship between the orbital radius of a satellite and its period. \(\dfrac{r^3}{T^2}=\dfrac{G M}{4 \pi^2}\) --- 5 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M8 2024 HSC 24
An absorption spectrum resulting from the passage of visible light from a star's surface through its hydrogen atmosphere is shown. Absorption lines are labelled \(W\) to \(Z\) in the diagram.
- Determine the surface temperature of the star. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Absorption line \(W\) originates from an electron transition between the second and sixth energy levels. Use \(\dfrac{1}{\lambda}=R\left(\dfrac{1}{n_{ f }^2}-\dfrac{1}{n_{ i }^2}\right)\) to calculate the frequency of light absorbed to produce absorption line \(W\). (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain the physical processes that produce an absorption spectrum. (3 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M8 2024 HSC 23
Development of models of the atom has resulted from both experimental investigations and hypotheses based on theoretical considerations. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Probability, MET2 2024 VCAA 9 MC
At a Year 12 formal, 45% of the students travelled to the event in a hired limousine, while the remaining 55% were driven to the event by a parent.
Of the students who travelled in a hired limousine, 30% had a professional photo taken.
Of the students who were driven by a parent, 60% had a professional photo taken.
Given that a student had a professional photo taken, what is the probability that the student travelled to the event in a hired limousine?
- \(\dfrac{1}{8}\)
- \(\dfrac{27}{200}\)
- \(\dfrac{9}{31}\)
- \(\dfrac{22}{31}\)
Functions, MET2 2024 VCAA 8 MC
Some values of the functions \(f: R \rightarrow R\) and \(g: R \rightarrow R\) are shown below.
\begin{array} {|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \quad \ x \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad \ 1 \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad \ 2 \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad \ 3 \quad \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \quad f(x) \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad \ 0 \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad 4 \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad 5 \quad \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \quad g(x) \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad 3 \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad 4 \quad \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \quad -5 \quad \\
\hline
\end{array}
The graph of the function \(h(x)=f(x)-g(x)\) must have an \(x\)-intercept at
- \((2,0)\)
- \((3,0)\)
- \((4,0)\)
- \((5,0)\)
Probability, MET2 2024 VCAA 7 MC
A fair six-sided die is repeatedly rolled. What is the minimum number of rolls required so that the probability of rolling a six at least once is greater than 0.95 ?
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
PHYSICS, M8 2024 HSC 22
The following graph, based on the data gathered by Hubble, shows the relationship between the recessional velocity of galaxies and their distance from Earth. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 6 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
PHYSICS, M5 2024 HSC 13 MC
The diagram shows two identical satellites, \(A\) and \(B\), orbiting a planet.
Which row in the table correctly compares the potential energy, \(U\), and kinetic energy, \(K\), of the satellites?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\ \rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textbf{} \rule[-1.5ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textbf{A.} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textbf{B.} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textbf{C.} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textbf{D.} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} \\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textit{Potential energy} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \textit{Kinetic energy} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} U_\text{A} > U_\text{B} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & K_\text{A} < K_\text{B} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} U_\text{A} < U_\text{B} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & K_\text{A} > K_\text{B} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} U_\text{A} > U_\text{B} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & K_\text{A} > K_\text{B} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} U_\text{A} < U_\text{B} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & K_\text{A} < K_\text{B} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
Calculus, MET2 2024 VCAA 4 MC
If \( { \displaystyle \int_a^b f(x) d x=-5 } \) and \( { \displaystyle \int_a^c f(x) d x=3 } \), where \(a<b<c\), then \( { \displaystyle \int_b^c 2 f(x) d x } \) is equal to
- \(-16\)
- \(16\)
- \(-4\)
- \(4\)
Probability, MET2 2024 VCAA 3 MC
A discrete random variable \(X\) is defined using the probability distribution below, where \(k\) is a positive real number.
\begin{array} {|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} x \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \ \ \ \ \text{0}\ \ \ \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \ \ \ \ \text{1}\ \ \ \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \ \ \ \ \text{2}\ \ \ \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \ \ \ \ \text{3}\ \ \ \ \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \ \ \ \ \text{4}\ \ \ \ \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{Pr} \ (X = x) \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 2k \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 3k \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 5k \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 3k \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & 2k \\
\hline
\end{array}
Find \(\operatorname{Pr}(X<4 \mid X>1)\).
- \(\dfrac{13}{15}\)
- \(\dfrac{11}{13}\)
- \(\dfrac{4}{5}\)
- \(\dfrac{8}{15}\)
Graphs, MET2 2024 VCAA 1 MC
The asymptote(s) of the graph of \(y=\log _e(x+1)-3\) are
- \(x=-1\) only
- \(x=1\) only
- \(y=-3\) only
- \(x=-1\) and \(y=-3\)
PHYSICS, M7 2024 HSC 12 MC
A rod has a length, \(\mathrm{L}_0\), when measured in its own frame of reference.
The rod travels past a stationary observer at speed, \(v\), as shown in the diagram.
Which option represents the relationship between the speed of the rod, \(v\), and the length of the rod as measured by the stationary observer?
- \( W \)
- \( X \)
- \( Y \)
- \( Z \)
PHYSICS, M5 2024 HSC 11 MC
A satellite is in a circular orbit.
What is the relationship between its orbital velocity, \(v\), and its orbital radius, \(r\)?
- \(v\) is directly proportional to the square of \(r\).
- \(v\) is inversely proportional to the square of \(r\).
- \(v\) is directly proportional to the square root of \(r\).
- \(v\) is inversely proportional to the square root of \(r\).
PHYSICS, M5 2024 HSC 9 MC
Object \(P\) is dropped from rest, and object \(Q\) is launched horizontally from the same height.
Which option correctly compares the projectile motion of \(P\) and \(Q\) ?
- The acceleration of \(P\) is less than the acceleration of \(Q\).
- The final velocity of \(Q\) is greater than the final velocity of \(P\).
- The time of flight of \(Q\) is greater than the time of flight of \(P\).
- The initial vertical velocity of \(P\) is less than the initial vertical velocity of \(Q\).
PHYSICS, M6 2024 HSC 8 MC
An ideal transformer produces an output of 6 volts when an input of 240 volts is applied.
What change would be needed to produce an output of 12 volts, using the same input voltage?
- Increase the number of turns on the primary coil
- Decrease the number of turns on the primary coil
- Increase the resistance connected to the secondary coil
- Decrease the resistance connected to the secondary coil
PHYSICS, M6 2024 HSC 4 MC
CHEMISTRY, M2 EQ-Bank 3
Balance the following chemical equations:
- \(\ce{HCl(aq) + Zn(s) -> ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)}\) (1 mark)
-
\(\ce{CuSO4(aq) + AgNO3(aq) -> Ag2SO4(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq)}\) (1 mark)
BIOLOGY, M6 2024 HSC 34
Discuss the ethical implications and impacts on society of the use of TWO biotechnologies. (7 marks)
--- 22 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2024 HSC 33
Female Jack Jumper ants (Myrmecia pilosula) have a single pair of chromosomes. During meiosis, crossing over occurs. The diagram shows the crossing over and the position of three genes on the chromosomes. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M8 2024 HSC 29
An epidemiological study was conducted to help model how many people will be affected by Type 2 diabetes globally in the future. Continuous data were collected from 1990 to 2020. From that data, the following data points were chosen to demonstrate the trend. \begin{array} {|c|c|} A prediction of the global population numbers suggests there will be about 9 billion \((9\ 000\ 000\ 000)\) people on the planet by 2040. Predict the number of people that will be affected by diabetes in 2040. Show working on your graph on the previous page and your calculations. (3 marks) --- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textit{Year} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \textit{Percentage of population affected} \\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \textit{} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \textit{by Type 2 diabetes (%)} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{1990} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \text{3.1} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{2000} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \text{3.7} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{2010} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \text{4.3} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex} \text{2010} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \text{5.6} \\
\hline
\end{array}
BIOLOGY, M8 2024 HSC 31
A study monitored the changes in the body temperature of a kookaburra (an Australian bird) and a human over a 24-hour period. The results of the study are shown in the graph. --- 2 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Some endothermic organisms can display torpor (a significant decrease in physiological activity). With reference to the graph, explain whether the human or the kookaburra was displaying torpor and if so, state the time this occurred. (3 marks) --- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2024 HSC 30
BIOLOGY, M7 2024 HSC 27
Milk pasteurisation (heating to approximately 70°C) was gradually introduced in America from the early 1900s. The graph shows the number of disease outbreaks in relation to raw (unpasteurised) and pasteurised milk in America from 1900-1975.
Explain the trends observed in the graph. In your response, refer to the role of Pasteur's work in pasteurisation. (5 marks)
--- 13 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M7 2024 HSC 26
Describe a plant disease and its effect on agricultural production. (4 marks)
--- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M6 2024 HSC 25
One-Eyed Jack was a rescue dog that had been injured and lost an eye before his owner adopted him. One-Eyed Jack was cloned and the clone was born with two eyes. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Describe how animals like dogs can be cloned. (4 marks) --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M8 2024 HSC 24
- Outline the cause of a disease due to environmental exposure. (2 marks)
--- 3 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
- Explain how an educational program or campaign can be used to decrease the incidence of a disease caused by environmental exposure. (3 marks)
--- 7 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M6 2024 HSC 23
Outline how ONE type of electromagnetic radiation can cause a germline mutation. (2 marks)
--- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M7 2024 HSC 22
A student designed and conducted a practical investigation to test for the presence of microbes in water and food samples. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
BIOLOGY, M5 2024 HSC 20 MC
Analyse the following four pedigrees.
Which row in the table correctly identifies the pedigree with the type of inheritance?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\ & \\
\\
\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{A.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{B.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{C.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textbf{D.}\rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}\\
\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\textit{Autosomal} & \textit{Sex-linked} & \textit{Autosomal} & \textit{Sex-linked} \\
\textit{dominant} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \textit{dominant} & \textit{recessive} & \textit{recessive} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{2} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{1} & \text{3} & \text{4} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{1} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{4} & \text{2} & \text{3} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{1} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt}& \text{3} & \text{2} & \text{4} \\
\hline
\rule{0pt}{2.5ex}\text{2} \rule[-1ex]{0pt}{0pt} & \text{4} & \text{1} & \text{3} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
BIOLOGY, M7 2024 HSC 15 MC
The graph shows the number of cases of Swine Flu (a viral respiratory illness) from May to July 2009 in Australia.
What effective control measures could have been introduced between May and July to limit the spread of the disease in Australia?
\begin{align*}
\begin{array}{l}
\ & \\
\\
\textbf{A.}\\
\\
\textbf{B.}\\
\textbf{C.}\\
\\
\textbf{D.}\\
\\
\\
\end{array}
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline
\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \textit{May-June} & \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \textit{July} \\
\hline
\text{Quarantine all people arriving in} & \text{Encourage people to wear masks and } \\
\text{Australia} & \text{wash hands regularly} \\
\hline
\text{Issue antibiotics to overseas visitors} & \text{Isolate people with symptoms} \\
\hline
\text{Encourage people to wear masks and } & \text{Quarantine all people arriving in} \\
\text{wash hands regularly} & \text{Australia} \\
\hline
\text{Isolate people with symptoms} & \text{Vaccinate all people arriving in} \\
\text{} & \text{Australia} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{align*}
CHEMISTRY, M7 2024 HSC 24
The boiling points for two series of compounds are listed. --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 12 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 2024 HSC 38
Compounds \(\text{A}\) and \(\text{B}\) are isomers with formula \(\ce{C3H7X}\), where \(\ce{X}\) is a halogen. The mass spectrum for compound \(\text{A}\) is shown. Compounds \(\text{A}\) and \(\text{B}\) undergo substitution reactions in the presence of hydroxide ions, producing alcohols \(\text{C}\) and \(\text{D}\). Compound \(\text{D}\) can be oxidised to a ketone; compound \(\text{C}\) can also be oxidised, but does not produce a ketone. Compound \(\text{E}\) can be produced by refluxing 3-methylbutanoic acid, with one of the alcohols \(\text{C}\) or \(\text{D}\), in the presence of a catalyst. The \({ }^1 \text{H NMR}\) spectrum for compound \(\text{E}\) contains the following features. Draw the structure of compounds \(\text{A}\), \(\text{B}\) and \(\text{E}\). Explain your answer with reference to the information provided. (7 marks) --- 20 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 2024 HSC 37
The relationship between the equilibrium constant, \(K_{eq}\), and \(\Delta G^{\circ}\) for any reaction is shown in the graph, for a limited range of \(\Delta G^{\circ}\) values.
The \(\Delta H^{\circ}\) and \(T \Delta S^{\circ}\) values for the reaction between copper\(\text{(I)}\) sulfide and oxygen are provided.
| \(\ce{Cu2S(s) +O2(g) \rightarrow 2Cu(s) +SO2(g) \quad \quad}\) | \(\Delta H^{\circ}=-217 \text{ kJ mol}^{-1}\) \(\Delta S^{\circ}=-3 \text{ kJ mol}^{-1}\) |
Explain, with reference to the information provided, why this reaction proceeds to completion rather than coming to equilibrium. (3 marks)
--- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
Networks, GEN2 2024 VCAA 15
An upgrade to the supermarket requires the completion of 11 activities, \(A\) to \(K\). The directed network below shows these activities and their completion time, in weeks. The minimum completion time for the project is 29 weeks. --- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- Use the following information to answer parts c-e. A change is made to the order of activities. The table below shows the activities and their new latest starting times in weeks. \begin{array}{|c|c|} A dummy activity is now required in the network. --- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
--- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 1 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\hline
\textbf{Activity} & \textbf{Latest Starting}\\
&\textbf{time} \text{(weeks)}\\
\hline A & 0 \\
\hline B & 2 \\
\hline C & 10 \\
\hline D & 9 \\
\hline E & 13 \\
\hline F & 14 \\
\hline G & 18 \\
\hline H & 17 \\
\hline I & 19 \\
\hline J & 25 \\
\hline K & 22 \\
\hline
\end{array}
CHEMISTRY, M7 2024 HSC 35
Unknown samples of three carboxylic acids, labelled \(\text{X , Y}\) and \(\text{Z}\), are analysed to determine their identities. \( Identify which structures 1, 2 and 3 in the table are acids \(\text{X , Y}\) and \(\text{Z}\). Justify your answer with reference to the information provided. (7 marks) --- 22 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\begin{array}{|l|c|c|c|}
\hline \textit{Acid } & X & Y & Z \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text {Volume of } \ce{NaOH \text{(mL)}} \\
\end{array} & 21.88 & 22.49 & 22.49 \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
CHEMISTRY, M6 2024 HSC 34
An aqueous solution of ammonia is added to a solution containing hydrochloric acid. A plot of conductivity against volume of ammonia solution added is shown. The temperature of the solution is kept constant throughout and the conductivity of the solution is corrected for dilution. The relative conductivities of some relevant ions are shown in the table. \begin{array}{|l|c|} Explain the shape of the graph. Include TWO balanced chemical equations in your answer. (4 marks) --- 13 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
\hline \textit{Ion } & \textit{Relative conductivity } \\
\hline \ce{H^{+}} & 4.76 \\
\hline \ce{OH^{-}} & 2.70 \\
\hline \ce{Cl^{-}} & 1.04 \\
\hline \ce{NH_4^{+}} & 1.00 \\
\hline
\end{array}
CHEMISTRY, M8 2024 HSC 33
Acetone can be reduced, as shown. --- 4 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 2024 HSC 31
The atom economy ( AE ) of a reaction is a measure of the mass of atoms in the starting materials that are incorporated into the desired product. Higher AE means lower mass of waste products. Urea can be produced in a variety of ways. One way is to react ammonia (high toxicity) with phosgene (high toxicity). Another way is to react ammonia with dimethyl carbonate (DMC, low toxicity). The chemical equations and AE for these two processes are provided. Which of these two processes is preferable for urea production? Justify your answer with reference to the information provided. (3 marks) --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M6 2024 HSC 29
150 mL of a 0.20 mol L\(^{-1}\) sodium hydroxide solution is added to 100 mL of a 0.10 mol L\(^{-1}\) sulfuric acid solution. Calculate the pH of the resulting solution, assuming that the volume of the resulting solution is 250 mL and that its temperature is 25°C. (4 marks) --- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M6 2024 HSC 28
Iodic acid and sulfamic acid are monoprotic acids. A 0.100 mol L\(^{-1}\) solution of iodic acid has a pH of 1.151, as does a 0.120 mol L\(^{-1}\) solution of sulfamic acid. Show that neither iodic acid nor sulfamic acid dissociates completely in water, and determine which is the stronger acid. (3 marks) --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 2024 HSC 27
The following procedure is proposed to test for the presence of lead\(\text{(II)}\) and barium ions in water at concentrations of 0.1 mol L\(^{-1}\). Explain why this procedure gives correct results when only barium ions are present, but not when both barium and lead\(\text{(II)}\) ions are present. Include ONE balanced chemical equation in your answer. (4 marks) --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 2024 HSC 26
The equilibrium equation for the reaction of iodine with hydrogen cyanide in aqueous solution is given. \(\ce{I_2(aq) + HCN(aq)\rightleftharpoons ICN(aq) + I^{-}(aq) + H^{+}(aq)}\) At \(t=0\) min, \(\ce{I2}\) was added to a mixture of \(\ce{HCN, I^{-}}\) and \(\ce{H^{+}}\), bringing \(\left[ \ce{I2}\right]\) to 2.0 × 10\(^{-5}\) mol L\(^{-1}\). After 3 minutes, the system was at equilibrium, and an analysis of the mixture found that half of the \(\ce{I2}\) had reacted. --- 0 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) --- --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M8 2024 HSC 25
The concentration of phosphate ions in washing machine waste water can be determined using colourimetry. A sample of washing machine waste water was collected and diluted by quantitatively transferring 1.00 mL of the solution to a volumetric flask and making up the volume to 1.000 L with distilled water. Standard phosphate solutions were prepared and analysed with a colourimeter using an accepted method. The standard calibration graph is shown. The diluted sample solution was then analysed using the same method as the standard solutions. The absorbance of this solution was found to be 0.64 . Determine the concentration of phosphate ions in the sample of washing machine waste water, in mol L\(^{-1}\). (4 marks) --- 8 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M5 2024 HSC 23
Consider the following equilibrium system.
\(\ce{\left[Co \left(H_2O\right)_6\right]^{2+}(aq) + 4Cl^{-} (aq) \rightleftharpoons\left[CoCl_4\right]^{2-}(aq) +6H_2O (l)}\)
\(\ce{\left[Co\left(H_2O\right)_6\right]^{2+}(aq)}\) is pink and \(\ce{\left[CoCl_4\right]^{2-}(aq)}\) is blue. When a solution of these ions and chloride ions is heated, the mixture becomes more blue.
Relate the observed colour change to the change in \(K_{e q}\). (3 marks) --- 10 WORK AREA LINES (style=lined) ---
CHEMISTRY, M7 2024 HSC 22
CHEMISTRY, M6 2024 HSC 16 MC
Which of the following is the overall reaction that takes place when a strong acid is added to a buffer containing equal amounts of acetic acid and acetate ions?
- \(\ce{HCOO^{-} +H_3O^{+} \rightarrow HCOOH + H_2O}\)
- \(\ce{CH_3COOH +OH^{-} \rightarrow CH_3COO^{-} + H_2O}\)
- \(\ce{CH_3COO^{-} +H_3O^{+} \rightarrow CH_3COOH + H_2O}\)
- \(\ce{CH_3COOH +H_3O^{+} \rightarrow CH_3C(OH)_2^{+} + H_2O}\)
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- …
- 114
- Next Page »